* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Earthquakes and Volcanoes
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
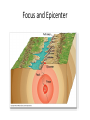
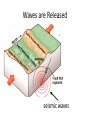
Earthquakes and Volcanoes p. 346 - 353 What is This? Why do Earthquakes Occur? • Stress builds up at a fault • Stress is a force that adds potential energy to the rock • As soon as the rock slips, energy is released Why do Earthquakes Occur? • When there is sudden movement along a fault • The fault suddenly breaks and slides Focus and Epicenter • The focus of an earthquake is the area underground where rock moves. The focus is where waves are sent out • The epicenter of an earthquake is the location on the earth’s surface directly above the focus Focus and Epicenter Waves are Released seismic waves P and S waves • P: Primary Wave – causes the initial jolt of the earthquake. Compresses the rock as it travels • S: Secondary Wave – slower and stronger wave. Shakes the ground in many directions Volcanoes • A volcano is a weak spot in the crust where magma comes to the surface. • Magma that reaches earth’s surface is called lava. magma lava Lava - Lava cools to form solid rock - Volcanic activity builds mountains! Volcanoes at Convergent Boundaries Island Arcs • String of islands at an oceanic – oceanic convergent boundary • Japan, New Zealand, Indonesia, Caribbean islands Volcanoes at Divergent Boundaries Hot Spot Volcanoes • Hawaii was formed this way • Hot area under the surface – plate moves on top. As the plate moves, a chain of volcanoes is formed. • Watch the animation: http://esminfo.prenhall.com/ science/geoanimations/anima tions/35_VolcanicAct.html What is a Tsunami? Earthquake or volcanic activity under the ocean can lead to strong waves, creating a tsunami.