lipid raft
... Huge percentage of non-fatty-acid-based lipids are built up from isoprene units Biosynthesis in 5 or 15 carbon building blocks reflects this Steroids, vitamins, terpenes Involved in membrane function, signaling, feedback mechanisms, structural roles ...
... Huge percentage of non-fatty-acid-based lipids are built up from isoprene units Biosynthesis in 5 or 15 carbon building blocks reflects this Steroids, vitamins, terpenes Involved in membrane function, signaling, feedback mechanisms, structural roles ...
Fatty Acids:
... Fatty acid is a carboxylic acid often with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids and their derivatives are consumed in a wide variety because they are used as raw materials for a wide variety of industrial products like, paints, surfactant, textiles, plastics, ...
... Fatty acid is a carboxylic acid often with a long aliphatic chain, which is either saturated or unsaturated. Fatty acids and their derivatives are consumed in a wide variety because they are used as raw materials for a wide variety of industrial products like, paints, surfactant, textiles, plastics, ...
Case Study: Membranes - Theoretical and Computational
... hydrocarbon chain with a carboxcylic acid head group. Although free fatty acids do not occur in nature, they are the hydrocarbon chains that make up the tail groups of most lipids. There are usually between 14 and 20 carbons within a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain; carbons are usually even in number. ...
... hydrocarbon chain with a carboxcylic acid head group. Although free fatty acids do not occur in nature, they are the hydrocarbon chains that make up the tail groups of most lipids. There are usually between 14 and 20 carbons within a fatty acid hydrocarbon chain; carbons are usually even in number. ...
... has been defined as a food that was practically free of sugar and energy thus qualifying as a “free” food for diabetic diets. Under the U.S. system, “free” refers to a level of energy or of a nutrient that is nutritionally trivial and physiologically inconsequential. Under the U.S. system, the frequ ...
The Lipid Layer: The Outer Surface of the Ocular Surface Tear Film
... fatty acid, bilayers are only formed with difficulty and after compression may not expand effectively again (Johnston and Chapman, 1988). Surprisingly both the monolayer surface potential and compressibility are greatly affected by the saturation or hydroxylation of the galactosphingolipid (Oldani e ...
... fatty acid, bilayers are only formed with difficulty and after compression may not expand effectively again (Johnston and Chapman, 1988). Surprisingly both the monolayer surface potential and compressibility are greatly affected by the saturation or hydroxylation of the galactosphingolipid (Oldani e ...
Dietary Fat, Saturated Fat, Trans Fat and
... what our body needs, are converted into fats and stored for later use. Although fat is important in the diet, many adults eat more fat than they should. Diets high in saturated fats and trans fats are a risk for heart disease. High total fat diets are a risk factor for cancer and obesity. By increas ...
... what our body needs, are converted into fats and stored for later use. Although fat is important in the diet, many adults eat more fat than they should. Diets high in saturated fats and trans fats are a risk for heart disease. High total fat diets are a risk factor for cancer and obesity. By increas ...
Лекция 3. Биологические мембраны. Обмен
... The prefix n- indicates the "normal" unbranched structure. For instance, "dodecanoic" simply indicates 12 carbon atoms, which could be arranged in a variety of branched forms. Thus "rc-dodecanoic" specifies the linear, unbranched form. ...
... The prefix n- indicates the "normal" unbranched structure. For instance, "dodecanoic" simply indicates 12 carbon atoms, which could be arranged in a variety of branched forms. Thus "rc-dodecanoic" specifies the linear, unbranched form. ...
Dietary Fat and Cholesterol - OSU Fact Sheets
... acids. Completely saturated fats and completely polyunsaturated fats are very rare in nature. Whether a fat is solid or liquid depends of the relative amounts of the different types of fatty acids and the temperature. Unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature and contain more unsaturate ...
... acids. Completely saturated fats and completely polyunsaturated fats are very rare in nature. Whether a fat is solid or liquid depends of the relative amounts of the different types of fatty acids and the temperature. Unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature and contain more unsaturate ...
