* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochemistry - Cloudfront.net
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
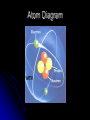
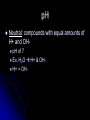
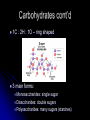
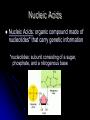
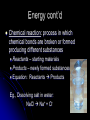
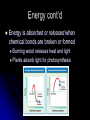
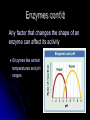
Biochemistry The Chemistry of Life Matter Anything that takes up space and has mass Matter is made of atoms Forms: Solid, Liquid, Gas http://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=DPizS4hKvyA&feature=pla yer_embedded Atoms Atom: smallest unit of matter that cannot be broken down by a chemical means Contains THREE main particles: Proton: + charge (in nucleus) Electron: - charge (around nucleus) Neutron: no charge (in nucleus) Atom Diagram 75005.wmv # of Atomic Particles p+ = 13 e- = 13 n0 = 14 p+ = e- = Atomic # n0 = Atomic mass - Atomic # Draw an Atom p+ and n0 in nucleus e- in shells around nucleus 1st shell: 2 e2nd shell: 8 e3rd shell: 8 eEtc. Fill inner shell before moving on Elements Element: a pure substance made up of only one kind of atom Elements (Isotopes) Isotopes: Same element that differs in amount of neutrons EX. C12 (Carbon 12) & C14 (Carbon 14) Same number of p+ and e-, only n0 differ Compounds Compounds: a substance made of the joined atoms of two or more elements EX. NaCl Sodium + Chlorine CO2 Carbon + Oxygen Bonds Connect atoms and compounds More stable…fills e- shells Different types: Covalent Ionic Hydrogen Bonds Covalent Bonds: two or more atoms SHARE electrons creates molecules Ex. H2O, CO2 Covalent Bond Video Bonds Ionic Bonds: Bonds created when electrons are gained or lost creates “ions” Ions: positively or negatively charged atoms, due to loss or gain of electrons Ionic Bond Video Bonds Hydrogen Bonds: a weak chemical attraction between “polar” molecules involving Hydrogen Ex. Water molecule + Water molecule Polarity Polar molecules: molecules with an unequal distribution of electric charges Properties of Water Hydrogen bonds in water cause… Cohesion: attraction between substances of the same kind Adhesion: attraction between different substances pH Acids: compounds that form Hydrogen ions [H+] when dissolved in water pH below 7 Ex. Hydrochloric acid : HCl H+ & Cl H+ > OH pH Bases: compounds that form Hydroxide ions [OH-] when dissolved in water pH above 7 Ex. Sodium Hydroxide: NaOH Na+ & OH H+ < OH pH Neutral: compounds with equal amounts of H+ and OHpH of 7 Ex. H2O H+ & OH H+ = OH Macromolecules Large molecules that contain Carbon 4 Main Types: Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates Carbohydrates: organic compounds made of Carbon, Hydrogen, and Oxygen Ex. Starches & Sugars Found in fruits, vegetables, and grains Source of short-term energy Carbohydrates cont’d 1C : 2H : 1O – ring shaped 3 main forms: Monosaccharides: single sugar Disaccharides: double sugars Polysaccharides: many sugars (starches) Lipids Lipids: non-polar molecules usually not soluble in water Ex. Fats, phospholipids, steroids, waxes Found in butter, oils, animal products Stores long-term energy, used for insulation, cushion Lipids cont’d Glycerol and three fatty acids – E-shaped 2 Types: Saturated: full of H (solid at room temp.) Unsaturated: not full of H (liquid at room temp.) Proteins Proteins: organic compound made of one or more chains of amino acids (principle component of all cells) Found in meat, nuts, eggs Proteins cont’d Chains of amino acids- folded or straight Used for “everything”- body functions Ex. hormones, enzymes, antibodies, body parts, etc. Nucleic Acids Nucleic Acids: organic compound made of nucleotides* that carry genetic information *nucleotides: subunit consisting of a sugar, phosphate, and a nitrogenous base Nucleic Acids cont’d 2 Main Forms: DNA- Deoxyribonucleic Aciddouble strand of nucleotides: (stores hereditary info) RNA- Ribonucleic Acidsingle strand of nucleotides (helps make proteins) ATP – Adenosine Triphosphate Main energy storage for cells Energy Energy: ability to move or change matter Exists in many forms (eg., light, heat, chemical energy, mechanical energy, electrical energy) Can be converted from one form to another Living things need energy for metabolism and to maintain homeostasis Energy cont’d Chemical reaction: process in which chemical bonds are broken or formed producing different substances Reactants – starting materials Products – newly formed substances Equation: Reactants Products Eg., Dissolving salt in water: NaCl Na+ + Cl- Energy cont’d Energy is absorbed or released when chemical bonds are broken or formed Burning wood releases heat and light Plants absorb light for photosynthesis Energy cont’d Activation energy: energy needed to start a chemical reaction Chemical “push” to get reaction going Enzymes Enzyme: substance that increases the speed of a chemical reaction Act as catalysts – reduce activation energy of a chemical reaction Enzymes cont’d Substrate: substance on which enzyme acts during chemical reaction Active site: spot on an enzyme that the substrate fits into Enzymes cont’d Any factor that changes the shape of an enzyme can affect its activity Enzymes like certain temperatures and pH ranges References Atom image-http://damienkatz.net/pics/atom.jpg Periodic Table image-http://www.corrosionsource.com/handbook/periodic/periodic_table.gif Balloon image-http://us.inmagine.com/168nwm/photoalto/paa222/paa222000010.jpg Electron shells image-http://homepages.ius.edu/GKIRCHNE/FigQChem.jpg Covalent Bond imagehttp://images.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://ghs.gresham.k12.or.us/science/ps/sci/ibbio/chem/notes/chpt2/water.gif&i mgrefurl=http://ghs.gresham.k12.or.us/science/ps/sci/ibbio/chem/notes/chpt2/water.htm&h=307&w=303&sz=17&hl=en&s tart=2&tbnid=9HupbZCmuuZ0VM:&tb Ionic Bond image- http://library.thinkquest.org/27819/media/ionic.gif Hydrogen Bond image- http://www.evolvingcode.net/data/hydrogen_bonding_attach/waterHbonds.gif Polar molecule image- http://www.school-for-champions.com/science/images/chempolar1.gif Physical Science Series: Chemical Bonding. United Learning (1998). Retrieved September 22, 2009, from Discovery Education: http://streaming.discoveryeducation.com / Water drop image- www.doctormelgar.com Lipid molecule image: biology.unm.edu/.../Summaries/Macromol.html Sugar molecule image: http://encarta.msn.com/encyclopedia_761565113/Sugar.html Sugar image- www.exploratorium.edu/cooking/candy/sugar.html Protein image- http://www-vis.lbl.gov/Vignettes/Downing1998/index.html Nucleotide image- www.msu.edu/.../ebertmay/drivers/nucleotide.jpg Pasta image - www.sheknows.com/articles/804691.htm Speeding car image - http://www.eyeflare.com/article/italian-speeding-fines-can-kill-your-vacation-budget/ Fireplace image - asootysolution.com/Firebox_Repairs.html Salt in water image - http://en.wikibooks.org/wiki/Wikijunior:The_Elements/Solutions