* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Amines
Aromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Asymmetric induction wikipedia , lookup
George S. Hammond wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Hydroformylation wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Hofmann–Löffler reaction wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
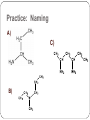
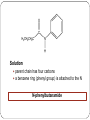
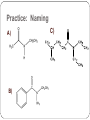
Amines and Amides Amines H (or R’) R-N functional group: amino weakly basic often have unpleasant odours boiling point and solubility higher than comparable hydrocarbons lower than comparable alcohols N-H bond is less polar than O-H bond H (or R”) subclassification: based on the number of alkyl groups that are attached to the N atom primary (1°), secondary (2°), or tertiary (3°) H H-N-H ammonia H R-N-H R’ R-N-H R’ R-N-R” 1° amine 2° amine 3° amine Same type of classification as seen in alcohols, amides, and alkyl substituent groups Naming Amines Name as an amino derivative of an alkane (IUPAC) For a primary amine: Identify the longest carbon chain that is attached to the –NH2 group. 2. Add the prefix amino- to the front of the alkane name. 3. Use a number to identify the location of the NH2. 1. Solution: • the parent chain has four carbons • NH2 group attached to C2 2-aminobutane For a secondary or tertiary amine: 4. use the N-prefix to denote the substituted groups on the N atom of the amino group. Solution: • the parent chain has two carbons • the –NH2 group is attached to C1 • two additional CH3 groups attached to the N N, N-dimethyl-1-aminoethane Name this amine. Is it a primary, secondary, or tertiary amine? CH3 CH2 CH2 – N – CH2 CH3 H CH3 Solution parent chain has three carbons amino group is attached to C2 isopropyl group attached to the nitrogen Secondary amine N-isopropyl-1-aminopropane OR N-propyl-2-aminopropane Polyamines amines that contain more than one –NH2 group prefixes: #, #-diamino- (2) and #, #, #-triamino- (3) when naming, use numbers to indicate locations of ALL NH2 groups NH2 NH2 CH2 C CH3 NH2 1,2,2-triaminopropane Practice: Naming A) C) B) Amides functional group: amide R N R’ (or H) R” (or H) weakly basic boiling point and solubility higher than comparable hydrocarbons and all other compounds most polar functional group! can accept H bonds and form H bonds (if 1° or 2 ° amide) Naming Amides suffix: -amide For a primary amide (N is attached to one C – the carbonyl): 1. Identify the longest carbon chain that includes the C=O portion of the amide group. 2. Change the ending to –amide. 3. Identify and name any substituent groups. Numbering starts at the amide end. Solution: • the parent chain has five carbons • ethyl group attached to C2 2-ethylpentanamide N,N,3-trimethylbutanamide For secondary and tertiary amides: 4. Carbon chains attached to the nitrogen: name these first, as alkyl groups, with N-prefix Solution parent chain has four carbons a benzene ring (phenyl group) is attached to the N N-phenylbutanamide Practice: Naming A) B) C) Reaction: Preparation of Amides condensation reaction between a carboxylic acid and an amine catalyzed by strong acid (H2SO4) O RC-O H carboxylic acid + H H N-R’ amine H2SO4 H2O O RC-N-R’ H O CH3C-OH + HN(H)-CH2CH2CH3 amine carboxylic acid H2SO4 O CH3C-N(H)-CH2CH2CH3 amide name the reactants b) name the amide that is produced c) in the amide name, which part is named first – the part derived from the acid, or from the amine? d) what is the other product of this reaction? a) O CH3(CH2)2C-N(H)-(CH2)5CH3 a) Draw the expanded structural formula for this molecule. b) Name the amide. c) Draw and name the two reactants that could be used to prepare this ether. Homework Read 1.8 (Nelson 12) Amines– Pg. 69-72 Amides – Pg. 74-76 AP unit package: Alcohols, Ethers, and Amines #10, 11a-d AP unit package: Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Esters #8c,d, 10b