* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PhotosynthesisCalving CycleON
Gaseous signaling molecules wikipedia , lookup
Cyanobacteria wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
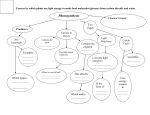
PhotosynthesisThe Basis for Life on Earth Part II Overview light reaction 1. 18 ATP are made from 18ADP + 18P 2. Water is split. e- + H are used for #3. 6 O2 are released. 3. 12 NADPH are made. Overview dark reaction The carbohydrate is made in the stroma. It requires enzymes every step. 1. 18ADP + 18P are made from 18 ATP. Energy is released 2. NADPH is oxidized to make NADP. The hydrogens are tranferred making a carbohydrate. 3. 3 CO2 are used to make a triose G3P (glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate) or PGAL phosphoglyceraldehyde. 2 of these make glucose This is the Calvin cycle. The various compounds only show the carbon skeleton, leaving the hydrogen and oxygen atoms off. The next slide after that includes the names of the molecules used in the cycle. The Calvin cycle will make one extra PGAL. PGAL is a triose. It takes 2 PGALs to make glucose, the hexose. So therefore the Calvin cycle needs to be "turned" twice in order to make a molecule of glucose. (Actually 6 times). 1. Carbon dioxide combines with ribulose biphosphate. Ru-Bp is a pentose monosacharide with 2 phosphate groups 2.It will form an unstable intermediate. 3. The intermediate will form 2 molecules of phosphoglyceric acid. 4. PGA will be phosphorylated by ATP to form DPGA In the Calvin cycle, CO2 is combined with A) a protein called rubisco B) ribulose biphosphate Ru-Bp C) phosphoenol phosphate (PEP) D) pyruvate B CO2 is combined with ribulose biphosphate which is a monosaccharide or carbohydrate. 5. DPGA is reduced by NADPH to form the triose, PGAL. A phosphate group is removed in this reaction. 6. In the last step, 5 molecules of glyceral aldehyde phosphate (G3P) or PGAL are needed to remake 3 molecules of Ru-BP. 3 ATP are needed to make this happen. 1 G3P is left over. PGAL is a triose. In order to make glucose, the Calvin cycle must be turned twice. This shows how 2 molecules of G3P or PGAL are turned into a molecule of glucose and how it can be turned into starch. Which of the following does not occur during the Calvin cycle? A) carbon fixation B) oxidation of NADPH C) release of oxygen D) regeneration of the CO2 acceptor E) consumption of ATP C The release of oxygen occurs when the protein complex associated with photosystem II breaks down water. While the glucose is needed for energy, there is a second reason why the Calvin cycle evolved; to provide a carbon skeleton so that other organic molecules or structures can be made. What must be added to the carbon skeleton in order for a plant to synthesize amino acids? A) hydrocarbons B) oxygen C) phospate groups D) amine groups E) organic acids D Amine groups must be added to a carbon skeleton in order for a plant to make amino acids Environmental factors affects the rate of photosynthesis. 1. Light intensity- At first an increase in the light intensity results in a corresponding increase in the rate of photosynthesis as the photosystems are activated. As the photosystems become saturated, an increase in light intensity will not increase the rate of photosynthesis. 2. Temperature- At first an increase in temperature results in an increase in the rate of photosynthesis because the molecules are moving faster, but at a higher temperature the reaction rate decreases because enzymes denature. 3. If a plant is given an increase in oxygen, the rate of photosynthesis decreases because of phenomenon of photorespiration. The enzyme that puts the CO2 onto ribulose biphosphate is rubisco. Sometimes rubisco can make a mistake and put oxygen on to ribulose biphosphate. This happens when the concentration of oxygen gas is greater than carbon dioxide. This happens when the plant is water stressed and the stomates are closed. Gas exchange takes through pores on the bottom of the leaf called stomates. Guard cells regulates stomates but as gas exchange occurs water leaves the stomates via transpiration. When a plant becomes water stressed, stomates close to conserve water. water, but this will stop gas exchange. This will increase the O2 and decrease CO2. Photorespiration begins. C3 photosynthesis is a plant that does the Calvin cycle and the light reaction. There are plants that modify C3 photosynthesis by adding an additional pathway- The leaf of a C3 plant (normal leaf). Chloroplasts are located in the palisade and spongy mesophyll. There are no chloroplasts in the bundle sheath cells. Which of the following is true for photorespiration to occur? A) Stomata are opened. B) There is an increase in absporption of amine groups. C) There is an increase in the amount of oxygen present. D) There is an decrease in the amount phosphates present C Photorespiration occurs when there is an increase in oxygen and decrease in carbon dioxide. This usually occurs when the stomata are closed. C4 photosynthesis includes the light reaction, the Calvin cycle and the Hatch-Slack pathway. These C4 plants also have a different anatomy. This Hatch-Slack pathway is able to deliver dwindling supplies of CO2 when the stomates are closed. The enzyme (PEP carboxylase) that fixes the CO2, combines it with a three carbon compound, phosphoenol pyruvate (PEP) to form a four carbon compound. This enzyme does not make a mistake like rubisco. The name of this enzyme is PEP carboxylase. The leaf of a C4 plant. There are no palisade mesophyll cells. Instead there is a layer of mesophyll around the the bundle sheath cells. Chloroplasts are located in the these mesophyll and spongy mesophyll. The chloroplast are different. The chloroplasts in the mesophyll have well defined thylakoids and specialize in the light reaction and the Hatch-Slack pathway. The thylakoids in the bundle-sheath chloroplast do not have defined thylakoids, are larger and store starch. This indicates the light reaction is not prevalent, and they do specialize in the Calvin cycle after the HatchSlack pathway delivers the CO2. Plants that use C4 photosynthesis include corn, sugar cane, and sorhum. Another variation of photosynthesis is CAM (crassulacean acid metabolism). These CAM plants include succulent plants and pineapples. Because of the intense heat and arid conditions, these plants only open up the stomates at night for gas exchange. Plants that use C4 photosynthesis include corn, sugar cane, and sorhum. The CO2 (like C4 photosynthesis) is fixed to PEP by PEP carboxylase. It is then converted to an organic acid and stored until the day. During day stomates are closed and the cell releases the CO2 from the organic acid and the Calvin cycle occurs. C3 photosynthessis(light reaction and Calvin cycle) is called this because the first stable product has 3 carbons. C4 photosynthesis (light reaction, Hatch-Slack, Calvin cycle) is called this because the first product made has 4 carbons. In what respect are the photosynthetic adaptations of C4 plants and CAM plants similar? A) In both cases, only photosystem I is used. B) Both types of plants make sugar without the Calvin cycle. C) In both cases, an enzyme other than rubisco carries out the first step in carbon fixation. D) Both types of plants make most of their sugar in the dark. E) Neither C4 plants nor CAM plants have thylakoids. C In both cases, an enzyme other than rubisco carries out the first step in carbon fixation.