* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 15 Section 2: Gene Technologies in Our Lives
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics in stem-cell differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Synthetic biology wikipedia , lookup
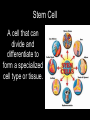
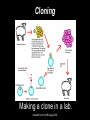
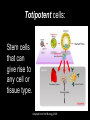
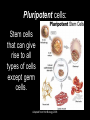
Chapter 15 Gene Technologies and Human Applications Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Genetic Engineering Imagine the appearance of an organism that has some genetically determined characteristics from two different species. Draw a picture of your imaginary organism. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Key Ideas • For what purposes are genes and proteins manipulated? • How are cloning and stem cell research related? • What ethical issues arise with the uses of gene technologies? Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 15 Section 1: The Human Genome Key Vocabulary Terms Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Genetic Engineering The deliberate alteration of the genetic material of an organism. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Recombinant DNA DNA created in the laboratory by combining DNA from different sources. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Clone An organism, cell, or piece of genetic material that is an identical genetic copy Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Stem Cell A cell that can divide and differentiate to form a specialized cell type or tissue. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 15 Section 1: The Human Genome Supplementary Vocabulary Words Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Recombinant, Transgenic, or Genetically Modified Organisms with recombinant genes Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Genetically Modified Organisms (GMOs): In everyday use, a common reference for organisms with recombinant genes Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Proteomics (PROH tee OHM iks): The study of how proteins interact within cells. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Cloning Making a clone in a lab. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Somatic-Cell Nuclear Transfer (SCNT): In this process, the nucleus of an egg cell is replaced with the nucleus of an adult cell. Then, the egg begins to develop into an embryo. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Genomic imprinting: The effect where chemicals in the reproductive system turn “on” or “off” certain genes in the developing gametes. These genes later affect development from embryo to adult. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Totipotent cells: Stem cells that can give rise to any cell or tissue type. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Pluripotent cells: Stem cells that can give rise to all types of cells except germ cells. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Multipotent cells: Stem cells that can give rise to just a few other cell types. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Ethical Conforming to moral standards Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Intellectual property (IP): The ownership of the ideas or plans that a person creates. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Patent A specific set of rights that allow an inventor to control and profit from the uses of his or her idea. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Chapter 15 Section 1: The Human Genome Notes Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Everyday Applications • Genetic engineering was first applied to bacteria, viruses, and plants and is now applied to many life-forms, such as: –Food Crops –Livestock –Medical Treatment –Basic Research Tools Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Genes Organisms may be modified to provide us with: ~a better food supply, ~clean up toxic waste, ~improved healthcare. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Cell Interactions Tissue culture cells can be studied closely and experimentally controlled. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 15-2 Gene Technologies Organisms with modified genes may be called: ~recombinant, ~transgenic, or ~genetically modified organisms (GMO) Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 15-2 Gene Technologies Manipulating Bodies and Development - Cloning Dolly 1997 Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Bodies and Development, continued Cloning, continued • Although scientists have successfully cloned many kinds of animals, only a few of the cloned offspring have survived for long. 4th, 6th, 7th Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Bodies and Development, continued Using Stem Cells • Some stem cells have more potential to differentiate than others. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Bodies and Development – Stem Cells Two main sources: 1. Adult – can develop into some types of cells (multipotent) 2. Embryonic – can develop into all cells except germ cells (pluripotent) Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 5th 15-2 Gene Technologies Stem Cells Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Manipulating Bodies and Development, continued Using Stem Cells • The use of embryos for stem cell research poses ethical problems. • An alternative source of embryonic stem cells is through SCNT. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Ethical and Societal Issues 1. Safety – Genes may be transferred to other organisms or cause harm to other organisms. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Ethical and Social Issues Safety • GMOs can have unforeseen effects. • Ecologists worry that we do not know enough to safely manipulate genes on a large scale. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 15-2 Gene Technologies Ethical and Societal Issues 2. Human Rights – Who should have access to our genetic data? Who should be tested? Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 Ethical and Social Issues Human Rights • The DNA of individuals can be tested for risks of genetic disorders. • This possibility raises many ethical questions. Adapted from Holt Biology 2008 15-2 Gene Technologies Ethical and Societal Issues A patent is a set of rights that allows an inventor to control and profit from his or her idea. Are genes part of nature, or intellectual property? 3. Property Laws – Since the 1980s, genes can be patented! Adapted from Holt Biology 2008