* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 6.2 Human Genetic Disorders
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression programming wikipedia , lookup
Dominance (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Pharmacogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Y chromosome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Neocentromere wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Heritability of IQ wikipedia , lookup
Behavioural genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic drift wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Public health genomics wikipedia , lookup
Genetic testing wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering in science fiction wikipedia , lookup
Microevolution wikipedia , lookup
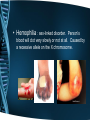
6.2 Human Genetic Disorders Can you see if there’s an abnormality in this picture? What is genetic disorder? • Def: Abnormal condition that a person inherits through genes or chromosomes • Ex. – – – – Cystic Fibrosis Sickle-Cell disease Hemophilia Down Syndrome Causes of Genetic Disorders • Some genetic disorders are caused by changes in the DNA of genes. Other disorders are caused by changes in the overall structure or number of chromosomes. Genetic Disorders • Cystic Fibrosis : body produces abnormally thick mucus in the lungs and intestines, making it hard for the person to breathe. Caused by a recessive allele on one chromosome – result of a mutation. • Sickle-Cell disease: Red blood cells change to a sickle shaped cell, which can clog blood vessels. Codominant allele. • Hemophilia : sex-linked disorder. Person’s blood will clot very slowly or not at all. Caused by a recessive allele on the X chromosome. • Down Syndrome – An extra copy of chromosome 21. Some degree of mental retardation.– Caused during meiosis: chromosomes fail to separate properly. Pedigrees • An important tool that geneticists use to trace the inheritance of traits in humans – a chart or “family tree” that tracks which members of a family have a particular trait. Managing Genetic Disorders * • Karyotype : picture of all the chromosomes in a cell. • Genetic Counseling: a couple that has a family history of a genetic disorder may turn to a genetic counselor for advice. • Dealing with Genetic Disorders: Modifying an affected person’s environment – ex. Through medicine, diet, or education – can help manage some disorders. • Sickle cell : take folic acid(vitamin) to help make red blood cells.