Lipids
... increases surface area of the hydrophobic lipid droplets so that the digestive enzymes, which work at the interface of the droplet and the surrounding aqueous solution, can act effectively. Emulsification is accomplished by two complementary mechanisms: 1. Use of the detergent properties of the bile ...
... increases surface area of the hydrophobic lipid droplets so that the digestive enzymes, which work at the interface of the droplet and the surrounding aqueous solution, can act effectively. Emulsification is accomplished by two complementary mechanisms: 1. Use of the detergent properties of the bile ...
O–CH 2 - IS MU
... ….on the contrary, there may be some undesirable effects of blocked prostanoid production, e.g. decline in blood platelet aggregation, decreased protection of endothelial cells and of gastric mucosa. Therefore drugs are being developed which would act as selective inhibitors of COX-2 without the adv ...
... ….on the contrary, there may be some undesirable effects of blocked prostanoid production, e.g. decline in blood platelet aggregation, decreased protection of endothelial cells and of gastric mucosa. Therefore drugs are being developed which would act as selective inhibitors of COX-2 without the adv ...
Dietary Fat, Saturated Fat, Trans Fat and
... and the myelin sheath around nerve fiber. The liver makes about 800 to 1500 mg of cholesterol each day, much more that the cholesterol provided in the diet, out of fragments from fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Cholesterol is made in many cells, but liver cells make the majority of cholesterol. In ...
... and the myelin sheath around nerve fiber. The liver makes about 800 to 1500 mg of cholesterol each day, much more that the cholesterol provided in the diet, out of fragments from fats, proteins and carbohydrates. Cholesterol is made in many cells, but liver cells make the majority of cholesterol. In ...
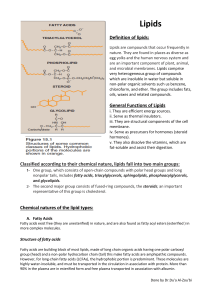
Lipids
... - Bile contains a large quantity of bile salts and the phospholipid lecithin. These components are the key elements that emulsify fat breaking globules into smaller pieces so that water-soluble pancreatic lipase can attack the surface. This emulsification process increases the total surface area of ...
... - Bile contains a large quantity of bile salts and the phospholipid lecithin. These components are the key elements that emulsify fat breaking globules into smaller pieces so that water-soluble pancreatic lipase can attack the surface. This emulsification process increases the total surface area of ...
Lipoprotein structure
... pre133-HDL) [4]. Because of their key role in cholesterol uptake from cells, the pre[31HDL have been studied quite intensively (J.E Kane, 1985). They contain 2 molecules of apo A1 per particle, and no apo A2 nor other proteins. Their mass ranges from 60 to 80 kDa, with a content of about 90% protein ...
... pre133-HDL) [4]. Because of their key role in cholesterol uptake from cells, the pre[31HDL have been studied quite intensively (J.E Kane, 1985). They contain 2 molecules of apo A1 per particle, and no apo A2 nor other proteins. Their mass ranges from 60 to 80 kDa, with a content of about 90% protein ...
LIPIDS
... Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. Cholesterol and other sterols are poorly absorbed. Overall, about 50% of dietary choleste ...
... Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. Cholesterol and other sterols are poorly absorbed. Overall, about 50% of dietary choleste ...
Dietary Fat and Cholesterol - OSU Fact Sheets
... acids. Completely saturated fats and completely polyunsaturated fats are very rare in nature. Whether a fat is solid or liquid depends of the relative amounts of the different types of fatty acids and the temperature. Unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature and contain more unsaturate ...
... acids. Completely saturated fats and completely polyunsaturated fats are very rare in nature. Whether a fat is solid or liquid depends of the relative amounts of the different types of fatty acids and the temperature. Unsaturated fats tend to be liquid at room temperature and contain more unsaturate ...
LIPIDS
... as fats, oils, waxes, cholesterol, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglyceride, diglyceride, phospholipids, and others. Although the term lipid is sometimes used as a synonym for fat, fats are in fact a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides and should not be conf ...
... as fats, oils, waxes, cholesterol, steroids, fat-soluble vitamins (such as vitamins A, D, E and K), monoglyceride, diglyceride, phospholipids, and others. Although the term lipid is sometimes used as a synonym for fat, fats are in fact a subgroup of lipids called triglycerides and should not be conf ...
fat facts
... Mom: Good job. What do the two oils have in common? Dolly: Well, basically, both oils are a blend of three different fats: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. Mom: Right, it’s the amount of each kind of fat that sets them apart. Can you tell the differences? Dolly: So, in each tablespoo ...
... Mom: Good job. What do the two oils have in common? Dolly: Well, basically, both oils are a blend of three different fats: saturated, monounsaturated, and polyunsaturated. Mom: Right, it’s the amount of each kind of fat that sets them apart. Can you tell the differences? Dolly: So, in each tablespoo ...
Chapter 19: Lipids
... c. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) The VLDL remnants are converted primarily to LDL, which is removed from the circulation mostly by being absorbed into liver cells. For liver cell absorption of LDL to occur, the LDL must bind to the LDL receptor on the cell surface. People with familial hypercholest ...
... c. Low-density lipoproteins (LDL) The VLDL remnants are converted primarily to LDL, which is removed from the circulation mostly by being absorbed into liver cells. For liver cell absorption of LDL to occur, the LDL must bind to the LDL receptor on the cell surface. People with familial hypercholest ...
Fats and Nutrition - Canon
... Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in the body that helps make up skin tissue, aids in transportation of fatty acids in the body, and helps the body produce hormones. High cholesterol diets lead to clogged arteries and heart disease. Monounsaturated fats and Omega 3 fatty acids are show ...
