* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download What are Density Currents?
Atlantic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Great Pacific garbage patch wikipedia , lookup
Ocean Park Hong Kong wikipedia , lookup
Marine debris wikipedia , lookup
Pacific Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Southern Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean Research Group wikipedia , lookup
Marine pollution wikipedia , lookup
Indian Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Arctic Ocean wikipedia , lookup
Ecosystem of the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre wikipedia , lookup
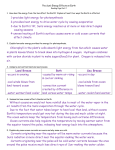
Oceans Topic: Seafloor Topography Objectives: • I will know seafloor features of the continental margin • I will know seafloor features of the deep ocean basin Water Planet • ¾ (75%) of the Earth’s surface is covered in water • No other planet in our solar system is covered by so much water • Earth is truly a water planet Oceans and You • Why Study the Oceans? • The Oceans supply us with food • The Oceans create our weather and greatly influence global climates • 44% of the world’s population live near the ocean • 50% of the worlds oxygen comes from the Ocean • Finally, many resources, such as food and energy come from the ocean Oceanography • People who study the ocean are called Oceanographers • Oceanography is the study of the physical, chemical, and biological aspects of the ocean • These include seafloor features, such as trenches; or life-forms that dominate the ocean Ocean Exploration • More is known about the surface of the moon than the surface of the deep ocean • Oceanographers first started mapping the ocean bottom in the 1950’s • Why?! • We needed to provide maps of the ocean bottom so our submarines could spy on other countries • It was thought that the ocean floor was flat • After mapping it, it was revealed that the ocean bottom was far more complex than previously thought Sonar • So how did we map the ocean bottom? • In the 1950’s, a new technology called sonar was developed • Sonar uses sound waves that bounce off the bottom of the ocean Sonar • Sonar is a system that uses sound acoustic signals and reflected echoes used to map the ocean bottom • Scientists measure the time it takes for the sound waves to strike the bottom and bounce back Here is how it works: What is Sonar? • A system that uses sound acoustic signals and _______echoes used to map the ocean bottom Answer Bank Subduction submerged Deep eroded flat Reflected Steep volcanic Features of the Ocean Floor • The ocean floor is divided into 2 major areas: – Continental Margins (submerged edge of continents) – Deep Ocean Basins (deeper parts of the ocean that lie over oceanic crust) Continental Margin Deep Ocean Basins Continental Margins • The continental Margin is made up of the submerged edge of continents • It composed of the continental shelf and continental slope • The continental shelf Margin is the flat Continental zone of shallow water near the edge of a continent • The continental slope is the edge of a continent that drops off into deep water Continental Shelf Continental Slope What are features of the Continental Margin? Continental _____zone of Shelf: shallow water near the edge of a continent Continental The _____edge of a Slope: continent that drops off into deep water Please Draw and label: Answer Bank Subduction submerged Deep eroded flat Reflected Steep volcanic Deep Ocean Basins • Deep ocean basins also have distinct features • These features include broad, abyssal plains, submerged volcanoes called seamounts, mountain ranges; and deep sea trenches Mid-Ocean Ridge – Abyssal Plains – Underwater volcanic extensive flat areas Guyot - flat wave mountain chain where Deep Oceanislands Basin of the deep ocean eroded 2 plates pull away from each other Seamounts – submerged volcanic mountains Trench - Long steep depression that forms as a result of tectonic plate subduction Where is the Trench??? • Here is a picture of the ocean floor near Alaska, compliments of Google earth • Outlined in red is a trench where two plates collide and one subducts Where is the Trench??? • Outlined in red is a trench where two plates collide and one subducts Mid-Ocean Ridge Seamounts D E G A F E D B C Where is the mid-ocean ridge? Where is a trench? Where is the abyssal plain? Where is a Seamount? Where is the continental shelf?? Where is the continental slope??? What are features of the Deep Ocean Basins? Long steep depression that forms as a result of tectonic plate_______ Abyssal Plains: Extensive flat areas of the _____ ocean. Cover 50% Underwater ______mountain Mid-Ocean chain where 2 plates pull away Ridges: from each other _______ volcanic mountains Seamount: Trenches: Guyot: Flat, wave-______ seamount Answer Bank Subduction submerged Deep eroded flat Reflected Steep volcanic Summarize: 1. The continental _____ is the zone of shallow water near the edge of a continent and the continental ____ is the steep edge of a continent that drops off into deep water 2. Mid____ ___are Underwater volcanic mountain chains where 2 plates pull away from each other 3. ____ ____are Extensive flat areas of the deep ocean. 