* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download TCR rearrangement and selection in the thymus
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Lymphopoiesis wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
X-linked severe combined immunodeficiency wikipedia , lookup
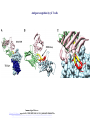
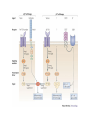
Part II Lecture on TCR rearrangement and selection in the thymus 22nd November 2012 by Mike Clark, PhD Reader in Therapeutic and Molecular Immunology Department of Pathology Division of Immunology Cambridge University UK CB2 1QP www.antibody.me.uk ab and gd T-cells • See earlier lecture on TCR genes and rearrangements • a and d locus on the same chromosome so rearrangement of one results in isotypic exclusion of the other gd cells have more limited number of segments but much more variability in CDR3 ab cells are the major population and the majority see antigen as peptide presented in the context of MHC-class I and class II molecules • A smaller proportion of T-cells see alternative antigens MHC restricted ab TCR Mucosal-associated invariant T-cells MAIT • Subset of ab T cells in humans and mice which are DN (CD4- CD8-) • Restricted by non-polymorphic, nonclassical MHC molecule MR1 • Over expression of (semi) invariant TCRa chains and b chains • Secrete g-interferon and Il-17 • Reviewed by Bourhis et al (2011) Trends in Immunology 32: 212-218 NKT-cells • Have properties of both T-cells and NK-cells • Express a (semi) invariant abTCR • Recognition of lipids and glycolipids presented by CD1d • Can express FcgR CD16, CD56, NK1.1 • Produce g-interferon, IL-4, IL-2, TNF-a • Role in immunity against bacteria such as mycobacterium • Review by Jerud et al (2006) Transfusion Medicine and Hemotherapy 33:18-36 doi:10.1159/000090193 gd-T cells • Smaller subset of T-cells ~2% • Higher abundance in gut mucosa (intraepithelial lymphocytes IELs) • Not MHC restricted and may be able to recognise whole proteins and phosphoantigens • A sizeable population of mouse gd T-cells recognise the non-classical class-1 T10 and T22 • Reviewed in Chien & Konigshofer (2007) Immunological Reviews 215: 46-58 Antigen recognition by γδ T cells Immunological Reviews Volume 215, Issue 1, pages 46-58, 2 FEB 2007 DOI: 10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00470.x http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/j.1600-065X.2006.00470.x/full#f6 ab T-cell development • Early thymocyte precursor (ETP) DN1 stage differentiate into CD44 CD117 (c-Kit) • DN2 cells become CD25+ and start to rearrange b (or gd) chains • DN3a cells lose CD44 expression and characterised by expression of pre-TCR b chain plus invariant pre TCRa chain. • Differentiate into high CD27 expressing DN3b cells and following pre-TCR selection lose CD25 expression • DN4 with surface expression of CD24, CD71 and CD98 and start to rearrange a chain • Diffentiate into DP (CD4+CD8+) cells where positive and negative selection can take place Notch regulation of early thymocyte development Yashiro-Ohtani et al (2010) Seminars in Immunology 22: 261-269 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2010.04.015 Cortical (cTEC) and medullary (mTEC) epithelial cells regulate distinct stages of T cell development and selection. Anderson and Takahama (2012) Trends in Immunology 33:256-263 http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.it.2012.03.005 cTEC (cortical thymic epithelial cells) • Responsible for positive selection of ab-TCR (low) DP cells • Low affinity induces survival • Differentiate to TCR(high) SP CD4 or CD8 • High affinity results in programmed cell death • Unique processing of peptides may occur in cTECs mTEC (medullary thymic epithelial cells) • • • • • • • Expression of chemokine receptors induces positively selected SP thymocytes to migrate towards the thymic medulla. TCR engagement in immature SP cells induces TNF superfamily cytokines such as RANKL (receptor activator of nuclear factor kB ligand) Receptor for RANKL expressed by mTECs but not by cTECs mTECs have promiscuous gene expression promoted by the nuclear protein Aire Responsible for deletion of autoreactive T-cells May also get indirect presentation of self-peptides through neighbouring dendritic cells. Positively selected thymocytes spend about 4-5 days in the medulla before being exported to the circulation gd versus ab T cell development Ciofani & Zuniga-Pflucker (2010) Nature Reviews Immunology 10:657-663 http://doi:10.1038/nri2820 T-cell development extra resources and reviews • YouTube video from Janeway, Garlandscience http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=odLLr6mjaUQ • YouTube video from Handwritten tutorials http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=08H5CmDaRjU • Lecture notes from Stephen Cobbold in Oxford http://users.path.ox.ac.uk/~scobbold/Teaching/POSSEL.pdf