* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download No Slide Title
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Molecular ecology wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Personalized medicine wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
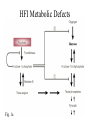
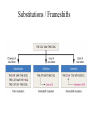
Genetics… …in the news. Final cumulative, but overwhelming focus on… • Virus Paper, • Sugar Paper, • Microarrays, lecture and supported readings in Chapters 8 and 9, • Chimp Paper, • Pheromone Paper, • PCR, Northerns, Southerns, other technology covered in papers. Due: Wednesday, Dec. 9th, Biology Office by 4:30, email by midnight. Genotypes and Phenotypes (societies, politics and human nature) Nature Reviews | Genetics, (3), June 2002, pp 7 Hereditary Fructose Intolerance • Fructose intolerance was first noted in severely ill infants with recurrent hypoglycemia (low blood sugar) and vomiting, occurring at the time of weaning when fructose or sucrose is added to the diet. – hypoglycemia, – depletion of ATP resources, – degradation of purines (G and A in DNA), – hypermagnesemia. Failure to Thrive Identification • 1962: a 3-year-old brother of a severely affected infant was found to have hepatomegaly (enlarged liver), and hypoglycemic shock that was precipitated by an oral test dose of fructose, – although he was clinically healthy. He had a marked aversion to sweets and fruit. • 1963: 2 adults, aged 33 and 39 years were identified with the same condition. In addition to the aversion to fructose-containing foods, remarkable absence of dental caries was noted. • The defect resides in aldolase B, which catalyzes the cleavage of fructose-1-phosphate to form dihydroxyacetone phosphate and D-glyceraldehyde. Aerobic Respiration 101 “Please start memorizing here.” “And, please know this.” Glycolysis 205 Prepatory Phase You’ve learned the conversion of glucose into triose phosphates. 300-level Understanding aldolase B We Don’t Live by Glucose Alone Liver, Kidney, Intestinal Mucosa • In aldolase 'B'-deficient tissues, cytoplasmic accumulation of fructose-1-phosphate leads to sequestration of inorganic phosphate, – results in the activation of AMP deaminase that catalyzes the irreversible deamination of AMP to IMP (inosine monophosphate), a precursor of uric acid. – depletion of tissue ATP occurs through massive degradation to uric acid, and the impairment of regeneration by oxidative phosphorylation in the mitochondria because of inorganic phosphate depletion (lost to phosphorylated sugars). • In the cell, ATP exists largely as a 1:1 complex with magnesium. Depletion of ATP in tissues leads to higher concentrations of magnesium. HFI Metabolic Defects Fig. 1a 300-level Understanding aldolase B Blocked How is HFI diagnosed? • The only definitive way to ascertain if one is suffering from HFI is to have one of two tests: 1) An enzymatic assay to determine aldolase activity. The aldolase is obtained from patient liver tissue in an invasive surgical procedure called a liver biopsy. 2) A fructose tolerance test. Fructose is injected intravenously under controlled conditions where acute glucose, fructose, and phosphate levels are monitored. Genetic Screens • Three mutations in this Aldolase B apparently account for >75% of all HFI mutations. • Genetic screens are performed using the polymerase chain reaction technique (PCR) followed by hybridization with allele-specific oligonucleotides (ASOs). • While this test is relatively harmless and effective, the screen does not monitor >95% of HFI mutations (many are unkown and require further research ), and is not considered diagnostic. – in other words, a negative result does not necessarily mean someone does NOT suffer from HFI, – while this test is NOT diagnostic, if it is positive it may aid in making a clear diagnosis. HFI Incidence Rate • The world-wide incidence rate of HFI remains unknown due to the difficulty of HFI diagnosis. The first report of an incidence rate was from Switzerland, where over a five year period that included 100,000 births, five cases of HFI were reported. – the degree of deviation in this estimate of 1 in 20,000 births is large and the incidence rate may range from 1 in 12,000 to 1 in 58,000. • It is likely that the incidence rate varies quite widely among different ethnic groups. Until easier and more effective methods of diagnosis are available from research involving different ethnic groups, the incidence rate will remain unclear. • Recent data suggest that the incidence rate could be closer to 1 in 10,000 If so, the carrier frequency would be 1 in 50. James, C.L., Rellos, P., Ali, M., Heeley, A.F., and Cox, T.M. (1996) Neonatal screening for HFI: frequency of the most common mutant aldolase B allele (A149P) in the British population. J. Med. Genet. 