* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry power point
Chemical biology wikipedia , lookup
Living things in culture wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Biomolecular engineering wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Abiogenesis wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Hypothetical types of biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
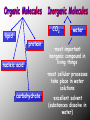
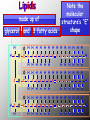
BIOCHEMISTRY • ALL LIVING THINGS ARE COMPOSED OF THE FOLLOWING BASIC ELEMENTS •CARBON •HYDROGEN •NITROGEN •OXYGEN •PHOSPHOROUS •SULFUR “CHNOPS”, Essential Elements • A MOLECULE CONTAINING CARBON IS • CALLED AN ORGANIC MOLECULE * H2O and CO2 are inorganic molecules CO2 lipid protein nucleic acid carbohydrate water •most important inorganic compound in living things •most cellular processes take place in water solutions •excellent solvent (substances dissolve in water) The Nature of Matter • ATOM is the basic unit of matter “unable to be cut” • Subatomic particles are the neutrons (no charge), electrons (- charge), protons (+ charge). • Compound- chemical combination of two or more elements • Element- pure substance made of one type of atom (periodic table) WATER Characteristics: ¾ of the earth is water, water expands as it freezes, ice is less dense that liquid H2O (floats), Polarity: A water molecule is polar because there is an uneven distribution of electrons between the oxygen and hydrogen atoms so…… it acts like a magnet Hydrogen bonds: attraction between the H atom and the O atom; weak bonds THERE ARE 4 BASIC CARBON COMPOUNDS IN ALL LIVING THINGS: (BIOCHEMICAL MOLECULES) 1. CARBOHYDRATES 2. LIPIDS 3. PROTEINS 4. NUCLEIC ACIDS CARBOHYDRATES •INCLUDES SUGARS, STARCHES, AND CELLULOSE •PROVIDES short term ENERGY FOR ORGANISMS •4 calories/gram •SUGARS: MONOSACCHARIDES (SINGLE SUGARS) DISACCHARIDES (DOUBLE SUGARS) •MAY BE LINKED TOGETHER TO FORM POLYSACCHARIDES (MANY SUGARS) •PLANTS STORE ENERGY IN POLYSACCHARIDE - STARCH •ANIMALS STORE ENERGY IN POLYSACCHARIDE-GLYCOGEN PLANTS – JOIN SIMPLE SUGARS TOGETHER TO MAKE - CELLULOSE CELLULOSE – A polysaccharide in the cell walls of plants -Cellulose we eat comes from vegetables, fruits, whole grain breads and cereals -Your body CANNOT break down, no nutritional value (fiber) LIPIDS INCLUDES FATS, OILS, WAXES, PHOSPHOLIPIDS, AND STERIODS. •Energy= 9 calories/gram •FATS - ACT AS INSULATORS •WAXES - HELP PLANTS CONSERVE WATER •OILS - MAKE SOME BIRDS FEATHERS WATERPROOF •PHOSPHOLIPIDS – MAIN COMPONENT OF CELL MEMBRANE •STEROIDS– HORMONES THAT AFFECT CELL ACTIVITY *Non-polar molecules that are not soluble in water LIPIDS • • • • • A concentrated source of energy Store other nutrients, such as Vitamin A Protect vital organs Help keep our skin from drying out Insulate the body against changes in environmental temperature *The body uses lipids to make cell membranes, hormones and the oils in your skin and hair made up of glycerol H H C and 3 fatty acids Note the molecular structure’s “E” shape O H H H H H H H H H H H H H H O C C C C C C C C H H H H H H C C C C C C C H H H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H H C O C C C C C C C C H H H H H H C C C C C C C H H H H H H H O H H H H H H H H H H H H H H H C H O C C C C C C C H H H H H H C C C C C C C C H H H H H H H LIPIDS • Saturated fats: have no double bonds between the carbons and contain max number of hydrogen atoms -usually solid at room temperature, most come from animal products • Unsaturated fats: fats with double bonds -most are liquid at room temperature, come from plants (usually referred to as oils) *Monounsaturated – one double bond *Polyunsaturated – many double bonds PROTEINS •COMPOSED OF SMALLER MOLECULES CALLED AMINO ACIDS • CONTAIN NITROGEN, CARBON, HYDROGEN & OXYGEN •MAKE UP MORE THAN HALF THE DRY WEIGHT OF ORGANISMS PROTEINS • Provide body with materials needed for growth and repair • Builds muscles, skin and blood • Complete: contain all 8 essential a.a. (food that comes from animals) • Incomplete: lack some of the essential a.a. (food that comes from plants) PROTEINS Include: • enzymes that promote chemical reactions • structural functions such as collagen in skin, ligaments, tendons, and bones • proteins found in muscles and hair • antibodies – fight infection by killing bacteria • Hemoglobin - carries oxygen in blood NUCLEIC ACIDS •LARGE COMPLEX MOLECULES CONTAINING HEREDITY MATERIAL 1. DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID -D N A 2. RIBONUCLEIC ACID- R N A •D N A CARRIES INSTRUCTIONS THAT REGULATE CELL ACTIVITIES •R N A –uses information from DNA to tell the ribosomes what proteins to make. NucleicAcids • Made up of nucleotides containing a sugar, a phosphate, and a Nitrogen base Includes: nitrogen sugar *Adenine base *Thymine *Guanine phosphate *Cytosine Monomers (subunits) • Carbohydrates- Monosaccharides (sugars) • Proteins- Amino Acids • Lipids- Glycerol and fatty acids • Nucleic acids- Nucleotides