* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lecture 1. Introduction to Biochemistry
Epoxyeicosatrienoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Low-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
15-Hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid wikipedia , lookup
Cholesterol wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
High-density lipoprotein wikipedia , lookup
Phospholipid-derived fatty acids wikipedia , lookup
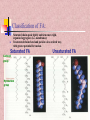
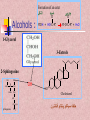
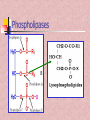
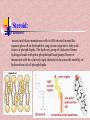
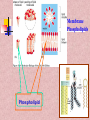
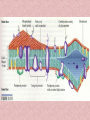
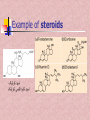
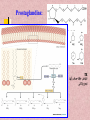
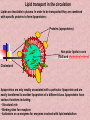
In the name of Gad عناوین مطالب -1اهمیت لیپیدها -2طبقه بندی لیپیدها -3اسیدهای چرب -4اسیدهای چرب غیر اشباع -5اسیدهای چرب ترانس و سیس -6انواع اسیدهای چرب -7خواص اسیدهای چرب -8الکلها -9تری آسیل گلیسرولها -10فسفو آسیل گلیسرول -11کاردیو لیپین وپالسمالوژن -12فسفولیپازها -13ترپنها ،مومها -14اسفنگولیپیدها -15استروئیدها -16غشاءها سلولی -17پروستاگالندین ها -18لیپو پروتئین ها Lipids لیپیدها حاللیت کمتری در آب دارند و بیشتر در حاللهای آلی حل مانند اتر، بنزن ..حل میشوند. لیپیدها مولکولهای دو قطبی ( )amphipathicهستند. لیپیدها جزئ اصلی غشاهای سلولی محسوب می شوند. لیپیدها مبنع غنی از انرژی محسوب می شوند 1 .گرم 9Kcal ..... لیپیدها در انتقال ویتامینهای محلول در چربی ((Vit ِD, A, E, K لیپیدها نقش حفاظتی در برابر سرما دارند. لیپیدها در غشائ سلولهای عصبی درکمک به انتقال امواج عصبی نقش دارند. چربی O R'-O-C-R'' + H2O Formation of an ester: اسید الکل O "R'OH + HO-C-R Classification of Lipids: Lipids are classified into Three great classes: Those that only contain fatty acids + ROH = (simple lipids); -Lipids : fatty acids + Glycerol =TG - Waxes : fatty acids+ Long alcole Those that contain fatty acids + ROH+ another Substance (complex lipids). - phospholipids -Glycolipids -Lipoprotien -Sphingolipids Steroids Fatty Acids Fatty acids = carboxyl group + a long hydrocarbon chain HO C O C H2 H2 C C H2 H2 C C H H2 C C H2 H2 C C H2 H2 C C H2 H2 C C H2 H2 C CH3 OH OH O O 16:0 =Palmitic Acid=Hexadecanoic acid 18:1 =Oleic acid=9-Octadecenoic acid Saturated fatty acids are single bonds in all carbon-carbon bonds; Unstaurated fatty acids contain one or more double bonds in hydrocarbon chains; Fatty acids can be named in three ways. See above figure and table 6.1 9 - Number of carbon +Enoic انوئیک -Number of carbon + Anoic آنوئیک 18:1 اسید اولئیکω9 Classification of FA: Saturated chains pack tightly and form more rigid, organized aggregates (i.e., membranes); Unsaturated chains bend and pack in a less ordered way, with greater potential for motion. Saturated FA Carboxyl group Hyrocarbon group Unsaturated FA Trans & Cis form of USFA trans form of oleic acid w3 W9, w9 w6 w6 cis form of oleic acid غشائ سلولهای شبکیه چشم Common Fatty Acids Saturated fatty acids: Unsaturated fatty acids: Octadecadienoic acid Octadecatrienoic acid Eicosatetraenoic acid Structural Consequences of Unsaturation اسید شولمگریک اسید چرب حلقوی است. اسید فیتانیک اسید چرب شاخه دار است . اسید پروستانوئیک Other Fatty Acids: Cyclic fatty acid آسید آراشیدیک Properties of Fatty Acids: Melting Point -SFA number of carbon ..... MP -USFA number of double bound …. MP Saponification (mg KOH ……1gr FAT) Number of COOH Number of saponification کربنه4اسید بوتیریک کربنه24اسید لیگنوسریک Properties of Fatty Acids: Hydrogenation USFA + H2 SFA Binding with O2 O2 + USFA -Epoxide ((اپوکسید -ketoHydroxide )(کتو هیدروکسید -En –Diol)(اندیول -Proxide)(پرواکسید Binding With I2 I2 + USFA ( (یا عدد یدیIndies of iodine…..(gr of I2 ….100 gr fat) Formation of an ester: الکل Alcohols : اسید O R'OH + HO-C-R" چربی O R'-O-C-R'' + H2O 1-Glycerol 3-Estrols 2-Sphingosine OH H2C OH H C CH H3N+ CH OH HO Cholesterol HC (CH2 )12 sphingosine CH3 حلقه سیکلو پنتانو فنانترن Lecture 15. Lipids 13 Triglycerols (triglycerides) Triglycerols consist of a glycerol esterified with three fatty acids If all fatty acid chains are the same, the molecule is called triacylglycerol (e.g., tristearin) •TG is most important of Storage lipids in fat tissue And non polar. Phosphoacylglycerols a polar head group (X): serine, choline, ethanolamine, glycerol, or inositol. polar "kink" due to double bond non-polar x Hydrogen Phosphatidic acid Ethanolamine Phosphatidylethanolamine Choline Phosphatidylcholine Serine Phosphatidylserine Inositol Phosphatidylinositol