* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Weathering and Erosion
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
Plate tectonics wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
Ring of Fire wikipedia , lookup
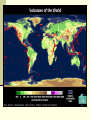
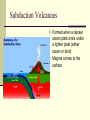
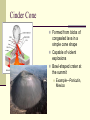
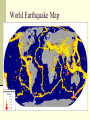
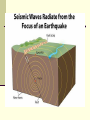
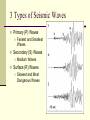
Changing Earth’s Surface Weathering and Erosion Changes to Earth’s Surface Earth’s crust is constantly in a process of change Weathering Erosion Deposition Weathering The process by which rocks are broken down into small pieces called sediment Caused by Wind Water Glaciers Meteorites Erosion Occurs when weathered material is carried away by wind or water Responsible for some of our most impressive natural monuments Example—The Grand Canyon Deposition Occurs when sediment is dropped off at a new location Wind or water slows down or comes to a stop Example—River Delta Changing Earth’s Surface Volcanoes Plate Tectonics Theory that the lithosphere is divided into plates that are always moving Pangaea Supercontinent that once existed over 350 million years ago Evidence: Puzzle piece fit of the continents, fossil and soil matches on different continents Responsible for the formation of volcanoes and earthquakes Volcanoes Form when magma rises to Earth’s surface Pyroclastic Flow Ashes, Gases, and Magma that ooze or explode from volcanoes Can form at divergent boundaries or subduction zones Divergent Volcanoes Plates above the asthenosphere separate Magma rises up As lava cools, new crust is formed May be oozing or explosive Divergent Volcano Subduction Volcanoes Formed when a denser ocean plate sinks under a lighter plate (either ocean or land) Magma comes to the surface Shield Volcano Broad and flat volcano Resemble a shield laying on its side Built up slowly over thousands of years, most often in layers of hardened lava Mostly ooze lava from vents Example—Mauna Loa, Hawaii Composite Volcano Formed of alternating layers of ashes and hardened lava May be dormant for many years before exploding rapidly or may ooze for thousands of years Example—Crater Lake, OR Cinder Cone Formed from blobs of congealed lava in a simple cone shape Capable of violent explosions Bowl-shaped crater at the summit Example—Paricutin, Mexico Changing Earth’s Surface Earthquakes World Earthquake Map Earthquakes Energy released from the snap and slide of Earth’s crust at a fault line Fault Focus 2 or more plates slide past one another Point inside Earth where an Earthquake begins Epicenter Point on Earth’s surface where Earthquake waves begin 3 Types of Seismic Waves Primary (P) Waves Fastest and Smallest Waves Secondary (S) Waves Medium Waves Surface (R) Waves Slowest and Most Dangerous Waves Earthquake Waves Measured with a seismograph Scaled using the Richter Scale Scale of 1-10 1 = least amount of damage 10 = greatest amount of damage