* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit 5 – Structure of the Earth
Geomagnetic reversal wikipedia , lookup
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
Schiehallion experiment wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Geological history of Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Supercontinent wikipedia , lookup
Mantle plume wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
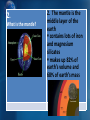
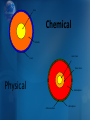
1. What is the crust? http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw /6222-mountain-building-earthsinner-crust-video.htm 1. The crust is the outmost layer of the earth. Is made of hard rocks contains silicon and oxygen (silicates) and aluminum 5 km to 50 km thick 2. What is the mantle? 2. The mantle is the middle layer of the earth contains lots of iron and magnesium silicates makes up 82% of earth’s volume and 68% of earth’s mass 3. What is the core? Core Mantle Crust http://videos.howstuffworks.com/sciencechannel/29142-100-greatest-discoveriesthe-core-of-the-earth-video.htm 3. The core is the innermost layer of the earth contains iron and nickel metals very dense makes up 16% of earth’s volume and 32% of earth’s mass Core Chemical Mantle Inner Core Crust Outer Core Physical Mesosphere Asthenosphere Lithosphere 4. What is the lithosphere? 4. The lithosphere is a cool, solid outer layer of the earth includes the crust and outer mantle 100 km thick floats on the plastic asthenosphere 5. What is the asthenosphere? 5. The asthensoshpere is a hot semi-liquid layer of the mantle just below the lithosphere. Is soft and flows. 6.What is the mesosphere? 6. The mesosphere is a solid layer of the inner mantle. Pressure keeps rocks from melting. 7.What is the outer core? 7. The outer core is a liquid inner layer Mostly liquid iron Thought to be the source of the earth’s magnetic field. 8.What is the 8. The inner core inner core? is the innermost part of the earth. o 4000 C 4500oC – 9. Who was Alfred Wegener 9. Around 1912, Wegener, a German geologist and astronomer, proposed that continents move • Pangaea – supercontinent formed when all of earth’s landmasses were joined • Scientists didn’t believe him for almost 50 years 10. What evidence supports Pangaea? 10. Fossils of same species on all continents Same rock formations across continents Ancient glaciers were in the tropics 11. When and how was the ocean floor mapped? http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hs w/9068-discovering-mathmeasuring-distance-and-depthvideo.htm 11. The ocean floor was mapped in the 1950s using sonar. 12. How does sea floor spreading occur? 12. Mid-ocean ridge is a huge crack where the hot mantle pushes upward. Crust is older as you move outward from the ridge Magnetic field reverses http://videos.howstuffworks.com/hsw/2656 0-earth-science-the-spreading-seafloorvideo.htm 13. Describe plate tectonics 13. Lithosphere is divided into plates that constantly move Continental Plates – lighter Oceanic Plates – heavier http://videos.howstuffwork s.com/hsw/8638-insidethe-earth-continentaldrift-video.htm 14. What are divergent boundaries? 14. Divergent boundaries are plates that move apart. Examples: Mid-oceanic ridge Great Rift Valley in Africa 14. What are convergent boundaries? 14. Convergent plates occur when plates run into each other ( subduction zone) Examples: Oceanic to oceanic – Japan Oceanic to continental – Andes Mountains in South America Continental to continental – Himalayan Mountains in Asia Oceanic to continental – Andes Mountains in South America Continental to continental – Himalayan Mountains in Asia 15. What is a transform boundary? 15. In a transform boundary, plates slide in opposite directions. Example: San Andreas Fault, California