* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 18. Introduction to Metagenomes
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA nanotechnology wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
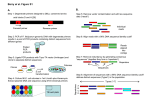
Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metagenome definitions: a refresher course Natalia Ivanova MGM Workshop September 12, 2012 Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metagenome definitions Metagenome is a collective genome of microbial community, AKA microbiome (native, enriched, sorted, etc.). Metagenomic library (or libraries) is constructed from isolated DNA (native, enriched, etc.). Metagenomic library can be single-end (AKA standard) or paired-end Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metagenome definitions Single-end (standard) metagenomic library will produce contigs upon assembly (i. e. longer sequences based on overlap between reads) Any Ns found in contigs correspond to low quality bases ATGCAAAGGCCGCATCCAGCAGGTT TACGTTTCCGGCGTAGGTCGTCCAA Paired-end metagenomic library will produce scaffolds upon assembly (non-contigous joining of reads based on read pair information) Ns found in scaffolds correspond either to low quality bases or to gaps of unknown size ATGCAAAGGCCGCATCC AGCAGGTT NNNNNN TACGTTTCCGGCGTAGG TCGTCCAA Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Amplified and Unamplified Libraries Amplified Library Unamplified Library Fragmentation (1ug) Fragmentation (1ug) Double SPRI End repair / Phosphorylation End repair / Phosphorylation SPRI Clean Double SPRI A-tailing with Klenow exoSPRI Clean A-tailing with Klenow exo- DNA Chip Adaptor Ligation Heat Inactivation DNA Chip Adaptor Ligation SPRI Clean PCR 10-cycle Amplification SPRI Clean qPCR Quantification DNA Chip SPRI Clean qPCR Quantification DNA Chip Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metagenome definitions (contd): Unless the community has very low complexity (i. e. dominated by one or a few clonal populations), assembly at 100% nucleotide identity will be very fragmented. overlap = alignment of reads at x% identity What to do with k-mer based assemblies? Use multiple k-mer settings, combine assemblies with an overlap-layout consensus assembler like minimus2 using minimal % identity of 95%. Tradeoff between overlap length and % identity. Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Reasoning behind combining multiple assemblies Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Trimming does not appear to be ideal for this process Assembly Pipeline v.0.9 CPU time intensive, no known metagenomic Kmer prediction algorithm A snapshot of older (454Illumina) metagenome assembly pipeline Picking best kmer – manual proces 7 Advancing Science with DNA Sequence Metagenome definitions (contd): overlap = alignment of reads at x% identity Assembly of sequences at less than 100% identity => population contigs and scaffolds representing a consensus sequence of species population isolate contig species population contigs Advancing Science with DNA Sequence 2 more important definitions 1. Sequence coverage (AKA read depth) How many times each base has been sequenced => needs to be considered when calculated protein family abundance Per-contig average coverage Per-base coverage => per-gene coverage 2. Bins Scaffolds, contigs and unassembled reads can be binned into sets of sequences (bins) that likely originated from the same species population or a population from a broader taxonomic lineages Advancing Science with DNA Sequence What IMG does and doesn’t do • Scaffolds and contigs are generated by assembly – not provided in IMG/M • Sequence coverage can be computed by the assembler based on alignments it generates (preferable) or can be added later by aligning reads to contigs – the latter can be provided in IMG/M • Bins are generated by binning software – not provided in IMG/M • Scaffolds, contigs and unassembled reads are annotated with non-coding RNAs, repeats (CRISPRs), and protein coding genes (CDSs); the latter are assigned to protein families (COGs, Pfams, TIGRfams, KEGG Orthology, EC numbers, internal clusters) – is provided in IMG/M Advancing Science with DNA Sequence What’s the difference between IMG and MG-RAST, IMG and CAMERA? • We prefer to assemble the data longer sequences -> better quality of gene prediction and functional annotation longer sequences -> chromosomal context and binning -> population-level analysis • But we don’t provide assembly services except for metagenomes sequenced at the JGI we may be able to help with assembly of 454 we’re not equipped to assemble massive amounts of Illumina data http://galaxy.jgi-psf.org Contact person: Ed Kirton, [email protected] • IMG does not provide tools for analysis of 16S data from the metagenome itself we do assembly -> assembled 16S sequences are generally not very reliable BLASTn of reads matching conserved regions is misleading we do pyrotags or i-tags for every metagenome sequenced at the JGI http://pyrotagger.jgi-psf.org