* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Functional Genomics
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
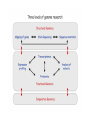
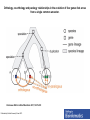
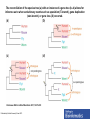
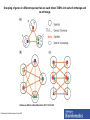
Functional Genomics Branches of Genomics Structural Genomics Metagenomics Genomics Comparativ e Genomics Functional Genomics Why We Need Functional Genomics Organism E. coli yeast C. elegans Drosophila Arabadopsis mouse human # genes % of genes with inferred function Completion date of genome 4288 6,600 19,000 12-14K 25,000 ~30,000? ~30,000? 60 40 40 25 40 10-20 10-20 1997 1996 1998 1999 2000 2002 2000 How to determine functionally related genes? • 40% if predicted genes in newly sequenced genomes cannot be assigned function based on sequence similarity. • Genes sharing a common pattern of expression in many different experiments are likely to be involved in similar processes. – Gene A regulates Gene B, or vice versa – Gene A and Gene B are regulated by Gene C Orthology, co-orthology and paralogy relationships in the evolution of four genes that arose from a single common ancestor. Kristensen D M et al. Brief Bioinform 2011;12:379-391 Published by Oxford University Press 2011. The reconciliation of the species tree (a) with an instance of a gene tree (b–d) allows for inference as to when evolutionary events such as speciation (T-branch), gene duplication (star-branch), or gene loss (X) occurred. Kristensen D M et al. Brief Bioinform 2011;12:379-391 Published by Oxford University Press 2011. Grouping of genes in different species that are each others’ BBHs into sets of orthologs and co-orthologs. Kristensen D M et al. Brief Bioinform 2011;12:379-391 Published by Oxford University Press 2011. Clusters of Orthologous Groups (COG) • Identification of orthologs is critical for reliable prediction of gene function in newly sequenced genomes. • The purpose of COG is to serve as a platform for functional annotation of newly sequenced genomes and for study of genome evolution. Links • Unicellular clusters (COGs): – http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/COG/grace/uni.html • Eukaryotic orthologous groups (KOGs): – http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/COG/grace/shokog.cgi • 2003 paper • 2011 paper