... Cholesterol is a fat-like substance found in the body that helps make up skin tissue, aids in transportation of fatty acids in the body, and helps the body produce hormones. High cholesterol diets lead to clogged arteries and heart disease. Monounsaturated fats and Omega 3 fatty acids are show ...
Glycerol + Fatty acids
... ● Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids . ● Structures and properties of phospholipids, sphingolipids, waxes, terpenes and steroids. ...
... ● Saturated and unsaturated fatty acids . ● Structures and properties of phospholipids, sphingolipids, waxes, terpenes and steroids. ...
Summary of Chapter 4 – Lipids
... immune response. Phospholipids, including the lecithins, have a unique chemical structure that allows them to be soluble in both water and fat. In the body, phospholipids are major constituents of cell membranes; the food industry uses phospholipids as emulsifiers. Sterols include cholesterol, bile, ...
... immune response. Phospholipids, including the lecithins, have a unique chemical structure that allows them to be soluble in both water and fat. In the body, phospholipids are major constituents of cell membranes; the food industry uses phospholipids as emulsifiers. Sterols include cholesterol, bile, ...
chapter_6_ppt
... – Transport lipids through bloodstream – Composed of: • Triglycerides, protein, phospholipids, cholesterol ...
... – Transport lipids through bloodstream – Composed of: • Triglycerides, protein, phospholipids, cholesterol ...
Ch5LIPIDS
... The triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and protein carriers form LIPOPROTEIN Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system • MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. ...
... The triglycerides, cholesterol, phospholipids, and protein carriers form LIPOPROTEIN Once these lipoproteins leave the cell, they become CHYLOMICRONS and enter the lymph system • MCTs, short-chain fatty acids and glycerol are absorbed directly into bloodstream. They do not enter the lymph system. ...
PowerPoint presentation file for this
... • These foam cells are then deposited into the lining of the artery wall. • This process, known as atherosclerosis, causes plaque deposits to enlarge, artery walls to lose elasticity, and the passage through the artery to narrow. ...
... • These foam cells are then deposited into the lining of the artery wall. • This process, known as atherosclerosis, causes plaque deposits to enlarge, artery walls to lose elasticity, and the passage through the artery to narrow. ...
3-Lipids
... most common tests is the lipid profile. 2. This panel of tests includes measures of triacylglycerol and cholesterol in the form of lipoprotein-cholesterol molecules, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The results of testing for these lipids ...
... most common tests is the lipid profile. 2. This panel of tests includes measures of triacylglycerol and cholesterol in the form of lipoprotein-cholesterol molecules, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-C) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C). The results of testing for these lipids ...
File
... • Largest, least dense, contain many triacylglycerols • Synthesised in endoplasmic reticulum of epithelial cells in small intestine, then enter blood stream • Carry fatty acids to where they are used or stored • The chylomicron remnants (without fats but still containing cholesterol) move to liver • ...
... • Largest, least dense, contain many triacylglycerols • Synthesised in endoplasmic reticulum of epithelial cells in small intestine, then enter blood stream • Carry fatty acids to where they are used or stored • The chylomicron remnants (without fats but still containing cholesterol) move to liver • ...
Lecture 17
... it is needed for cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, and the synthesis of steroidal hormones, most cholesterol is found esterified with a fatty acid at the -OH It can also help clogs arteries when high levels form plaque ...
... it is needed for cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, and the synthesis of steroidal hormones, most cholesterol is found esterified with a fatty acid at the -OH It can also help clogs arteries when high levels form plaque ...
The reactions of hypochlorous acid, the reactive oxygen species
... One of the major issues has been whether the reaction of HOCl with lipids of low density lipoprotein (LDL) yields predominantly chlorohydrins or lipid hydroperoxides. Electrospray mass spectrometry provided direct evidence that chlorohydrins rather than peroxides are the major products of HOCl- or M ...
... One of the major issues has been whether the reaction of HOCl with lipids of low density lipoprotein (LDL) yields predominantly chlorohydrins or lipid hydroperoxides. Electrospray mass spectrometry provided direct evidence that chlorohydrins rather than peroxides are the major products of HOCl- or M ...
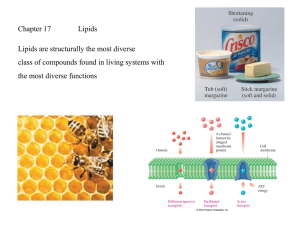
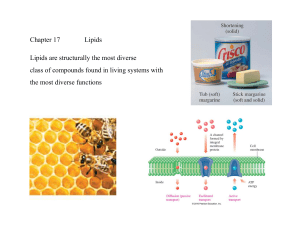
Chapter 17 Lipids Lipids are structurally the most diverse
... it is needed for cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, and the synthesis of steroidal hormones, most cholesterol is found esterified with a fatty acid at the -OH It can also help clogs arteries when high levels form plaque ...
... it is needed for cell membranes, brain and nerve tissue, and the synthesis of steroidal hormones, most cholesterol is found esterified with a fatty acid at the -OH It can also help clogs arteries when high levels form plaque ...
Fatty acids
... and are broken down into glycerol and FA. Once released into the blood, FFA bind to serum albumin for transport to tissues that require energy. The glycerol also enters the bloodstream and is absorbed by the liver or kidney where it is converted to glycerol 3phosphate by the enzyme glycerol kinase. ...
... and are broken down into glycerol and FA. Once released into the blood, FFA bind to serum albumin for transport to tissues that require energy. The glycerol also enters the bloodstream and is absorbed by the liver or kidney where it is converted to glycerol 3phosphate by the enzyme glycerol kinase. ...