* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
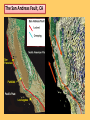
CHAPTER 8: EARTHQUAKES and EARTH’S INTERIOR ROOTS: Crypto = hidden (cryptography) Cumul = mass (cumulative) Cycl = circle (cycle) De = reduce (decelerate) Deca = ten (decade) Deci = one tenth (decibel) Dem = people (democracy) Demi = less than (demigod) Dendr = tree (dendriform – treelike) Dent = tooth (dentist) California Earthquake! Terrashake! http://visservices.sdsc.edu/projects/scec/teras hake/2.1/ CH 8.1 What is an Earthquake? Earthquake = the vibration of Earth produced by the rapid release of energy. Focus = point inside Earth where the earthquake starts. Epicenter = location on the surface directly above the focus. Epicenter and Focus http://www.pbs.org/wnet/savageearth/animations/earthquakes/index.html Fault = fracture in Earth’s crust where movement has occurred. 1906 San Francisco Earthquake Western side of fault moved 4.7 meters to the north. Over people were homeless. Over 225,000 3000 people died. The San Andreas Fault, CA Based on the movements of the San Andreas fault the Elastic Rebound hypothesis was developed. A. Existing Fault B. Forces deform and put pressure on rocks. C. The pressure overcomes the strength of the rocks. The rocks break and slip. D. The pressure is relieved and the ground stops moving. Pg.. 220 Figure 4 Elastic Rebound Hypothesis http://www.sceyencestudios.com/animation.htm UNCONFORMITY ????? http://www.classzone.com/books/earth_scien ce/terc/content/visualizations/es2902/es2902 page01.cfm?chapter_no=visualization Most earthquakes are produced by the rapid release of elastic energy stored in rock that has been subjected to great forces. When the pressure on the rock exceeds the strength of the rock, the rock suddenly breaks. Aftershocks and Foreshocks Foreshocks = small earthquakes that occur prior to a larger earthquake. Aftershocks = small earthquakes that occur following a larger earthquake. Foreshocks and Aftershocks http://earthquake.usgs.gov/learning/animations/animation.php?flash_title=Foreshocks +Flash+Animation&flash_file=aftershock&flash_width=400&flash_height=275