* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download HIV-1 Protease - Illinois State University
Endogenous retrovirus wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthetic reaction centre wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Discovery and development of neuraminidase inhibitors wikipedia , lookup
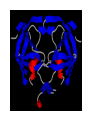
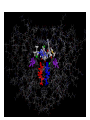
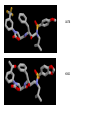
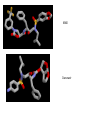
HIV-1 Protease HIV-1 Protease is one of the targets in the therapeutic treatment of AIDS. It cleaves the nascent polyproteins of HIV-1 and plays an essential role in viral replication. There are quite a few different inhibitors in existence for HIV-1 Protease. Due to the rapid rate of viral replication and the high error rate of reverse transcriptase result in HIV-1 mutants resistant to inhibitor action. Peptide bond hydrolysis Collectively, a total of 16 hydrogen bonds were identified in the interaction between HIV-1 protease and KNI-272. 9 of the 16 hydrogen bonding interactions were water mediated. HIV-1 Protease enzyme molecule is a homodimer of two polypeptide chains each containing 99 amino acid residues , and a single active site formed at the dimer interface. The two monomers are covalently joined through a short linker. Protein structure with MVT-101 inhibitor (shown in green) Vertical view Tiger Face! Below is the KNI-272 inhibitor bonded to the active site of HIV-1 Protease. The main interactions in the active site involve hydrogen bonding with four aspartates. Asp-25 is in red, while Asp-29, Asp 125, and Asp 129 are green. Also shown are three water molecules, HOH-301, HOH566, HOH608, which play a crucial role in bonding. Interactions betwixt HIV-1 protease and its inhibitor should strongly depend on the ionization state of the catalytic active site; KNI- 272 affinity to HIV-1 protease depends on pH. At maximum affinity, only Asp-25 is protonated. AD78 KB62 KB60 Darunavir • two Asp-Thr-Gly catalytic triads (residue numbers 25, 26, and 27 on one chain and 125, 126, and 127 on the second). The two Asp's act as the main catalytic residues in the active site and use a water molecule to help break the protein chain that binds in the tunnel. HIV-1 Protease Inhibitor Km (μM) Vmax (nmol/(min*mg) Saquinavir 1.4 30.7 Nelfinavir 3.6 20.8 Indinavir 2.1 99.9 Amprenavir 46.9 96.4 Ritonavir 0.06 77.3 Saquinavir 1.19 93.6 Indinavir 0.47 112.2