* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Landforms
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
Tectonic–climatic interaction wikipedia , lookup
Geomorphology wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
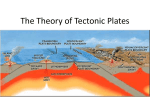
Do Now • Google the following and label them on your map! • The 5 largest: • Volcanoes in the world (Red) • Mountains in the world (Brown) • Recorded Earthquakes in the world (Blue) –Create a key on your map! Plate Movement Song/Skit • Your group will create a song or skit to inform the class how plates on the earth move – Include the three types of plate movement and what landform is created as a result • Guidelines: – Song- Must be at least 15-20 lines. Every group member must present. Turn in song! – Skit- Must be informational yet entertaining. Every group member must have a part. CAN NOT HAVE a Narrator!! Turn in script! Landforms Forces below Earth’s Surface • Geology- the study of Earth’s physical structures and the processes that have created them • Forces below Earth’s surface are key to shaping landforms • Four important zones in Earth’s Interior – Core-Center: like a nuclear furnace, divided into inner(solid) and outer core (dense liquid metal) – Mantle- Most of Earth’s mass – Crust- 25 miles thick. Currents carry heat from core through the mantle to the crust Internal Forces • Plate Tectonics: how forces within Earth create landforms – Plates can be compared to the cracked shell of a hard boiled egg • Plates move slowly across the upper mantle: process called continental drift – Plate boundaries: the crust is subject to stressing that lead to melting, bending, and breaking – Volcanoes often form long rows that signal a plate boundary – Earthquakes-Tectonic forces cause masses of rock to break, very common near plate boundaries • Theory of plate tectonics is used to explain the history of Earth’s surface – Pangaea- All continents were apart of one supercontinent Plate Movement • Three types of movement at plate boundaries – Divergent, Convergent, Transform • Divergent (Spreading): crust stretches until it breaks; creating rift valleys and oceanic ridges • Convergent (Collide): Found on ocean floors and continental edges; On ocean floors colliding creates trenches. On continental boundaries, colliding creates folds and faults (mountains) • Transform (Move laterally): Move past each other, some low mountains are created and broad valleys; earthquakes are frequent Move Laterally Forces on Earth’s surface • Weathering: Breaking and decaying of rocks over a period of time; SLOW process – Chemical- substances in air and water react with rock- dissolves the rock – Physical- heating and cooling, freezing and thawing, roots of trees- breaks or cracks the surface • Erosion: Movement of surface material from one location to another – Water-Rainfall, rivers, and waves: ExampleGrand Canyon – Wind- Abrasion-blast particles of sand against rock, from one place to another (sand dunes) • Dust from Sahara in Africa goes across the Atlantic Ocean to the Caribbean Islands – Ice-Glaciers-can level anything in their path, grind rocks into sediment Plates build the land up while weathering and erosion wear it down and make it flat!! Shapes of the Land • Landforms are broken up into three groups – Created by tectonic processes • Volcanoes and mountains – Created by erosion • Plateaus – Created by sediment deposited by ice, water, and wind • Sand Dune