* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PPT 2 - ap biology
Genetics and archaeogenetics of South Asia wikipedia , lookup
Hybrid (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Species distribution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive evolution in the human genome wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Dual inheritance theory wikipedia , lookup
Polymorphism (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Koinophilia wikipedia , lookup
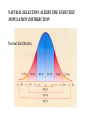
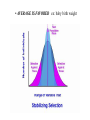
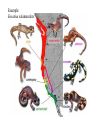
NATURAL SELECTION ALTERS THE EXPECTED POPULATION DISTRIBUTION Normal distribution • AVERAGE IS FAVORED ex: baby birth weight • ONE EXTREME SELECTED Ex: Peppered moths • BOTH EXTREMES SELECTED Can lead to speciation Normal curve Disruptive selection ex: butterfly mimics VARIATION ALSO EXISTS BETWEEN POPULATIONS i.e. due to geographic factors Island Fox Urocyon littoralis U. littoralis from separate islands are physically / genetically distinct. Channel Islands, CA Ex: the average number of caudal (tail) vertebrae Can be a gradual change, called a cline Ex: A ‘ring species Variants can/do interbreed where range overlaps But adjacent variants do not interbreed where the circle closes Example: Ensatina salamanders NOT ALL VARIATION IS HERITABLE Phenotype is influenced by environment as well In mammal species that colonize islands, big ones have a tendency to shrink while small ones are apt to enlarge mainland island island mainland OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION Genetic Drift Populations experience unique (and random) mutations, becoming less alike over time River divides the population OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION Genetic Drift OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION Founders Effect A few individuals are the founders of a new population; this group lacks all the variations of the original population OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION Founders Effect Summer 1995: at least 15 iguanas survived Hurricane Marilyn on a raft of uprooted trees eventually colonizing Anguilla. These were the first Iguana iguana, to reach the island. Will this population become distinct in time? OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION The Bottleneck Effect OTHERS FACTORS leading to EVOLUTION The Bottleneck Effect The effect of loss of prairie habitat on greater prairie chickens in Illinois. The bottleneck led to reduced genetic variation, as measured by number of alleles per locus. The reduced genetic variation is also reflected in lowered egg hatching rates. Gene Flow populations become more alike as genes are exchanged hybridization seeds, pollen seeds, pollen Genetic engineering plasmid exchange hitch-hikers