* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of neurodegenerative diseases wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
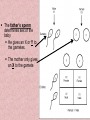
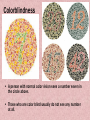
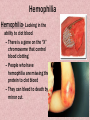
Warm Up #6 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 2/08 What happens to the chromosome # in mitosis? What happens to the chromosome # in meiosis? What is the abbreviation for the steps in mitosis? What’s the abbreviation for the steps in meiosis? Draw a picture showing difference between mitosis & meiosis during metaphase (use 6 chromosomes) Agenda 2/08 • Sex-linked trait notes • Group practice (w/cards) • Card share-out (bonus points) Learning Target • I can describe and explain the differences between codominant, incomplete dominant, polygenic, and sex-linked traits CH 11 Notes #6 Sex-linked Traits 2 Ways to reproduce 1. Sexual: sperm and egg make offspring Examples: dogs mating to make puppies, male flower pollinates a female flower **Advantage: shuffles genes to keep populations healthy** 2. Asexual: one individual clones itself Examples: bacteria divide to reproduce, a new tree grows from a stump Fish fertilizing eggs Degusia (animal) cloning it’s own head Snakes mating Plant cloning itself How do you become a boy or girl? First 22 pairs of chromosomes are called autosomes Sex is determined by the 23rd pair of chromosomes (Called “X” and “Y”) Females: XX Males: XY Question • Does the mother or father determine the sex of the baby? Or both? The father’s sperm determines sex of the baby He gives an X or Y to the gametes. The mother only gives an X to the gamete What are the % chances of having a boy or girl? • Chances of having either sex: always 50% Check for Understanding • A couple are having a baby, what are the chances the baby will be a girl? 50% • A couple have had 3 girls, what are the chances their next child will be a girl? 50% • A couple have had 13 girls. What are their chances their next child will be a girl? 50% Sex-linked genes are genes found on a sex chromosome • Examples: XrXR XrY Sex-linked Genes • Sex-linked recessive traits will show up more often in males because they only have 1 X chromosome XR = normal Female • XRXR = Normal • XRXr = Normal • XrXr = Disease Xr = disease Male • XRY = Normal • XrY = Disease Carriers = Fem • Carrier: A female who has an allele for a genetic disease but does not show the disease. – Carrier genotype: XRXr • Males cannot be carriers because having 1 allele for the disease gives them the disease. – XrY = diseased Examples of sex-linked traits in humans: 1. Color Blindness 2. Hemophilia 3. Muscular Dystrophy 4. Male pattern baldness 5. Sickle cell anemia Colorblindness • Cannot tell the difference between red and green colors: • People with red-green color blindness see either a three or nothing at all. • Those with normal color vision see an 8. Colorblindness • A person with normal color vision sees a number seven in the circle above. • Those who are color blind usually do not see any number at all. A female carrier (XNXn) and a man with normal vision (XNY) have kids. What are the chances their kids are colorblind? XN Normal vision is dominant (N) XN Colorblind is recessive (n) Girls _______% Boys_______% Xn Y Hemophilia Hemophilia- Lacking in the ability to clot blood – There is a gene on the “X” chromosome that control blood clotting – People who have hemophilia are missing the protein to clot blood – They can bleed to death by minor cut. A female carrier (XHXh) and a man with hemophilia (XhY) have kids. What percentage of their kids have hemophilia? Xh Normal clotting is dominant (H) XH Hemophilia is recessive (h) Girls _______% Boys_______% Xh Y Muscular Dystrophy - Results in weakening/ loss of muscles - Caused by defective version of gene that codes for muscle Here’s the results • For girls: 0% have the trait • For boys 50% have it. • Percentage is higher for boys because whatever X they get determines the trait, for girls they have to get 2 recessive X’s. M X m X M X M M X X M m X X Y M X Y m X Y Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=H1HaR 47Dqfw Group practice • Get with other people with card number • Different suits have different jobs • Last 5 min: Randomly calling to give answers! Leader: Keeps the group on task Time Keeper: Keeps track of time, keeps things moving Note Checker: Makes sure all members are using their notes on the problems