* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download T-DNA Mutagenesis
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Gene desert wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Genomic imprinting wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
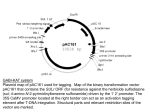
T-DNA Mutagenesis Transfer-DNA Mutagenesis: a chemical or physical treatment that creates changes in DNA sequence which can lead to mutation strains that are passed on to the next generation. -PURPOSE: To create loss of function mutations in order to determine the function of a gene. -HOW DOES THIS WORK: Vector transmission by way of Agro plant is randomly inserted into the nuclei chromosomal sites. RB T-DNA LB T-DNA Flanking Region KAN Pdi2 -Agro? Agrobacteria tumefaciens is a bacteria found on certain plants that were found to cause tumors on wounded plant areas. Found to contain Ti (Tumor inducing) plasmid that creates a mutation in the plants genomic sequence. The Ti plasmid’s ability to integrate itself into a DNA sequence was isolated and the tumor inducing quality was taken out. -LOSS OF FUNCTION MUTATIONS: is when a mutation is created in such a way that death does not occur so as to observe the effects on the plant by the loss of a certain gene. In other words, a gene is knocked out and the plant is grown and observed for any differences between the mutant strain and the control strain. Thus facilitating (understanding) the function of that knocked-out gene. T-DNA in the Arabidopsis Genome T-DNA – from Ti plasmid in the Agrobacteria tumefaciens.. Uses the insertional quality to carry foreign genes into the plant genome. Pdi2 A LB T-DNA Primer F1 Wild Type R1 primer -VALID TEST RESULTS: To achieve valid data from the gel results. Homozygous cells must be used, not Heterozygous. RB T-DNA LB T-DNA Flanking Region KAN Pdi2 Genotype - Segregation -HOMOZYGOUS: 2 of the same (genes). On gel, homozygous will only produce one band on either the wild type control side or the T-DNA control side, not both. Needed for accurate results. -HETEROZYGOUS: different genes. On gel, will produce a band on both the WT control side and the T-DNA control side. Not used for verification of T-DNA. -GEL ELECTROPHORESIS: 1. Verify if sample is homozygous, 2. Verify that T-DNA knockout is not there, 3. Verify that T-DNA is there and inserted. WT A1 A2 TDNA+ - WT+ A1 A2 WT A1 A2 WT+ - WT - WT A1 A2 TDNA+ - WT A1 A2 WT+ - WT A1 A2 TDNA+ - WT A1 A2 TDNA+ - WT A1 A2 WT+ - -disrupted genes do not make RNA. That function has been knocked out. -F1 and R2 primer will make WT. -F1 and LB primer will make T-DNA knockout. Pdi2 A LB T-DNA Primer F1 Wild Type R1 primer Future Advances in Biotechnology Mutagenesis Research: BEFORE AFTER