* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Wear protective eye wear, lab coat and closed toe shoes while in the
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
X-inactivation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
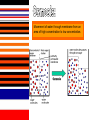
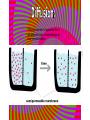
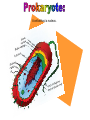
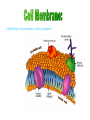
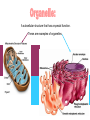
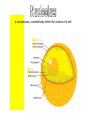
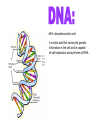
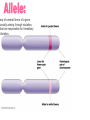
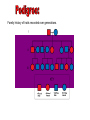
A method of research in which a problem is identified, relevant data are gathered, a hypothesis is formulated from these data, and the hypothesis is empirically tested. Is the part of the experiment that stays the same. The part of the experiment that changes or is being tested. A variable in an experiment that isn’t affected by any other variables it is paired with. A variable that is affected by a different variable or a certain event. An example of this could be a thermometer. An explanation or guess that can be tested with further investigation. Lab safety is extremely important because if you aren’t cautious you could seriously hurt your self or someone else. 1. Wear protective eye wear, lab coat and closed toe shoes while in the lab. 2. Make sure your area is ALWAYS clean. 3. No food or drinks in the lab. 4. Do not leave any chemicals open or unattended. The movement of particles through a membrane against a concentration gradient with the use of ATP. The movement of a substance through a cell membrane without the use of energy. The maintenance and stability of a cell, organism, or population in it’s environment. This is a picture of the common Flu virus attacking blood cells. Movement of water through membrane from an area of high concentration to low concentration. The movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration. Increased water pressure that occurs from osmosis. A solution with higher concentration than the membrane it crosses or passes through. A solution with lower concentration than the membrane it crosses. Equal solute concentrations on either side of a selectively permeable membrane. All organisms are made of one or more cells that are derived from other cells. Both of these men contributed to the cell theory. Theodor Schwann Matthias Schleiden A complex cell that has a nucleus enclosed by a membrane. A cell without a nucleus. A bilipid layer that encloses a cell’s cytoplasm. A subcellular structure that has a special function. These are examples of organelles. ER with little or no ribosomes on its surface. ER with many ribosomes on its surface. A cell organelle of a eukaryotic cell that supplies the cell with ATP by performing oxidative respiration. A cytoplasmic organelle on which proteins are synthesized. a definite wall that is part of plant cells. a conspicuous, rounded body within the nucleus of a cell. openings in a nuclear membrane which allow passage of molecules between the nucleus and surrounding cytoplasm. Division of a single cell into two identical “daughter” cells. part of the process of gamete formation, consisting of chromosome conjugation and two cell divisions, in the course of which the diploid chromosome number becomes reduced to the haploid. AKA: deoxyribonucleic acid A nucleic acid that carries the genetic information in the cell and is capable of self-replication and synthesis of RNA. AKA: ribonucleic acid any of a class of single-stranded molecules transcribed from DNA in the cell nucleus or in the mitochondrion or chloroplast. Type of molecule that forms an important part of nucleic acid, composed of a nitrogen-containing ring structure. any of various proteins, as pepsin, originating from living cells and capable of producing certain chemical changes in organic substances by catalytic action, as in digestion. the process by which double-stranded DNA makes copies of itself, each strand, as it separates, synthesizing a complementary strand. the process by which genetic information on a strand of DNA is used to synthesize a strand of complementary RNA. the process by which a messenger RNA molecule specifies the linear sequence of amino acids on a ribosome for protein synthesis. a sudden departure from the parent type in one or more heritable characteristics, caused by a change in a gene or a chromosome. any of several forms of a gene, usually arising through mutation, that are responsible for hereditary Variation. the one of a pair of alternative alleles that masks the effect of the other when both are present in the same cell or organism. that one of a pair of alternative alleles whose effect is masked by the activity of the second when both are present in the same cell or organism. a type of grid used to show the gametes of each parent and their possible offspring. Condition in which a trait is intermediate between two parents. Both alleles for a gene are expressed when present. Trait that is determined by a gene found on the x chromosome. A cross that involves two pairs of contrasting trait. Family history of traits recorded over generations. Science of naming and classifying organisms. Organisms belonging to the kingdom anamalia. One of the two kingdoms of prokaryotes that survive in extreme environments. (salt lakes, marshes, swamps, etc.) One of the two kingdoms of prokaryotes; Considered to be the most common. Heterotrophic eukaryotic organisms reproducing by spores. A photosynthetic organism or one related to it. A diverse collection of organisms making up the kingdom protista; Because of their characteristics, they do not fit into any of the other kingdoms.