* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mendelian Inheritance of Human Traits
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Tay–Sachs disease wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Medical genetics wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
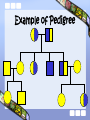
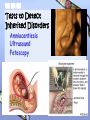
Simple Inheritance, Pedigrees, & Karyotypes Pedigrees • Similar to family trees • A graphic representation of genetic inheritance Pedigree Symbols Female Affected Carrier Female Female Mating Male Affected Carrier Male Male Example of Pedigree Simple Recessively Inherited Disorders • Disorder only seen if two recessive alleles are inherited. Cystic Fibrosis • Leads to excess amounts • of mucus in the digestive and respiratory tract • Can be treated Sickle-Cell Anemia • Proteins on blood are changed, thus changing the shape of the blood • Abnormal red blood cells they are shaped like a sickle, or half –moon. Tay-Sachs Disease • Leads to lipids accumulating in the central nervous system • Children with disease can not control their bodily functions (muscles) Tay-Sachs Disease problem breaking down lipids; change diet to fix Phenylketonuria (PKU) • Body can’t break down an enzyme found in milk; causes nerve damage • PKU children appear normal at first • Leads to the build up of the amino acid: phenylalanine • Can lead to mental retardation Albinism • lacking melanin in skin Dominantly Inherited Traits • Trait or Disorder seen if one dominant allele inherited Different Dominantly Inherited Traits • Free Earlobes • Hitchhiker’s Thumb Cleft Chin Widow’s Peak Polydactyly – presence of more than 5 fingers and toes Huntington’s Disease • Dominantly Inherited • Neurological disorder that causes lack of muscular control • Onset around age 30 Sex-Linked Traits • Traits determined by genes carried on the sex chromosomes (X-chromosome) • Ex: colorblindness, hemophilia, muscular dystrophy Red-Green Color Blindness • Common in males • People who have red-green color blindness can’t differentiate these two colors What Colors Do You See? Hemophilia • More common in males • Causes a problem with blood clotting Carrier: an individual heterozygous for a specific trait…(carries the trait can pass to their offspring) Chromosomal Mutations • Mutation: change in the DNA • Nondisjunction: chromatids or homologous chromosomes stick together instead of separating…they do not disjoin or come apart • Trisomy: has one extra chromosome • Monosomy: missing one chromosome Nondisjunction •Down Syndrome – trisomy 21 (extra chromosome on 21st) •Turner Syndrome – XO (missing sex chromosome) Klinefelter’s Syndrome XXY males XYY Condition Tests to Detect Inherited Disorders Amniocentiesis Ultrasound Fetoscopy Karyotypes • Chart of chromosomes used to diagnosis chromosomal disorders. • Chromosomes are arranged in order from the largest to the smallest • Also used to determine gender Example Karyotype