4. _____ are submerged volcanic mountains Please draw the diagram below and label the following features: Continental shelf and slope, Seamount, Mid-ocean ridge, Abyssal Plains Please draw and label the features: Answer Bank Seamount Shelf Abyssal plains Ocean ridges slope Topic: Ocean Currents Objectives: I will know factors which influence water density I will know the difference between surface currents and deep ocean density currents I will know how the surface currents and density currents connect up forming the ocean conveyor Ocean Water Density • • • • • • • What do you think effects ocean water density? How cold the water is? Perhaps, how salty the water is? Actually, the answer is both! Water becomes more denser (heavier) as it becomes colder Water also becomes more dense (heavier) with increasing salinity This is why people can float in the great Salt Lake in Utah Ocean Water Density • If we were to boil salty water, only the water molecules would evaporate, leaving behind the salt, creating a saltier mixture • As a result the salty water is more dense! • Do you remember where on earth salinity was greatest, or where water was the most dense? What factors effect Ocean water density? • _____ and _____ effect water density • The colder and saltier the water is, the more dense it is Answer Bank Equator Poles Wind Desnity(2) Temperature(2) salinity Ocean Currents: 2 Types • There are 2 types of currents: -There are deep water density currents driven by differences in density -And there are surface currents driven by wind What are the 2 types of currents? • Surface currents powered by ___ and density currents powered by ______ and _____ Answer Bank differences Equator Poles Wind Density Temperature(2) salinity Surface Ocean Currents Ocean surface currents If you recall, the earth Is If you Ocean further currents recall, move heat heat travels are very important for distributing heated unequally from the sun: from From the hotequator to cold to areas, thewould Heat, without them the earth Direct solar radiation at the equator AsAnd a result poles byradiation convection currents Be asurface much colder place indirect solar at the develop poles Surface Ocean Currents • Surface currents move water horizontally, or parallel to the earths surface • They deliver warm water to the poles by convection • They spin clockwise in the northern Hemisphere and counter clockwise in the southern hemisphere Simplified Ocean Current Surface Ocean Currents • Ocean currents form as a result Westerlies ofThe 2 things: Coriolis Effect and – Global wind The continents cause Tradewinds patterns The currents to curve Coriolis to– the right effect in the northern hemisphere, and to the left in theTradewinds southern hemisphere Westerlies Simplified Ocean Current What are surface currents? • Current that flows like a river in the top 100 meters of the ocean due to _____ winds and the ____effect • They distribute heat from the ____ to the ____ spinning clockwise in the northern hemisphere and counter clockwise in the southern Answer Bank Equator hemisphere Poles Wind coriolis Density(2) Temperature(2) Salinity global Surface Ocean Currents • There are generally 2 types of surface currents: warm and cold • Warm currents come from the warm tropics or equator • Cold currents come from the cold polar zones Simplified Ocean Current Surface Currents • In reality, ocean currents are not that simplified • However, the general movement is still the same -- clockwise in the northern hemisphere, counter-clockwise in the southern hemisphere Simplified Ocean Current How are the currents spinning in the Northern Hemisphere? How are the currents spinning in the Southern Hemisphere? Clockwise in the Northern Hemisphere Counter-Clockwise in the Southern Hemisphere Where are the warm currents coming from? Where are the cold currents coming from? What current is of the West coast ? What current is of the East coast ? Warm Gulf Stream current Cold California Current Gulf Stream • For as many years as ships have sailed, sailors have used surface currents and global wind patterns to help them travel quickly • During the American colonial era, ships floated on the 100km wide Gulf Stream current to go from North America to England Gulf Stream • The Gulf Stream is a warm water current that delivers warm water from the equator up along the east coast of North America • This current keeps the climates of Iceland and Great Britain mild or moderate • Remember, warm ocean currents create warmer than normal climates What are the 2 types of surface currents? • Warm currents from the _____ Example: Gulf Stream current • Cold currents from the____ • Ex: California Current Answer Bank Equator Poles(2) Wind warm Desnity(2) Temperature(2) Salinity equator Density Currents Iceberg Tropical Regions Polar Regions Therefore, cold salty water This density flows backout to the 60o 0o Warm watercurrent from the When seawater freezes, it equator locks sinks at the toward polar regions As it the moves the Equator along the ocean bottom the salt and water becomes saltier moves toward the Poles Bringing oxygen and nutrients with it poles, it begins to cool And the density current is complete What are Density Currents? • Deep water currents that form due to _____ and salinity differences Answer Bank Equator Poles(2) Wind warm Desnity(2) Temperature(2) Salinity equator Thermohaline Conveyor • The thermohaline conveyor is a global circulation of ocean water that combines warm surface currents and cold deep water density currents Deep Water Density Currents • This deep water density current is called the Thermohaline Conveyor • Remember “thermo” means temperature or heat and “haline” means salt---the 2 things regulate ocean water density Thermohaline Conveyor • Colors in blue indicate saltier, colder, density currents • Colors in Red indicate warmer, surface currents What is the Thermohaline Conveyor? • A global ocean current that combines warm_____ currents and cold_____ currents Answer Bank Equator Poles Wind Density(2) Temperature(2) Salinity surface Summary: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5) Surface currents are powered by global ____and ______ affect Surface currents spin ______in the northern hemisphere and _____clockwise in the southern hemisphere