* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Parts of Speech
Modern Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Portuguese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Untranslatability wikipedia , lookup
Georgian grammar wikipedia , lookup
English clause syntax wikipedia , lookup
Old Irish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Preposition and postposition wikipedia , lookup
Comparison (grammar) wikipedia , lookup
Morphology (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Lithuanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Lexical semantics wikipedia , lookup
Ojibwe grammar wikipedia , lookup
Macedonian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old Norse morphology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Arabic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Old English grammar wikipedia , lookup
Zulu grammar wikipedia , lookup
Japanese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Swedish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Modern Hebrew grammar wikipedia , lookup
Icelandic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Ancient Greek grammar wikipedia , lookup
Serbo-Croatian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian nouns wikipedia , lookup
Scottish Gaelic grammar wikipedia , lookup
Compound (linguistics) wikipedia , lookup
Vietnamese grammar wikipedia , lookup
Romanian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Latin syntax wikipedia , lookup
Esperanto grammar wikipedia , lookup
French grammar wikipedia , lookup
Italian grammar wikipedia , lookup
Turkish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Yiddish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Danish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Spanish grammar wikipedia , lookup
Malay grammar wikipedia , lookup
Pipil grammar wikipedia , lookup
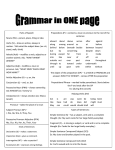
Parts of Speech Noun-person, place, thing, or idea • Common noun-general name; not capitalized (ex: boy, desk, building) • Proper noun-a particular name; always capitalized (ex: Alabama, Bob, English) • Concrete noun-an object detected through one of the senses (ex: wall, perfume, rain) • Abstract noun-an idea, quality or characteristic (ex: honesty, happiness, love) • Singular noun-only one (ex: bike) • Plural noun-two or more (ex: bikes) • Collective noun-group of people or things (ex: team, staff, herd) • Compound noun-formed from two or more words: one word (hotdog), hyphenated (Chick-fil-a, sister-in-law), and separate compound words (parking lot) • Possessive noun-shows ownership (ex: book’s pages) Pronouns-a word used in place of a noun or another pronoun • Antecedent-the word for which the pronoun stands. • Personal pronouns-simply take the place of a noun (ex: Susie was sad. She felt blue.) • Possessive pronouns-show ownership (ex: Susie was still sad. She slashed her boyfriend’s tires to make her feel better.) • Reflexive pronoun-reflects back to the subject of the sentence or the subject of the clause in which it appears (ex: Susie lets herself into the house after school.) • Intensive pronoun-used to emphasize a noun or pronoun anywhere in the sentence. It can be taken out the sentence without altering the meaning. (ex: I will go, but the tourists themselves will remain at the site.) • Indefinite pronoun-refers to things that are not specifically identified; usually no antecedents (ex: Everyone was invited to the party) • Interrogative pronoun-introduces a question (ex: What is that?) • Relative pronoun-introduces a noun clause or an adjective clause (ex: The students, who are eager to learn, couldn’t write the notes fast enough.) Verbs-expresses an action, a condition, or a state of being • Action verb-expresses a physical or mental action (ex: I carried my books to class. I wanted to leave them in my locker.) • Linking verb-links a word in the predicate to the subject; expresses a condition or state of being; be aware that some of the verbs that express condition can be used as action or linking (ex: I smelled the flowers. They smelled sweet.) • Auxiliary verbs (helping verbs)-combined with verbs to form verb phrases. Adjectives-limits the meaning of a noun or pronoun • Answers the questions: What kind? Which one? How many? How much? • Definite articles-the • Indefinite articles-a, an • Proper adjectives-formed from proper nouns; always capitalized (ex: Alabamians) Adverbs-modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. • Answers the questions: Where? When? How? To What Extent? • Intensifiers-adverbs that defines to what degree an adverb or adjective is (ex: too, so, very) Prepositions-shows the relationship between a noun or pronoun and another word in a sentence. • Prepositional phrases • Compound prepositions Conjunctions-connects words or groups of words • Coordinating conjunctions-connect words or groups of words of equal importance in a sentence. • Correlative conjunctions-word pairs that serve to join words or groups of words. • Subordinating conjunctions-introduce subordinate clauses-clauses that cannot stand alone-and join them to independent clauses • Conjunctive adverbs-used to express relationships between independent clauses. Interjections-word or phrase that expresses emotion • Mild interjection-only separated from the rest of the sentence by a comma. • Strong interjection-separated entirely from any other sentences usually with an exclamation point.