33 , 837-841. Tolan, D.R. (1995) Molecular Basis of Hereditary Fructose Intolerance: mutations and OMIM http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=229600 Aldolase B Mutations Alsolase B, 364 amino acids • > 21 mutations have been reported; – 15 of these are single-base substitutions, • resulting in 9 amino acid replacements, • 4 (stop) codons, • and 2 putative splicing defects. – The other 6 were deletions. • Recurrent mutations were observed in exons 5 and 9. Analysis suggests that the A149P and A174D mutations originated from single founders and achieved a relatively high frequency through genetic drift. Mutant Classifications …by their effect on DNA Substitutions Mutant Classifications …by their effect on DNA i d deletions and insertions 1 base? 2 base? 3 base? etc. Substitutions / Frameshifts Mutant Classifications …by their effect on DNA inversions translocations Trinucleotide Repeat Expansions FMR1 Fragile X Mental Retardation 1 ...GCGCGGCGGTGACGGAGGCGCCGC TGCCAGGGGGCGTGCGGCAGCG... cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg cgg …CTGGGCCTCGAAGCGCCCGCAGCCA cgg cgg cgg cgg ... cgg cgg cgg cgg > 230 Mutant Alleles • .1 FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, ALA149PRO] – • 2. FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, ALA174ASP] – • In addition, in 11 unrelated Italian patients, researchers found a G-to-C transversion in exon 9 which resulted in substitution of lysine for asparagine at position 334. 8. FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, ARG3TER] – • A 1-bp deletion in codon 288 causing a frameshift. The mutation seems restricted to Sicilian subjects. 6. FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, ASN334LYS] – • Point mutation found in Italy, Switzerland, and Yugoslavia but not in the UK, France, or the United States. 3. FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, LEU288DEL] – • A G-to-C transversion in exon 5 resulted in a substitution of proline for alanine at position 149 of the protein within a region critical for substrate binding. A consanguineous family from eastern Turkey, has a C-to-T transition in codon 3 changing arg to stop codon. 11. FRUCTOSE INTOLERANCE [ALDOB, LEU182DEL, VAL183DEL ] – In a 6-year-old patient with a 6-bp deletion in exon 6 of the aldolase B gene that led to elimination of 2 amino acid residues, leu182 and val183, but left the message in-frame. On the other allele, the patient carried the asn334-to-lys mutation (#6). Structure/Mutation Sites • Aldolase B associates in quartenary structure as a homotetramer, – A149P and A174D mutations result in a reduced affinity between sub-units. • Other mutation may retain quaternary structure, but lack enzymatic activity. Modern Disease 2003 = ~65 kilos (USA) CLINICAL MANAGEMENT • Limit fructose and related sugars…sucrose and sorbitol, – difficult, if not impossible in modern, Western society. G6PD… …in the news. Sickle Cell Malaria Worldwide distribution of G6PD deficiency: 1995 Sickling and G6PD Deficiencies heterozygote benefit • Heterozygotes carrying alleles for red blood cell sickling disorders, and for glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency are resistant to malaria, – sickle cell allele (Hb S), when expressed, prevents the plasmodium from breaking down host haemoglobin, slows growth, – G6PD mutations result in a ~50% reduction of risk for malarial infection, • However, these deficiencies have severe consequences in certain cultural and environmental circumstances. Slave Trade conservative estimates Estimates Range to 20,000,000. Two-thirds destined for the sugar industry. G6PD Disease in Modern Culture • First seen in WWII, AfricanAmerican soldiers receiving an anti-malaria drug experienced haemolysis. • Presently, – Sulphonamides, – Anti-pyretic drugs, – Broad Beans. NADPH producing reactions Antioxidant Production Case Study • 21 yo male medical student with malaria • Treated with primaquine • Four days later: – – – – – – Black colored urine Low RBC count Elevated reticulocyte count RBC with Heinz bodies Low hemoglobin Elevated serum bilirubin • Pt recovered in a few days Drug Interactions Antimalarials: * Primaquine * Pamaquine * Chloroquine Analgesics (which contain aspirin or phenacetin, such as: * Aspirin * Bufferin * Anacin * Excedrin * Empirin * APC Tablets * Darvon Compound * Coricidin Antibiotics: * Sulfanilamide * Sulfapyridine * Sulfadimidine * Sulfacetamide * Glucosulfone sodium * Nitrofurantoin * Furazolidone * Nitrofurazone * Dapsone * Sulfoxone * Sulfisoxazole Anthelmintics: * B-Naphthol * Stibophen * Niridazole Miscellaneous: * Probenecid * Thiazide Diuretics * Phenothiazine * Chloramphenicol * Orinase * Dimercaprol * Methylene blue * Naphthalene (moth balls) * Vitamin K * Fava beans G6P is a Research Juggernaut • Mary Lyons (Lyons hypothesis, think Barr bodies) used G6P to demonstrate X-linked inactivation, • Evolution... analysis of Mediterranean allele (A-) at this locus indicates that it evolved independently from other alleles and has increased in frequency at a rate that is too rapid to be explained by random genetic drift. • – Tishkoff et al. (2001) used statistical modeling to demonstrate that the A- allele arose within a past 3,840 to 11,760 years and the “Med” allele arose within the past 1,600 to 6,640 years. – Tishkoff et al. (2001) concluded that the results support the hypothesis that malaria has had a major impact on humans only since the introduction of agriculture within the past 10,000 years and provide a striking example of the signature of selection on the human genome. Others, including DNA “fingerprinting” applications. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov:80/entrez/dispomim.cgi?id=305900 Sugar? Society? Biotechnology? Questions? ? 1, and 2 indicate steps that are blocked in HFI patients. What causes this (genetically, physiologically)? Wednesday / Friday • Wednesday: Pheromone Paper, Quiz, • Friday: Review, – Final will be posted on the web site, ~1 pm Friday.