* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Clinical Manifestation
Onchocerciasis wikipedia , lookup
Toxocariasis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex virus wikipedia , lookup
Microbicides for sexually transmitted diseases wikipedia , lookup
Middle East respiratory syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Staphylococcus aureus wikipedia , lookup
Cryptosporidiosis wikipedia , lookup
Chagas disease wikipedia , lookup
African trypanosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Henipavirus wikipedia , lookup
Gastroenteritis wikipedia , lookup
Herpes simplex wikipedia , lookup
Toxoplasmosis wikipedia , lookup
Traveler's diarrhea wikipedia , lookup
West Nile fever wikipedia , lookup
Hookworm infection wikipedia , lookup
Carbapenem-resistant enterobacteriaceae wikipedia , lookup
Tuberculosis wikipedia , lookup
Sexually transmitted infection wikipedia , lookup
Marburg virus disease wikipedia , lookup
Leptospirosis wikipedia , lookup
Antibiotics wikipedia , lookup
Neisseria meningitidis wikipedia , lookup
Clostridium difficile infection wikipedia , lookup
Trichinosis wikipedia , lookup
Dirofilaria immitis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis C wikipedia , lookup
Anaerobic infection wikipedia , lookup
Sarcocystis wikipedia , lookup
Human cytomegalovirus wikipedia , lookup
Schistosomiasis wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Lymphocytic choriomeningitis wikipedia , lookup
Fasciolosis wikipedia , lookup
Coccidioidomycosis wikipedia , lookup
Oesophagostomum wikipedia , lookup
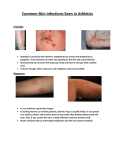
Surgical Infection Dr. Weiguo Hu 胡伟国 Dr. Weihua Qiu 邱伟华 Department of Surgery Rui Jin Hospital Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine Key Points: Definition Classifications Etiology Clinical Manifestation Management Specific Surgical Infections Characteristics of Hand Infections Definition: Infections be treated by surgical intervention Infections following surgical procedure (wound or distant site) Classifications:Characteristic Non-specific infection Furuncle & Carbuncle Cellulitis & Erysipelas Hand infection Acute appendicitis Acute peritonitis Breast abscess Classifications:Characteristic Specific infection Tuberculosis Fungal infection Tetanus Gas gangrene Classifications:Course of Disease Acute infection (<3w) Most non-specific infection Tetanus Gas gangrene Chronic infection (>2M) Tuberculosis Sub-acute infection (3w-2M) Urine tract infection Fungal infection Classifications:Others Opportunistic Infection Superinfection Nosocomial Infection Classifications:Others Local phase Systemic phase Skin infection Bacteremia Soft-tissue infection Sepsis Hand infection Abscess Etiology:Pathogenic Microorgansim Bacteria Endotoxin Virus Ectotoxin Fungi Enzyme Etiology:Local Factors Trauma Ischemia and Hypoxia Obstruction Presence of Foreign Bodies and Necrotic Tissues Ionizing Radiation Edema Etiology:Systemic Factors Severe Trauma DM Cancer, Chemotherapy Leukemia AIDS Immunodeficiency Malnutrition Results:Non-specific Infections Cure Dissemination Abscess formation Bacteriamia & Sepsis & SIRS & MODS Chronic infection Results:Specific Infections Mixed infection Systemic infection Tuberculosis Tetanus, gas gangrene Opportunistic infection Fungi Clinical Manifestation: Localized surgical infection Redness Swelling Pain Heat Loss of function Clinical Manifestation: Localized surgical infection Fever Chills Tachycardia Leukocytosis & left shift of WBCs Synergistic Gangrene caused by streptococci & staphylococci (self-injection with heroin) Clinical Manifestation: Severe Systemic Infection (Gram-positive) Chill, Fever Flushing Warm Extremities Metastatic abscess Shock in late phase Clinical Manifestation: Severe Systemic Infection (Gram-negative) Chill, Fever Cold Extremities Shock in early phase Oliguria High-output heart failure Disturbed sensorium Diagnosis: HPI Physical Examination General Condition Regional Symptoms Mal-function of Related Organs Characteristic Manifestations Diagnosis: Lab Test CBC Culture Sensitivity Test Others CT Ultrasonic X-ray Physical Exam: Intravenous cannula---purulent drainage or thrombophlebitis Rectal examination---pelvic abscess Auscultation of chest---pneumonia Physical Exam: Exudate Accumulation of extracellular fluid Color, odor, character Be useful in categorizing the causative organism Gram stain an essential procedure for diagnosis and treatment Breast abscess Physical Exam: Biopsy Being necessary for diagnosis sometimes Especially for granulomatous infection Tuberculosis blastomycosis Culture: Exudate Blood the most reliable diagnosis for treatment Both aerobic and anaerobic culture Diagnostic step for unknown source Fail to capture causative organisms in bacteremia Unnecessary to diagnose sepsis Sputum Urine Management: General Supporting Temperature Control Management of Water and Electrolytes Balance Nutrition Supplement Hypoalbuminemia Uderlying Factors Vital Signs Monitor Management: Immobilization of the infection area Effective local care Relief of swelling & pain Proper Dressing Physical Therapy to increase local blood supply to facilitate exudation Management: Surgical Therapy Debridement of Infected or necrotic tissues Harboring foreign objects & microorgnisms Poor blood supply Decreasing host resistance Skin Grafting Paracentesis Drainage of Abscess Removal of Foreign Body Simple appendicitis treated by early operation Neglected, perforated appendicitis with a complex lower abdominal abscess associated with necrosis of adjacent tissue Principle of Antibiotics Management: Indications: Acute sever trauma and infection Prophylactic Management Management:Antibiotics Bacteriostatic agents Prevent growth of bacteria Bacteriocidal agents Actually kill bacteria Management:Antibiotics Effective agent against the infecting organism Adequate contact between agent and organism Absence of toxic side effect of the agent Augmentation of host defenses to maximize antibacterial effects Management:Antibiotics Culture before antibiotic therapy Administer antibiotics on empiric basis before the laboratory reports Culture and sensitivity test (Evidence basis) a combination of antibiotics for probable polymicrobic infection Colonization & Superinfection: Colonization The quantitative appearance of changes in the microflora that are induced by antibiotic therapy Superinfection A new microbial disease introduced or potentiated by antibiotic therapy Superinfection is frequently the result of colonization. Antibiotic Prophylaxis for potentially contaminated wounds Only an adjunct and NOT a substitute to good surgical technique Antibiotic Prophylaxis Clean procedure Clean contaminated procedure Contact of the interior of respiratory, urinary,GI tracts Contaminated procedure no antibiotics are necessary Complicated by gross spillage of intestinal contents or wounds secondary to trauma Dirty wounds In contact with intraabdominal or perirectal abscess Antibiotic Prophylaxis Malnourished Obese Elderly Immunodeficient Shock or MOF Poor blood supply to the operative region Antibiotic Prophylaxis early and enough for adequate tissue and body fluid levels Being necessary to maintain adequate tissue levels intra-operatively length of operation and serum half-life of antibiotics Cellular site of inhibition Bacteriocidal Cell wall synthesis Barrier function of cell membrane penicillin cephalosporins vancomycin amphotericin B Bacteriostatic nystatin polymyxin Protein synthesis in ribosome aminoglycosides tetracycline chloramphenicol Erythromycin clindamycin DNA replication Griseofulvin Thanks! Definition: Being best treated by operative intervention Being following surgical procedure (wound or distant site) Clinical Manifestation: Localized surgical infection Superficial wound infection due to hemolytic Streptococci