* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download METABOLIC PATHWAYS & ENZYMES
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Light-dependent reactions wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Metabolic network modelling wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Oxidative phosphorylation wikipedia , lookup
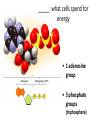
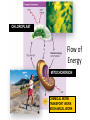
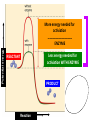
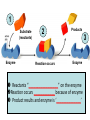
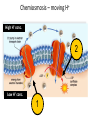
Metabolism – the Dynamic Cell Spring 2013 - Althoff Reference: Mader & Windelspecht Ch. 6) Lec 06 • Energy • ATP: Energy for Cells • Metabolic Pathways & Enzymes • Oxidation-Reduction What is Energy? = the __________________, quantified by… _______ = amount of heat required to raise the temperature of 1g of water 10C Potential Energy Kinetic Energy • ___________ energy • Energy of ____________ • Constantly converted to • Constantly converted to kinetic energy potential energy Successful organisms “_____” the energy game __________ LAWS • FIRST LAW OF THERMODYNAMICS (LAW OF CONSERVATION OF ENERGY) Energy cannot be created or destroyed, but it can be changed from one form to another • SECOND LAW OF THERMODYANMICS Energy cannot be changed from one form to another without a loss of usable energy. Also associated with the term __________ --the relative amount of disorganization associated with every energy transformation MORE organized LESS organized GLUCOSE CARBON DIOXIDE & WATER LESS Entropy • Less ___________ • More potential energy • More organized MORE Entropy • More ____________ • Less potential energy • Less organized _____: what cells spend for energy • 1 adenosine group • 3 phosphate groups (triphosphate) CHLOROPLAST Flow of Energy MITOCHONDRION CHEMICAL WORK TRANSPORT WORK MECHANICAL WORK Functions of ATP… • ______________ WORK —ex: protein, lipid, carbohydrate synthesis or breakdown of those complex organic molecules • ______________ WORK —ex: move molecules from one location to another, especially across the plasma membrane • ______________ WORK —ex: muscle contractions, cilia and flagella to beat, chromosomes to be moved __________________ = all of the chemical reactions that occur in a cell during growth and repair Metabolic Reactions • _____________ REACTIONS —ENERGY REQUIRED, RESULTS IN _______________ OF COMPOUNDS • _____________ REACTIONS —ENERGY REQUIRED, RESULTS IN _______________ OF COMPOUNDS (chemical bonds are broken) METABOLIC __________ = series of linked reactions that begin with a particular reactant (i.e. SUBSTRATE) and terminate with an end product ____________ = protein molecule that functions as a catalyst in a chemical reaction (i.e, metabolic pathways) • Enzymes ____________ these reactions • Enzymes only speed up reactions, they ______________ make reactions that are not possible to begin with • Enzymes can “bring together” molecules that will react to each other AND reduce the ___________________ • Enzymes can be “_____________” METABOLIC PATHWAYS & ENZYMES • A metabolic pathway can be represented by a simple diagram. E1 E2 E3 E4 E5 E6 A B C D E F G – The letters A-G indicate ________________ – The letters E1-E6 represent _______________. – A is the substrate for E1, B is the substrate for E2, and so on. Potential energy More energy needed for activiation ________________ ENZYME Less energy needed for activiation WITH ENZYME REACTANT PRODUCT Reaction Rate of Reaction (product per unit of time What affects enzymes? Temperature 0C Rate of Reaction (product per unit of time) What effects enzymes? pH 1 Substrate (reactants) Enzyme 2 Reaction occurs Products 3 Enzyme Reactants “_________________” on the enzyme Reaction occurs ____________ because of enzyme Product results and enzyme is ‘______________’ Say it with “…______”: NAMING OF ENZYMES Substrate/Reactant • Lipid • Urea • Maltose • Lactose • Sucrose • Ribonucleic acid • some proteins • some proteins • Etc. Enzyme Lipase Urease Maltoase Lactase Sucrase Ribonuclease Trypsin Pepsin Oxidation & Reduction • OXIDATION – _______ of electron(s) by molecules during the oxidation-reduction process • REDUCTION –_______ of electron(s) by molecules during oxidation-reduction process • Both processes all take place at the same time • Take place during photosynthesis and cellular respiration For the record… • PHOTOSYNTHESIS is the _________ of CELLULAR RESPIRATION 6CO2 + 6H20 + ENERGY C6H1206 +6O2 PHOTOSYNTHESIS: H2O is oxidized, CO2 is reduced C6H1206 +6O2 6CO2 + 6H20 + ENERGY CELLULAR RESPIRATION: C6H12O6 is oxidized, O2 is reduced ________________ – moving H+ • The production of ATP due to a hydrogen ion (H+) ___________ across a membrane • Occurs in _________________ and _________________…the energy organelles of cells Starts with H+ pump pumping H+ _______ the membrane Completes when H + ions cross back through the membrane through an ________________ complex Mader, p115 – summary, Fig. 6.13 Chemiosmosis – moving H+ High H+ conc. 2 Low H+ conc. 1