* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Day 3 - artisanbreads
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid signaling wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
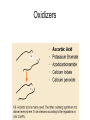
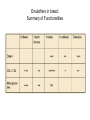
Day 5 • • • • Dough technology Formula Development Pita O-tentic Dough Conditioners • • • • • • • IMPROVERS Oxidizers- Improve gluten Reducing agents- Improve extensibility Emulsifiers- Bond water to other molecules Enzymes- Catalysts Vital wheat gluten- Added to weak flour Yeast nutrients- Added to no time conditioners • Fillers- Bulking agent Oxidizers Reducing Agents Emulsifiers • What? Emulsifier will assure optimal mixing of fat and water. • They are able to link waterloving and fatloving parts of the gluten chains, so a better developed gluten network is obtained. • 2 types: – Dough strengtheners – Crumb softeners 5 Types of Emulsifiers • DATEM- Diacetyl tartaric acid ester and mono- and diglycerides • SSL- Sodium Stearoyl Lactylate • CSL- Calcium Stearoyl Lactylate • Mono- and Diglycerides- Made from palm fat ( tryglycerides) Emulsifiers in bread: Summary of Functionalities Enzymes • Affect starch, proteins and fat • Break larger molecules into smaller ones The 6 Enzymes Classes 1. Oxidoreductases GOX, COX, HOX involve the movement of electrons from one molecule to another 2. Transferases catalyze the transfer of groups of atoms from one molecule to another 3. Hydrolases Amylase, Xylanase, Lipase, Protease • catalyze the reaction between a substrate and water and bind water to certain molecules 4. Lyases Lipoxygenase • catalyze the addition of molecular groups to molecules which are connected by so-called double bonds 5. Isomerases • catalyze the transfer of groups of atoms from one position to another 6. Ligases Transglutaminase • join molecules together using so-called covalent bonds What are Enzymes? ° not alive, can not move ° does not reproduce itself ° no mineral material ° all enzymes = proteins; all proteins ≠ enzymes ° small: 10000 x smaller than a bacteria ° complex 3-D structure ° essential to all forms of life ° biocatalyst = speeds up (or slows down) chemical reactions ° specific activity * Amylase ---------> Amylum (starch) * Protease ---------->Proteins * Lipase ------------>Lipids (fat) ° activity = (T, pH, t) ° Used for food, non-food and pharmaceuticals ° cost = (production yield, intellectual property, application) Amylase $3.30/lb; Urokinase $6.6million/lb. Uses for Enzymes Stabilize variation in wheat quality (type & climatological) main ingredient of a baked product is also the most variable one! Balance existing enzyme activities Volume, softness, dough handling, shelf-life... Formula Development • No more than 1000g finished dough- 2 breads • Start with Final Dough percentages • Determine % of pre-fermented flour • Present draft on Wednesday • Make levain • Formula development sheet for each iteration • If you need any ingredients- let me know Formula development • Do at least 1 formulation/day • Can vary flours and starters- Wheat, rye, whole wheat, Corn, potato • Finished bread to be presented Day 14 • Final paperwork due Day 14 • If you are using a variation of a bread, you must reference that bread and make substantial changes Pita • Flat bread- Middle East and Mediterranean areas • Baked in very hot oven to create pocket O-tentic Baguette • O-tentic- dough additive manufactured by Puratos • Mixture of enzymes and dough conditioners • Gives artisan flavor and appearance • Short fermentation time • 2% added to basic dough Today’s Production • As per Production Schedule • Sous Chef: Cook sausage, chop jalapenos, grate cheese