* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Non-specific Immune Response
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
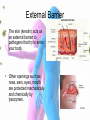
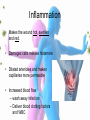
Immune Response Non-Specific Immunity Defence mechanisms Non-Specific (Response is immediate and the same for all pathogens) Physical Barrier Phagocytosis Specific Response is slower and specific to each pathogen Cell mediated response T lymphocytes Humoral response B lymphocytes Ear wax is bactericidal (kills bacteria) Phagocytes are attracted to the wound site by chemicals released by the damaged tissue. They engulf and digest bacteria The skin’s keratin (hard protein) outer layer is waxy and impermeable to water and pathogens Blood clotting seals wounds Secretions contain lysozyme, an enzyme that breaks down bacterial cell walls causing cells to burst The action of mucous and cilia prevent entry of pathogens into lungs Acid kills any bacteria that enters with food Harmless bacteria competitively exclude pathogenic bacteria Vaginal secretions are acidic Large number of microbes live in this region and are well adapted to the salty conditions. They are harmless and reduce colonisation by other bacteria External Barrier • The skin (keratin) acts as an external barrier to pathogens that try to enter your body. • Other openings such as nose, ears, eyes, mouth are protected mechanically and chemically by lysozymes. External Barriers • Mucous and cilia prevent entry to mouth • Blood clotting seals wounds • Acid in stomach stops and vagina Lysozyme • Foreign material which tries to enter your body is often trapped in mucous. • Lysozyme is an enzyme secreted in your tears, saliva and nasal secretions. • Lysozyme kills bacteria by breaking down their cell walls Inflammation • Makes the wound hot, swollen and red. • Damages cells release histamine • Dilated arterioles and makes capillaries more permeable • Increased blood flow – wash away infection – Deliver blood clotting factors and WBC How do we recognise our own body cells • Major Histocompatability Complex (MHC) attached to the plasma membrane of cells. • Mostly proteins but can also be carbohydrates (eg glycoproteins) • Identify cells as being self or foreign What are Anitgens? An antigen is any part of an organism that is recognised as being non-self by the immune system and stimulates the immune response. (anti –antibody, gen-generator) – Usually proteins or glycoproteins on the cell plasma membrane or cell wall of invading pathogen. Where do we find antigens? • Antigens can be found: – Phagocytes displaying antigens – Body cells invaded by viruses display antigens – Transplanted cells will have non-self antigens – Cancer cells will have different anigens on their surface. These are all called antigen-presenting cells (APC) Phagocytes • Engulf antigens and digest them • Two types: – Neutrophils – 70%WBC – Engulf 5-20 bacteria – Macrophages – 4% WBC – Engulf >100 bacteria • Engulfed material is enclosed within a vacuole and digested with hydrolytic enzymes from lysosomes • Dead phagocytes create pus • Phagocytes then PRESENT THE ANTIGENS on their surface A Level Question a) What is a pathogen? [1] b) When a pathogen enters the body it may be destroyed by phagocytosis. Describe how. [4] Use the following Key words in the correct order: • • • • • Antigen Presenting Cell (APC) Engulf and destroy/hydrolysis Phagosome/vacuole/vesicle Phagocyte Lysosome Answers a) (micro)organism that causes disease/harm to body/an immune response b) i) phagocyte attracted by a substance/recognises foreign antigen ii) antigen/pathoden engulfed iii) Enclosed in vacuole/vesicle/phagosome iv) Lysosome contains enzymes fuses with phagosome v) Pathogen digested/molecules hydrolysed vi) Phagocyte presents antigen (APC)