* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 2.3 Carbon based molecules powerpoint mod
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
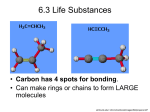
2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Objective: SWBAT: Summarize the Characteristics of organic compounds IOT: Identify the function and structure of biomolecules 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules KEY CONCEPT Carbon-based molecules are the foundation of life. Meaning all living things are based on carbon-based molecules. 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Carbon atoms have unique bonding properties. • Carbon atoms form stable bonds with four other atoms (Hydrogen, Oxygen, Nitrogen and/or Carbon), this makes it suited for the construction of complex molecules. • Chemically, this is due to carbons 4 valence electrons which make it able to form 4 bonds to achieve stability. Valence electrons – electrons in the outermost energy level; these are the electrons that are available to bond with other atoms 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Many carbon-based molecules are made of many small subunits bonded together called monomers. – Monomers join together to form a polymer. • Assembling & Disassembling Polymers via Chemical Reactions – Hydrolysis- water interacts with a polymer breaking the bonds that link monomers to each other. Break a polymer down into monomers – Dehydration synthesis- bonds are formed linking monomers together while losing water molecules. Build a polymer by bonded a bunch of monomers 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Four main types of carbon-based molecules are found in living things. 1. Carbohydrates • Chemical Make-up Carbohydrates are made of C, H, and O in a 1:2:1 ratio • Monomer/Polymer – Monomer: Monosaccharides – Polymer: Polysaccharides 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Functions Carbohydrates can be broken down to provide energy for cells. Some carbohydrates are part of cell structure. • Example Carbohydrates include sugars, cellulose, starches Polymer (starch) Polymer (cellulose) monomer Starch is a polymer of glucose monomers that often has a branched structure. Cellulose is a polymer of glucose monomers that has a straight, rigid structure 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules 2. Lipids • Chemical Make-up Composed of C, H and a little O • Monomer/Polymer – Monomer: Fatty acids bonded to glycerol – Polymer: Lipids • Examples Triglycerides (fats, oils) phospholipids, steroids (cholesterol, hormones) and wax. Triglyceride 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Fats and oils have different types of fatty acids. – saturated fatty acids – unsaturated fatty acids Chemical Structure 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Saturated versus Unsaturated fats Saturated fats butter, dairy products, meat- which remains solid at room temperature. –“Bad” because in excess raise cholesterol –Saturated or full- no more hydrogen (or other atoms) can be added Unsaturated fats avocado, soybean oil, canola oil and olive oil. –“Good” –Unsaturated or not full- More hydrogen can be added 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Functions Lipids have several different functions. – broken down as a source of energy – make up cell membranes – used to make hormones- control important body functions 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules 3. Proteins • Chemical Make-up Made up of C, H, O, S and N • Monomer/Polymers – Monomer: Amino acids (Twenty different amino acids are used to build proteins in organisms.) – Polymer: Polypeptides or Proteins (bunch of amino acids) R group Amino group Carboxyl 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules • Examples - Can be found in foods like beans, nuts and meat - Enzymes - Hormones • Functions - Different proteins have different functions - Major functions include structural support, - Speed up chemical reactions (enzymes) - Communication via hormones 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Nucleic acids • Make-up Made up of C, H, O, P and N • Monomer/Polymer – Nucleotides (are made of a sugar, phosphate group, and a nitrogen base.) – Nucleic acids A phosphate group deoxyribose (sugar) nitrogen-containing molecule, called a base 2.3 Carbon-Based Molecules Examples – DNA deoxyribose nucleic acid – RNA ribonucleic acid DNA Functions – DNA stores genetic information; holds instructions for controlling EVERYTHING that happens in a cell. RNA – RNA builds proteins