Cardiolipin & Plasmalogen پالسمالوژن=آلدئید چرب+مونوآسیل گلیسرول پیوند وینیل اتر کارديولیپین=فسفاتیدات +فسفاتیدات+گلیسرول دی فسفاتيدل گليسرول Phospholipases B Lecture 15. Lipids 18 Waxes Waxes are esters of long-chain alcohols with long-chain fatty acids; Waxes are water-insoluble due to the weakly polar nature of the ester group. استر اسید چرب با الکلهای با زنجیره بلند هستند Lecture 15. Lipids 19 Terpenes Terpenes are a class of lipids from two or more molecules of 2-methyl-1,2butadiene, or isoprene; Example of a terpene molecule: CHO all-trans-retinal All sterols (including cholesterol) and steroid hormones are terpene-based molecules OH Sphingolipids: Sphingolipids are derivatives of the lipid sphingosine, which has a long hydrocarbon tail, and a polar domain that includes an amino group. H2C OH H C CH H3N+ CH HC (CH2 )12 OH H2C O OH H C CH NH CH C R ceramide HC (CH2 )12 CH3 R-OH + sphingosine CH3 The amino group of sphingosine can form an amide bond with a fatty acid carboxyl, to yield a ceramide. Ceramides usually include a polar head group, Sphingomyelins OH H2C CH3 OH H C H3C CH O H2 C N+ H2 C O CH3 P O phosphocholine NH H2C CH sphingosine O C ceramide OH H C CH NH CH HC O R O fatty acid (CH2 )12 CH3 FA + Spingosine Ceramide + phosphocholine Sphingomyelin C R HC (CH2 )12 CH3 ceramide ((سرامید Sphingomyelin)(اسفنگومیلین CH2OH O OH H OH Sphingoglycolipids H H H OH O H H2C OH O cerebroside with -galactose head group Ceramide + monosaccharide Ceramide + monosaccharide + sialic acid Ceramide + monosaccharide +sulfate H C CH NH CH C R HC (CH2 )12 CH3 Cerebrosides)(سربروزید Gangliosides(GM) )(گانگلیوزید Sulfatides )(سولفاتید Hydrogen Phosphocholine Ceramide Sphingomyelin Glucose glucosylcerebroside Oligosaccharide Gangliosides Steroid: Cholesterol, an important constituent of cell membranes, has a rigid ring system and a short branched hydrocarbon tail. HO Cholesterol Cholesterol is largely hydrophobic. But it has one polar group, a hydroxyl, making it amphipathic. Steroid: Cholesterol inserts into bilayer membranes with its OH oriented toward the aqueous phase & its hydrophobic ring system adjacent to fatty acid chains of phospholipids. The hydroxyl group of cholesterol forms hydrogen bonds with polar phospholipid head groups.However interaction with the relatively rigid cholesterol decreases the mobility of hydrocarbon tails of phospholipids. Membrane Phospholipids Phospholipid Example of steroids اسید کولیک اسید کنوداکسی کولیک Prostaglandins: :TX انقباض عظله صاف رگها تجمع پالکتی Prostaglandins inhibitors Dexamethasone indomethacin ibuprofen تجمع پالکتی را افزایش می دهندتنظیم عبور یونها از غشائالتهابتنظیم متابولیسم کلسیم وعضله-ترشح موسین از معده Lipid transport in the circulation Lipids are insoluble in plasma. In order to be transported they are combined with specific proteins to form lipoproteins: Proteins (apoproteins) HO Non polar lipids in core (TAG and cholesterol esters) O R O O HO Cholesterol R R HO Apoproteins are only weakly associated with a particular lipoprotein and are easily transferred to another lipoprotein of a different class. Apoproteins have various functions including: • Structural role • Binding sites for receptors • Activators or co-enzymes for enzymes involved with lipid metabolism Lipoproteins HDL LDL & VLDL Chylomicrons Assembled in intestinal mucosal cells. They enter the lymphatic system and enter the blood via the thoracic duct. They contain mostly TAG. Nascent chylomicrons contain apoprotein B48 but pick up others apoproteins from high density lipoproteins (HDL) once they enter the circulation. Apoprotein phospholipid Cholesterol ester Cholesterol TAG (86%) Function is to transport dietary TAG to the adipose tissues where it can be stored as fat or to muscles where the constituent fatty acids can be used for energy. The five classes of lipoprotein (all contain characteristic amounts TAG, cholesterol, cholesterol esters, phospholipids and apoproteins) Increasing density Class Diameter (nm) Source and function Major apoliproteins Chylomicrons (CM) 500 Intestine. Transport of dietary TAG A, B48, C(I,II,III) E Very low density lipoproteins (VLDL) 43 Liver. Transport of B100, C(I,II,III) , E Low density lipoproteins (LDL) 22 Formed in circulation by partial breakdown of IDL. Delivers cholesterol to peripheral tissues B100 High density lipoproteins (HDL) 8 Liver. Removes “used” cholesterol from tissues and takes it to liver. Donates apolipoproteins to CM and VLDL A, C(I,II,III), D, E endogenously synthesised TAG