* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Beyond Guilt and Fear
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
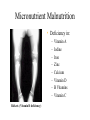
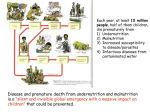
Malnutrition Defined Text extracted from The World Food Problem Leathers & Foster, 2004 http://www.lastfirst.net/images/product/R004548.jpg Malnutrition • Overnutrition • Undernutrition – Secondary Malnutrition – Micronutrient Malnutrition – Protein Energy Malnutrition • Most important Protein Energy Malnutrition Undernutrition http://www.answers.com/topic/percentage-population-undernourished-world-map-png-1 Secondary Malnutrition • Diet normal • Food not digested or absorbed – Diarrhea – Parasites Tapeworm Micronutrient Malnutrition • Deficiency in: – – – – – – – – Rickets (Vitamin D deficiency) Vitamin A Iodine Iron Zinc Calcium Vitamin D B Vitamins Vitamin C Vitamin A Deficiency • 500,000 children become blind each year – xerophthalmia • Half of these will die within a year of becoming blind • Rice diet lacking green vegetables – Vitamin supplements help: cost $3/year – Golden Rice could help Iodine Deficiency • Iodine deficiency – affects 740 million people worldwide – single greatest cause of preventable brain damage in babies – Goiter – Stillbirth – Miscarriages – Mental Retardation • Prevented by iodized salt • Best sources of natural iodine – Sea weed – Sea food Goiter (thyroid enlargement) Iron Deficiency Anemia • Affects 2 billion people, • 90% live in developing countries – 39% of preschool children – 52% of pregnant women • Reduced – physical activity – mental activity • Increased – – – – birth mortality Worms Malaria HIV • High iron rice could help Iron, Vitamin A & Iodine Deficiency http://www.css.cornell.edu/FoodSystems/Micros&AgriMan1ref.htg/img4.gif Other Deficiencies • Zinc – Growth retardation – delayed sexual maturation – skin and eye lesions – 48% of world at risk for zinc deficiency • Calcium – Osteoporosis: bone loss • Vitamin D – Rickets: bone malformation Other Deficiencies • Vitamin C – Causes Scurvy: problem in refugee camps • Niacin – Causes Pellagra: dermatitis, diarrhea, dementia – Due to diet high in maize (low in tryptophan) • Thiamin – Causes Beriberi – Due to diet high in polished rice • Folate – Birth defects: Anancephaly and Spina Bifida Protein Energy Malnutrition (PEM) • Underconsumption of calories or protein • Most important form of malnutrition • Associated with poverty – Not enough food – Poor quality food • Kwashiorkor – Extreme protein deficiency Kwashiorkor • Marasmus – Extreme calorie deficiency Kwashiorkor • Protein deficiency often associated with weaning onto thin cereal gruels. – Cassava – Plantains • Bloating of the stomach due to edema – Fluid leaking into body – Wasted muscles • Antibodies degraded to provide protein to body – Infection – Dysentery – Death Marasmus • Calorie deficiency – Lack of food – Poorest populations – Neglected • Infants • children • Protein used for energy • Results in wasting – Deterioration of tissues • Brain development impaired Balanced Protein • Protein are made of amino acids • Essential amino acids – Body cannot make – Required in diet • Animal proteins have perfect balance of amino acids – Meat – Milk – Eggs Complementing Proteins • Plant proteins are deficient in different essential amino acids • Cereals – Low in lysine • Beans – Low in methionine • Must eat both cereal and beans together to get balanced amino acids – Complementing proteins Rice and Beans Calorie Deficiency • Most widespread problem among poor • Cannot get enough calories (energy) in diet – Most get enough protein • Calorie requirements vary – – – – Age Sex Pregnancy Lactation Nutritional Needs • RDA – Recommended Daily Allowance – Level of nutrients adequate for 97-98% of the group – Good target for individuals • EAR – Estimated Average Requirement http://www.fda.gov/diabetes/pyramid.gif – Level of nutrients adequate for ½ individuals in group – Always lower than RDA – Good target for average intake of a group