BIO216 - National Open University of Nigeria
... the position of –OH group on the carbon atom adjacent or next to the carbon atom that is most distant from the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar. Diastereoisomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror image of each other and need not contain chiral atoms. Epimers are diastereoisomers ...
... the position of –OH group on the carbon atom adjacent or next to the carbon atom that is most distant from the aldehyde or ketone functional group in the sugar. Diastereoisomers are stereoisomers that are not mirror image of each other and need not contain chiral atoms. Epimers are diastereoisomers ...
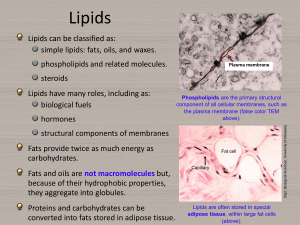
Lipids - faculty at Chemeketa
... melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double bond. stearic acid mp 69°C saturated oleic acid mp 13°C linoleic acid mp -17°C most unsaturated ...
... melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double bond. stearic acid mp 69°C saturated oleic acid mp 13°C linoleic acid mp -17°C most unsaturated ...
Chapter 17 Lipids
... melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double bond. stearic acid mp 69°C saturated oleic acid mp 13°C linoleic acid mp -17°C most unsaturated ...
... melting point than the unsaturated fatty acids. Because linoleic has two double bonds, it would have a lower mp than oleic acid, which has one double bond. stearic acid mp 69°C saturated oleic acid mp 13°C linoleic acid mp -17°C most unsaturated ...
Lipids NTR150
... Saturated fatty acids have a hydrocarbon tail that consists of single-bonded carbons only. Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one double bond in the hydrocarbon tail. Polyunsaturated fatty acids contain multiple double in the hydrocarbon tail. ...
... Saturated fatty acids have a hydrocarbon tail that consists of single-bonded carbons only. Monounsaturated fatty acids contain one double bond in the hydrocarbon tail. Polyunsaturated fatty acids contain multiple double in the hydrocarbon tail. ...
Lecture 18 Membranes 1: Lipids and Lipid Bilayers
... • longchain carboxylic acids, typically 14-24 C atoms • C16 & C18 most common (amphipathic) RCOO– with 0 - 4 double bonds, ...
... • longchain carboxylic acids, typically 14-24 C atoms • C16 & C18 most common (amphipathic) RCOO– with 0 - 4 double bonds, ...
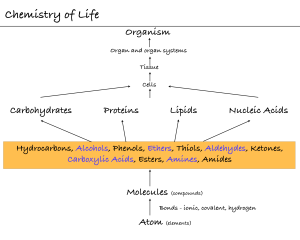
Chemistry of Life
... Lipids - Fats and Oils, triglycerides Triglycerides from animal sources are usually solids at room temperature - they are called Fats. There are exceptions the most notable being the triglycerides from fish. Triglycerides from animal plant sources are usually liquids at room temperature - they are ...
... Lipids - Fats and Oils, triglycerides Triglycerides from animal sources are usually solids at room temperature - they are called Fats. There are exceptions the most notable being the triglycerides from fish. Triglycerides from animal plant sources are usually liquids at room temperature - they are ...
Untitled - Shodhganga
... Fig.2.2. The steroid nucleus represents saturated carbons, unless specifically shown as double bonds. The methyl side chains attached to carbons 10 and 13 are shown as single bonds. At carbon 17, steroids usually contain a side chain. There are several steroids in the biological system. These includ ...
... Fig.2.2. The steroid nucleus represents saturated carbons, unless specifically shown as double bonds. The methyl side chains attached to carbons 10 and 13 are shown as single bonds. At carbon 17, steroids usually contain a side chain. There are several steroids in the biological system. These includ ...
Membranes 1: Lipids and Lipid Bilayers
... The hydrophobic effect provides the major driving force for the formation of ...
... The hydrophobic effect provides the major driving force for the formation of ...
Membranes 1: Lipids and Lipid Bilayers
... 3. Cholesterol: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly! • structure: 4 fused hydrocarbon rings (“steroid nucleus”) • planar, rigid, electrically neutral • amphipathic ("head" group = OH) • mainly in plasma membranes of animal cells; organelle membranes generally have less; rarely found in bacteria • functi ...
