* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Opening Activity
Microbial metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Biosequestration wikipedia , lookup
Multi-state modeling of biomolecules wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Isotopic labeling wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Size-exclusion chromatography wikipedia , lookup
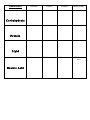
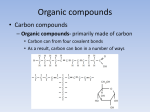
Quarter 1 Section: 1.5 Name: Opening Activity: Why is water considered a polar molecule? What types of bonds hold water molecules together? Latin Root Word: Review of Old Information: Capillary action demonstration results What happened to your celery stalk overnight? How do you know that the water reached the top of the plant (celery stalk)? Explain how this demonstration shows capillary action? New Information: Chapter 3-2 describes how carbon atoms bond to other atoms to form large organic molecules and how large organic molecules can also break apart into smaller molecules. Starting on page 52 complete the outline and activity over carbon compounds. Notes: The Carbon atom The ___________ atom is found in all living organisms. It readily forms ______ bonds. Large Carbon Molecules _____________ – only _____ molecule made of carbons _____________ – a chain of ______ monomers 4 Types of Macromolecules Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids What is a polymer (macromolecule)? A long molecule made up from lots of _________ molecules called _______________ The Making and Breaking of Polymers _________________________________ – is an anabolic process (requires energy) by which ________ molecules are chemically bonded through the use of enzymes and the ________ of _______. ________________ – is a catabolic process (releases energy) by which the bonds between monomers are _____________ by ____________ ____________. Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis All of the many compounds discovered can be classified in two broad categories known as… Which type of compounds must contain carbon? a. What are usually three other elements found in this type of compound? Draw an atom of carbon and explain how many bonds it can form with other elements due to its number of valence electrons? Define Compound: Many carbon compounds are made up from smaller molecules known as ____________. “Monomer” Monomers bond together to form more complex molecules known as _____________. “Polymer” What reaction has to occur to link monomers together to form polymers? Sucrose In the condensation reaction shown above, two sugar molecules glucose and fructose combine to form the sugar sucrose, which is common table sugar. In the formation of the bond between the two monomers, glucose releases a H+ ion and fructose releases a OH- ion, which combines to form water. Hint: Condensation is when gas is turned into water. In a condensation reaction monomers combine to form a polymer and water. The breakdown of polymers back into monomers is known as ___________________, which is the reversal of the condensation reaction. If hydrolysis is the reversal of a condensation reaction what has to be added to a polymer to break it down into monomers? Large polymers are called ________________________________. Activity: Complete the attached chart over the four macromolecules pg. 55-59. Biomolecules Monomer Polymer Examples Shape (Draw) Carbohydrate Will discuss later Will discuss later Will discuss later Protein Lipid Will discuss later Nucleic Acid