* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA Sequence Analysis
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Multilocus sequence typing wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
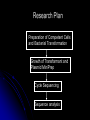
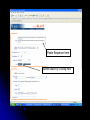
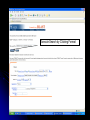
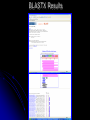
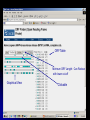
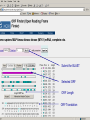
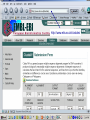
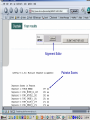
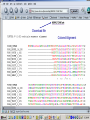
DNA Sequence Analysis Broad and Long Term Objective To characterize a single clone from an Emiliania huxleyi cDNA library using sequence analysis Research Plan Preparation of Competent Cells and Bacterial Transformation Growth of Transformant and Plasmid MiniPrep Cycle Sequencing Sequence analysis Today’s Laboratory Objectives To learn how to characterize a DNA sequence using various web based bioinformatics tools including: 1. BLASTN- has this piece of DNA been sequenced before? Does it look like anything already in GeneBank at the nucleotide level? 2. BLASTX- Can we identify the putative function of the transcripts? 3. ORF Finder- What does the open reading frame look like? Do we have a full length clone with an identifiable start and stop codon? 4. ClustalW- How does it compare with other sequences either at the nucleotide or amino acid level? What residues are conserved and thus likely to be important? And what residues are divergent? BLAST Database Search Tool BLAST (Basic Local Sequence Alignment Tool) Available on the internet and downloadable Quick and simple http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ The BLAST Family Program Query Sequence Database Target BLASTN Nucleotide (both strnds) Optimized for speed not accuracy Not good for distant homologues Dust Option (low complexity) Nucleotide Database BLASTX Nucleotide translated 6 frames Less sensitive to sequence errors and mismatches Useful for preliminary data/EST Dust Filter Option Protein Database TBLASTX Nucleotide translated 6 frames Good for ESTs and Single Pass Sequences, Very Slow Nucleotide Database Translated 6 frames BLASTP Protein Protein Database TBLASTN Protein Proteins against nucleotides and ESTs Nucleotide Database Translated 6 frames The Blast Algorithm Identify HSP’s (High Scoring Segment Pairs) default 11 bp or 3 aa Perfect match Slide query and target sequence across each other until the maximum number of HSP for that target is found The Blast Algorithm Score the Alignment a scoring matrx such as BLOSUM62 or PAM is used gaps introduced between GSP’s during sliding get negative score a match gets a positive score total alignment score is subjected to statistical analysis to calculate the significance vs. chance of the score Repeat for every sequence in the target database Return total results Paste Sequence here Submit Search by Clicking Here Execute Search by Clicking Format BLASTX Results Interpreting BLAST Results •Length •E-Value •Bit Score •Identities •Positives NCBI’s ORF FINDER and Open Reading Frames Begin with “ATG” start codon End with “TAA”, “TAG”, or “TGA” stop codons Can occur in any six possible reading frames Sense Strand: Antisense Strand: Frame +1 Frame +2 Frame +3 Frame -1 Frame –2 Frame -3 ORF Finder Algorithm Iterates over all frames: Iterate to the end of frame Find first/next Start codon Continues to the next Stop codon Records the size and location of ORF List OFRs sorted by length in descending order www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html ORF Table Minimum ORF Length: Can Redraw with lower cut-off Graphical View Clickable Submit for BLAST Selected ORF ORF Length ORF Translation Multiple Sequence Alignment with Clustal W Homologous residues in a set of sequences are aligned together in columns Ideally, homology reflects structural and evolutionary conservation Evolutionary history of a residue can be deduced from sequence alignments of sequences from different organisms http://www.ebi.ac.uk/clustalw/ Alignment Editor Pairwise Scores Download file Colored Alignment