... 3. Cholesterol: The Good, The Bad, and The Ugly! • structure: 4 fused hydrocarbon rings (“steroid nucleus”) • planar, rigid, electrically neutral • amphipathic ("head" group = OH) • mainly in plasma membranes of animal cells; organelle membranes generally have less; rarely found in bacteria • functi ...
Article PDF
... Lipid oxidation is a major cause of deteriorative changes in foods, especially in relation to sensory properties and concerning the formation of potentially harmful compounds. The oxidation process in food lipids involves a complex series of reactions and gives rise to a high number of different com ...
... Lipid oxidation is a major cause of deteriorative changes in foods, especially in relation to sensory properties and concerning the formation of potentially harmful compounds. The oxidation process in food lipids involves a complex series of reactions and gives rise to a high number of different com ...
Lipids PP
... they are saturated with Hydrogen. Usually solid at room temperature (e.g. butter, pork fat, etc.) • Unsaturated fats have one (mono) or more (poly) C=C double bonds. Usually liquid at room temperature (e.g. vegetable oils) • In general, unsaturated fats are more healthful than saturated ones ...
... they are saturated with Hydrogen. Usually solid at room temperature (e.g. butter, pork fat, etc.) • Unsaturated fats have one (mono) or more (poly) C=C double bonds. Usually liquid at room temperature (e.g. vegetable oils) • In general, unsaturated fats are more healthful than saturated ones ...
NSCC NTR150 Ch05 Fats (Lipids)
... Fatty Acids in Triglycerides Fatty acids can differ in • Length of their carbon chain • Level of saturation • Shape ...
... Fatty Acids in Triglycerides Fatty acids can differ in • Length of their carbon chain • Level of saturation • Shape ...
LIPIDS
... cytosol, serving as depots of metabolic fuel. In vertebrates, specialized cells called adipocytes, or fat cells, store large amounts of triacylglycerols as fat droplets that nearly fill the cell (Fig. 10–3a). Triacylglycerols are also stored as oils in the seeds of many types of plants, providing en ...
... cytosol, serving as depots of metabolic fuel. In vertebrates, specialized cells called adipocytes, or fat cells, store large amounts of triacylglycerols as fat droplets that nearly fill the cell (Fig. 10–3a). Triacylglycerols are also stored as oils in the seeds of many types of plants, providing en ...
Sensory Science - Institute of Food Technologists
... Sec. 135.110 Ice cream and frozen custard. (a) Description. (1) Ice cream is a food produced by freezing, while stirring, a pasteurized mix consisting of one or more of the optional dairy ingredients specified in paragraph (b) of this section, and may contain one or more of the optional caseinates s ...
... Sec. 135.110 Ice cream and frozen custard. (a) Description. (1) Ice cream is a food produced by freezing, while stirring, a pasteurized mix consisting of one or more of the optional dairy ingredients specified in paragraph (b) of this section, and may contain one or more of the optional caseinates s ...
Eicosanoid
In biochemistry, eicosanoids (preferred IUPAC name icosanoids) are signaling molecules made by oxidation of 20-carbon fatty acids.They exert complex control over many bodily systems; mainly in growth during and after physical activity, inflammation or immunity after the intake of toxic compounds and pathogens, and as messengers in the central nervous system.The networks of controls that depend upon eicosanoids are among the most complex in the human body.Eicosanoids are derived from either omega-3 (ω-3) or omega-6 (ω-6) fatty acids.In general, the ω-6 eicosanoids are pro-inflammatory; ω-3s are much less so.The amounts and balance of these fats in a person's diet will affect the body's eicosanoid-controlled functions, with effects on cardiovascular disease, triglycerides, blood pressure, and arthritis. Anti-inflammatory drugs such as aspirin and other NSAIDs act by downregulating eicosanoid synthesis.There are multiple subfamilies of eicosanoids, including the prostaglandins, thromboxanes, and leukotrienes, as well as the lipoxins and eoxins, and others. For each, there are two or three separate series, derived from either an ω-3 or an ω-6 EFA. These series' different activities largely explain the health effects of ω-3 and ω-6 fats.