Warm currents come from the ___ and cold currents come from the ____ Density currents develop from _____and _____ differences The thermohaline ______is a global ocean current that combines surface currents and density currents Answer Bank equator Coriolis Winds Poles Temperature Conveyor Salinity counter Topic: Ocean Environments Objectives: • I will know the difference between the benthic and pelagic zone • I will know the importance of phytoplankton and their role in the ocean • I will know the process of upwelling and it’s importance along California's coast Ocean Environments • The ocean can be divided into 2 parts • The Benthic zone and the Pelagic zone Ocean Environments • The benthic zone makes up the bottom of the ocean • Animals that live on the bottom live on the benthic zone Benthic Communities Ocean Environments • The pelagic zone makes up the open ocean • Animals that live in the open ocean live in the pelagic zone Pelagic Organisms Giant Squid Creatures of the abyss – Angler Fish Hag Fish Creatures of the abyss – viper fish and an angler fish What are the 2 major ocean environments? • Benthic zone-region that goes along the______ • Pelagic zone- _____ ocean region Answer Bank Nutrient 50% Open Bottom base Ocean Ecology • • • • The ocean produces 50% of the earth’s oxygen But what produces that oxygen? Phytoplankton! Phytoplankton, are microscopic plants that produce oxygen through photosynthesis • Phytoplankton live near the ocean’s surface where sunlight is present Ocean Ecology • If you remember, Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide, and Water are needed for photosynthesis • Oxygen is given off! So go on, take a deep Breath! Phytoplankton take in Sunlight, Carbon Dioxide, and Water for Photosynthesis Oxygen is given off! Phytoplankton form the base of the ocean’s food web Zooplankton eat Phytoplankton form the base the phytoplankton Small fish eat of the ocean’s food web the zooplankton Food Chain • • Zooplankton eat the phytoplankton Large fish eat the small fish and so on . . . . • Small fish eat the zooplankton • Large fish eat the small fish and so on . . . . What are phytoplankton? Answer Bank • Microscopic plants that produce ____ of the worlds oxygen through photosynthesis • They form the ____of the ocean’s food web Green areas Indicate phytoplankton Nutrient 50% Open Bottom base Upwelling This cold deep water contains high concentrations of nutrients • Phytoplankton take advantage of the nutrient rich waters growing in large numbers • This results in an increase in life along the coast Upwelling • Upwelling is a circulation in the ocean where deep, cold water replaces warm water along the coast • In upwelling, wind blowing offshore or parallel to the coast carries water away from the land What is Upwelling? • The movement of deep, cold and _____ rich water to the surface due to winds forcing water offshore Answer Bank Nutrient 50% Open Bottom base Summarize: • Animals that live in the benthic zone live on the _____ of the ocean and animals that live in the pelagic zone swim in the _______ ocean • Phytoplankton produce ____ of the worlds oxygen and are at the ____ of the food chain • _______ is the movement of cold nutrient rich water to the surface Answer Bank 50% Open Bottom(2) upwelling Topic: Salinity & Tides • Objectives: – I will understand ocean salinity and the amount of dissolved salt in the ocean – I will understand tides and what causes them Salinity • In sea water, the most abundant elements are sodium and chlorine • Sodium and Chlorine form together to make a mineral called halite or table salt to season our food • Rivers deliver these salts to the ocean • Salinity is the measure of the amount of solids dissolved in sea water 96.5% water 3.5% salt What is the Salinity of ocean water? • Ocean water consists of ___% water and ___% salt (sodium chloride) • High Evaporation rates in the tropics increase salinity in the ocean Answer Bank 96.5 3.5 Tides • If you ever visited tide pools at the beach, you know that the best time to go is at low tide • You might have even noticed the tide rise and fall while visiting the beach • The rise and fall of sea level is called a tide Tides • The tide is actually caused by a giant wave • The moons gravitational pull causes a massive bulge, or wave that pulls on the ocean as it orbits earth • As the crest of the wave approaches the shore, what kind of tide do you think we get? What Causes the Tides? • Put simply, the gravitational effect of the Moon and Sun • Remember, gravity is the mutual attraction between two objects; and the force between the two objects increases as their size and mass increases • Water responds to the gravitational pull of the Moon What Causes the Tides? • Two bulges of water form, one directly under the Moon and one on the opposite side of earth • As the earth spins, these bulges follow the moon and its daily movement • As the earth rotates, different locations on Earth’s surface pass in and out of high tide A Wave that Represents Tide -When is High Tide -When is Low Tide When is the biggest tides! What are tides and how are they formed? • Periodic rise and fall of the water level in the oceans and other large bodies of water caused by a massive wave created by the moon and sun’s _______ pull • Spring tides produce the Highest and lowest tides and occur when the sun and moon are _____ • Neap tides produce small changes in tides and occur when the moon earth and sun are at right angles to each other Answer Bank 96.5 gravitational 3.5 aligned Summarize: • The greatest tides (spring tide) occur when the moon and ____ are aligned • Smaller tides (neap tide) occur whe nte hsun and moon are at ____ angles to each other • Ocean water is made up of ___% salt and ___% water