* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Internal Structure of the Earth
Post-glacial rebound wikipedia , lookup
History of geomagnetism wikipedia , lookup
Spherical Earth wikipedia , lookup
Abyssal plain wikipedia , lookup
Geochemistry wikipedia , lookup
History of geology wikipedia , lookup
Age of the Earth wikipedia , lookup
History of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Future of Earth wikipedia , lookup
Large igneous province wikipedia , lookup
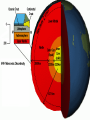
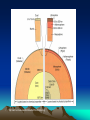
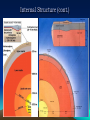
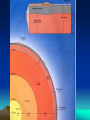
Internal Structure of the Earth Internal Structure (cont.) Crust – the outer, hardest layer of the lithosphere; continental crust (mostly granite, 2.7 g/cm³, 0-40 km) and oceanic crust (basalt 3.0 g/cm³, 010km) Lithosphere – crust and upper most, solid, rigid portion of the mantle – broken into pieces (0-100 km) Internal Structure (cont.) Asthenosphere – partially molten rock in the upper mantle; plastic consistency (100700km) Mohorovic Discontinuity (Moho) – the boundary between the Earth’s crust and the upper mantle -- averaging 8 kilometers (5 miles) in depth under the oceans and 32 kilometers (20 miles) in depth under the continents Internal Structure (cont.) Mantle – molten rock that has a much stiffer consistency than the asthenosphere – solid yet behaves like a liquid similar to a glacier (3.3 – 5.5 g/cm³, 700- 2900km) Outer Core – liquid iron and nickel (9.9 – 12.1 g/cm³, 2900 to 4980km) Inner Core – solid, iron and nickel (12.713.0 g/cm³, 4980 to 6370km) • http://earth.unh.edu/esci402/docs/Earth%20Interior.jpg Internal Structure (cont.) what some scientists think is going on… Internal Structure (cont.) ~ The End ~ Extra - Extra Come to me after school and sing… The first verse of the Hokey Pokey and get a PRIZE