* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Class 13 - Oct. 16 - Circuit Switching
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Telephone exchange wikipedia , lookup
History of wildlife tracking technology wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
History of smart antennas wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Number One Electronic Switching System wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
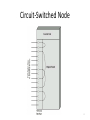
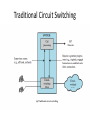
CSCI 465 Data Communications and Networks Lecture 13 Martin van Bommel CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 1 Switching Techniques • Transmission beyond local area requires intermediate switching nodes • Nodes concerned not with content but with movement of data • Two technologies of switching differ in way data is switched from one link to another – circuit switching versus packet switching CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 2 Circuit-Switching • Definition: – Communication in which a dedicated communications path is established between two devices through one or more intermediate switching nodes • Dominant in both voice and data today – e.g. PSTN is a circuit-switched network • Relatively inefficient – 100% dedication even without 100% utilization CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 3 Circuit-Switching Stages • Circuit establishment – end-to-end circuit established before any signals can be transmitted • Data transfer – point-to-point from endpoints to nodes – internal switching/multiplexing among nodes • Circuit disconnect – deallocate resources dedicated to circuit CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 4 PSTN • Public Switched Telephone Network • Four generic components – Subscribers - devices that attach to network – Local loop - link from subscriber to network – Exchanges - switching centers (end office - connected to subscribers) – Trunks - branches between exchanges (FDM or synchronous TDM) CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 5 Circuit-Switched Node 6 Circuit-Switching Node: Digital Switch • Provides transparent signal path between any pair of attached devices • Appears to devices as direct connection • Typically full-duplex CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 7 Circuit-Switching Node: Network Interface • Provides hardware and functions to connect digital devices to switch • Analog devices can be connected if interface includes CODEC functions • Typically full-duplex • Trunks to other switches carry TDM signals to provide links for multiple node networks CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 8 Circuit-Switching Node: Control Unit • Establishes on-demand connections – handle and acknowledge request – determine if destination is free – construct path through switch • Maintains connection while needed – maintain time-division for connection • Breaks down connection on completion CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 9 Blocking/Non-blocking Networks • Blocking – network is unable to connect two stations because all possible paths are already in use (acceptable for voice only) • Non-blocking: – permits all possible connection requests because any two stations can be connected (and may stay that way for a long time) CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 10 Switching Techniques Space-Division Switching – Developed for analog environment, but has been carried over into digital communication – Requires separate physical paths for each signal connection – Uses metallic or semiconductor “gates” Time-Division Switching – Used in digital transmission – Utilizes multiplexing to place all signals onto common transmission path – Bus must have higher data rate than the individual I/O lines CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 11 Circuit-Switched Networks: Routing • Requires balancing efficiency and resiliency • Traditional circuit-switched model is hierarchical, sometimes supplemented with peer-to-peer trunks • Newer circuit-switched networks are dynamically routed: all nodes are peer-topeer, making routing more complex CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 12 Alternate Routing • Possible routes between two end offices are predefined • Originating switch selects the best route for each call • Routing paths can be fixed (one route) or dynamic (multiple routes, selected based on current and historical traffic) CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 13 Control Signaling • Manage the establishment, maintenance, and termination of signal paths • Includes signaling from subscriber to network, and signals within network • In-channel signaling uses the same channel for control signals and calls • Common-channel signaling uses independent channels for controls – SS7 – Signaling System Number 7 CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 14 Traditional Circuit Switching Softswitch Architecture • latest trend in circuit-switching technology • computer running specialized software that turns it into a smart phone switch • costs less and provides more functionality • Media gateway (MG) – physical switching • Media gateway controller (MGC) – call processing logic CSCI 465 Data Communications & Networks 16 Softswitch