* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are Earthquakes?
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
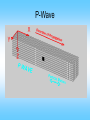
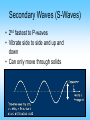
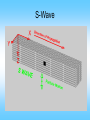
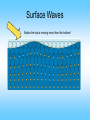
What are Earthquakes? Where Do Earthquakes Occur? • • Earthquakes occur near tectonic plate edges. A break in the Earth’s crust where plates slide past each other is called a fault. The Three Types of Faults Plate Motion Transform Boundary (shearing) Convergent Boundary (compression) Divergent Boundary (tension) Fault Name Strike Slip Fault Reverse Fault Normal Fault Fault Movement What Causes Earthquakes? • Caused by deformation of the plates. Rocks that are under stress and stretched will eventually break, causing an earthquake. • Elastic Rebound = when rocks suddenly break and spring back to their original shape. How Do Earthquake Waves Travel? There are 3 types of seismic waves: 1. Primary Waves: P-Waves 2. Secondary Waves: S-Waves 3. Surface Waves Click Here for animation! Primary Waves (P-Waves) • • • • Move the fastest Move in a straight line Compress and expand like an accordion Move through solids, liquids, and gases P-Wave Secondary Waves (S-Waves) • 2nd fastest to P-waves • Vibrate side to side and up and down • Can only move through solids S-Wave Surface Waves • Result of P-waves and S-waves when they reach the surface • Only travel in the crust! • Slowest seismic waves • Make the ground roll like ocean waves • Responsible for surface damage and falling buildings. Surface Waves Notice the top is moving more than the bottom! Surface Wave Diagram Earthquake Effects - Ground Shaking Loma Prieta, CA 1989 KGO-TV News ABC-7 Earthquake Effects - Ground Shaking Kobe, Japan 1995 Earthquake Effects - Ground Shaking Kobe, Japan 1995 Earthquake Effects - Surface Faulting Landers, CA 1992 Earthquake Effects - Landslides Source: National Geophysical Data Center Turnagain Heights, Alaska,1964 (upper left inset); Santa Cruz Mtns, California , 1989 Earthquake Location