* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Eye and hair color
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Skewed X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Ridge (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Polycomb Group Proteins and Cancer wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
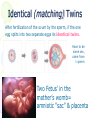
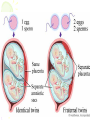
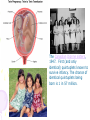
Parenting & Child Development Objective: 3.01 Hereditary vs. Environment I want you to stand up if you have…. • Father’s eye color and shape • Mother’s physical build • Father’s feet (appearance) • Mother’s hand size • Father’s hair texture and color • Mother’s skin color What does all of this have to do with??? • If you stood up, you received all of those genetic, physical features from your parents or grandparents. • We look the way we do because of our inherited traits Physical Traits are… •Characteristics connected with the body •Example: –Eye and hair color Heredity skin color 1.Passing on of certain characteristics from earlier feet generations. ears Each person inherits many characteristics from their parents, which include, but not limited to: color/shape of eyes hair texture color size of hands blood type physical build Heredity • Every baby receives 46 chromosomes – (tiny threadlike particles in the nucleus of every cell) • These chromosomes come in 23 pairs. – 2/46=23 2. The father’s sperm and mother’s ovum (egg) both contribute one chromosome to each pair. Heredity • Each chromosome has thousands of genes. – Determine child’s inherited characteristics. • For every inherited characteristic, a person receives two copies of a gene – 1 from mother – 1 from the father • If Both are the same, the child has that characteristic. – Ex: 2 genes for blue eyes gives the child blue eyes. Genes a. Recessive and Dominant Genes Recessive 1. Recessive is the weaker gene (-) 2. Dominant is the stronger gene (+) Dominant Scenario: • If a person receives two different genes, such as one for blue eyes and one gene for brown eyes, the dominant gene will express the characteristic over the weaker gene. – Brown eyes are dominant while blue eyes are recessive. • Therefore, the child will he born with brown eyes. DOMINANT & RECESSIVE CHARACTERISTICS DOMINANT TRAITS RECESSIVE TRAITS eye coloring brown eyes grey, green, hazel, blue eyes vision farsightedness normal vision normal vision normal vision dark hair non-red hair curly hair full head of hair widow's peak dimples unattached earlobes freckles broad lips immunity to poison ivy normal pigmented skin normal blood clotting normal hearing normal hearing and speaking normal- no PKU normal vision nearsightedness night blindness color blindness* blonde, light, red hair red hair straight hair baldness* normal hairline no dimples attached earlobes no freckles thin lips susceptibility to poison ivy albinism hemophilia* congenital deafness deaf mutism phenylketonuria (PKU) hair facial features other Recessive & Dominant Genes… Blonde hair What genes did the little girl receive from which parent? Mother Straight hair Mother Eye color ??both?? Male & Female Symbol Female/Male Determination • OVUM=EGG – Female cell needed for reproduction • SPERM – Male sex cell needed for reproduction How do you get a boy or girl? • Sperm sex • Ovum sex chromosome chromosome carries “X” OR “Y” carries “X” – Y=BOY • X=GIRL Who determines sex of the baby? Father=ALWAYS!!! Scenario • IF a sperm fertilizes THE egg and it’s an “X” chromosome, what will your baby be? BOY OR GIRL?? – GIRL=“X” Chromosome! • IF the sperm fertilizes THE egg and it’s a “Y’’ chromosome? – BOY=“Y” Chromosome! • What chromosome did your father contribute? – X or Y? A Unique Person • Heredity explains why brothers and sisters often resemble each other and why they can also look different. • Each sperm cell contains a different combination of genes. • When they combine in a fertilized egg, they produce a unique individual. • The particular combinations of genes brought together at conception determine traits. !!TWINS!! Here’s how it works Identical (matching) Twins After fertilization of the ovum by the sperm, if the one egg splits into two separate eggs its identical twins. Have to be same sex, came from 1 sperm Two Fetus’ in the mother’s womb= amniotic “sac” & placenta Fraternal (not matching) Twins • If two separate sperm fertilize two separate eggs, the result is fraternal twins, can be same or opposite sex The Canadian Dionne sisters, 1947. First (and only identical) quintuplets known to survive infancy. The chance of identical quintuplets being born is 1 in 57 million. Environment People Places Things that surround and influence a person The environment does not influence a person’s physical (bodily) traits. . Environmental Influences on Birth Defects • Not eating properly • Exposure – – – – – Diseases and/or infections Chemicals X rays Accidental injuries Toxoplasmosis – parasite in cat feces • Harmful substances – Drugs – Alcohol – Nicotine – Cigarettes Hereditary or Environmental Influences? –Uniqueness of a child comes from his or her heredity and environment. 1. Mary has a great sense of humor. 1. E 2. Sue has blue eyes. 1. H 3. Billy and his brother Tommy look alike. 1. H 4. Sammy goes to the library often. 1. E 5. Karen plays the trumpet quite well. 1. E, H 6. Mary has brown hair. 1. H 7. Judy lives in a nice house. 1. E 8. Tom is tall like his father. 1. H 9. Dana always scores high on tests in school. 1. E, H 10. Chanda has dark skin. 1. H Answers