* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 9D Urey Miller Experiment 7G Endosymbiosis
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
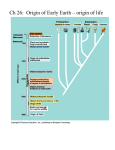
9D Urey Miller Experiment and 7G Cell Complexity http://highered.mcgrawhill.com/sites/9834092339/student_vie w0/chapter26/animation_-_millerurey_experiment.html Review: What are the four biomolecules? Organic Molecules • Molecules that contain bonds between carbon atoms. • Significant because many of them are IMPORTANT to LIVING things • Examples: Nucleic acids, ATP, amino acids, proteins Chain of Events that Led to Life • Formation of simple molecules • Joining of simple molecules to make complex molecules • Self-replicating molecules (RNA that replicates by itself) • Metabolic processes (LIFE!) Urey Miller Experiment Proposed that simple organic molecules could form in the conditions of early Earth. Accumulated in the ocean as “soup” Formed complex organic molecules from the simple ones Over time, cells (that live in no oxygen) anaerobic heterotrophs developed from these conditions Urey Miller Experiment • http://bcs.whfreeman.com/thelifewire/conten t/chp03/0301s.swf Checkpoint What was the overall goal of the Urey Miller experiment? To show that _______________ molecules could be formed from the smaller INORGANIC conditions of the _________________. 7G Cell Complexity • Now that we have the first cells… • How do we get complicated organelles? Earth’s atmosphere • The first cells lived when Earth’s atmosphere lacked oxygen. (NO OXYGEN!) • Over time, cellular processes such as photosynthesis and cellular respiration developed that INTRODUCED Oxygen to the atmosphere. Endosymbiotic Theory • Anaerobic Bacteria (lives without oxygen) engulfs an aerobic heterotrophic bacteria (lives in oxygen that can make ATP) • The bacteria becomes a mitochondria makes ATP for the cell. Endosymbiotic Theory • The bacteria with the mitochondria engulfs a photosynthetic bacteria. • The photosynthetic bacteria becomes the chloroplast uses sunlight to make SUGAR for the cell.