* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download How does it all work
Homologous recombination wikipedia , lookup
DNA sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA repair protein XRCC4 wikipedia , lookup
Zinc finger nuclease wikipedia , lookup
DNA profiling wikipedia , lookup
DNA replication wikipedia , lookup
DNA polymerase wikipedia , lookup
United Kingdom National DNA Database wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
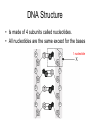
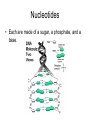
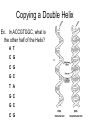
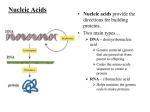
How does it all work? DNA • Supplies instructions for cells. • Is able to be copied Chargaff • Found that the bases bond together. adenine= thymine and guanine=cytosine Can you think of a mnemonic device to remember which two go together? Rosalind Franklin • Created images of DNA with x-rays. Watson & Crick • Built the double helix model (“The Ladder”). DNA Structure • Is made of 4 subunits called nucleotides. • All nucleotides are the same except for the bases 1 nucleotide Nucleotides • Each are made of a sugar, a phosphate, and a base. The Bases • The 4 bases are adenine, thymine, guanine, cytosine. • Each base is a different shape. • Each base is called by their 1st letter. Ex. A, T, G, C • Each group of three bases codes for one amino acid See page 128 in your book! Copying a Double Helix Ex. In ACCGTGGC, what is the other half of the Helix? A T C G C G G C T A G C G C C G How does DNA work? • 3 bases are organized to form a code of instructions to tell the cell what to do or how to copy…these instructions are called amino acids. But…how are the instructions moved to a cell or other parts of the body? Proteins • 50,000 different types • They act as messengers to deliver the amino acids (instructions). • Are the building blocks of life! Well, how does the DNA get on proteins to move around? What happens if there is a mistake in the order of the bases on the protein? Mutations • Occur when there is an error in the order of the amino acids on the protein. Ex. Deletion, substitution, insertion (extra) Ex. Sickle cell anemia Mutagen • Is a physical or chemical agent that causes a mutation in DNA. Ex. Radiaton Pretend you are a reporter for the New York Times Science section. You have been assigned to write a one-page, typed article informing readers about why DNA has been heralded as the most important molecules ever discovered. The 1st paragraph should explain the basic structure of the DNA molecule; the 2nd on why is DNA important. This is your quiz for this set of notes. You can use information from your book, PowerPoint notes, books from the library or in the room or the Internet. Paper is due on Friday December 7, 2007