* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbon
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Carbon sink wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
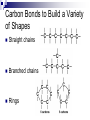
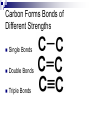
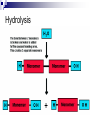
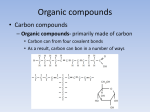
The “stuff” of life Organic Molecules What do they have in common? Living Organisms Are Chemical Factories All life is based on organic molecules - molecules that are built on a backbone of CARBON. - also contain Hydrogen - and many also have Oxygen - often contain functional groups – smaller molecules which are part of a larger molecule and give it unique properties Why are Organic Molecules based on Carbon? Carbon has unique properties - carbon is abundant – there’s lots of it - can bond with up to 4 other atoms - can bond readily with itself and other elements - makes chains with different shapes - shape determines function - forms bonds with different strengths Carbon can bond with up to four other atoms Carbon has 4 valence electrons Allows it to bond with 4 other atoms Carbon Bonds Readily with Itself This allows carbon to be the backbone of large and complex molecules. C C C C C C C C C C C Carbon bonds readily with other elements - in living things: Sulfur, Phosphorus, Oxygen, Nitrogen, & Hydrogen (SPONCH) Carbon Bonds to Build a Variety of Shapes Straight chains Branched chains Rings Carbon Forms Bonds of Different Strengths Single Bonds Double Bonds Triple Bonds Biomolecules are Macro(big)molecules All biological molecules (biomolecules) are large complex molecules – made of chains of smaller molecules 4 Types of biomolecules - Carbohydrates – sugars and starches - Lipids – fats and oils - Proteins - Nucleic Acids – DNA, RNA, ATP, ADP Biomolecules are Polymers Polymer –(poly = many mer = part) -Large molecules made of smaller molecules called monomers (mono = one mer = part) Polymer Each type of biomolecule has its own monomer Biomolecule Carbohydrate Lipid Protein Nucleic Acid Monomer_________ Monosaccharide Fatty Acid and Glycerol Amino Acid Nucleotide Condensation Reactions Condensation Reaction – Reaction which joins monomers together to form a polymer - called condensation reaction because a molecule of water is removed from the polymers during the reaction. - also called dehydration synthesis Condensation Reaction Hydrolysis Breaks Apart Polymers Hydrolysis – reactions which break the bonds between monomers in a polymer. Called hydrolysis because water is added at each broken bond Hydrolysis What should you know? Organic molecule Characteristics of carbon Biomolecule Macromolecule 4 types of biomolecules Monomer Monomers of each type of biomolecule Polymer Condensation reaction Hydrolysis