* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ole_Lund_June_4_2010..
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Hepatitis B wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Duffy antigen system wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Antimicrobial peptides wikipedia , lookup
Human leukocyte antigen wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
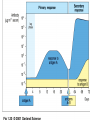
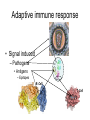
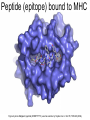
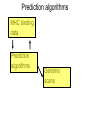
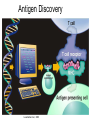
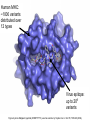
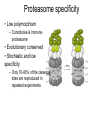
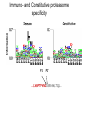
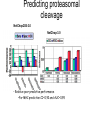
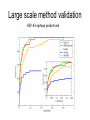
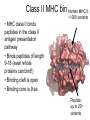
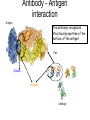
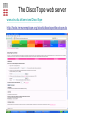
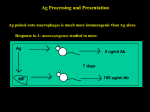
Immunological Bioinformatics Ole Lund Challenges of the immune system Outside Infection with microbe A Vaccine Infection Allergen -> with allergy microbe B Peptide Transplant drugs ations Time Creation Creation of self of an immune system/ Tolerance to self Autoimmunity (break of tolerance to self) Inside Cancer Effect of vaccines The Immune System • The innate immune system • The adaptive immune system Adaptive immune response • Signal induced – Pathogens • Antigens – Epitopes B Cell T Cell Presentation of peptides on MHC I Response to1:(5x20x20 0) = 1:2000 peptides 1:5 1:200 Figure by Eric A.J. Reits 1:2 Peptide (epitope) bound to MHC Figure by Anne Mølgaard, peptide (KVDDTFYYV) used as vaccine by Snyder et al. J Virol 78, 7052-60 (2004). Data driven predictions List of peptides that have a given biological feature YMNGTMSQV GILGFVFTL ALWGFFPVV ILKEPVHGV ILGFVFTLT LLFGYPVYV GLSPTVWLS WLSLLVPFV FLPSDFFPS CVGGLLTMV FIAGNSAYE Mathematical model (neural network, hidden Markov model) Search databases for other biological sequences with the same feature/property >polymerase“ MERIKELRDLMSQSRTREILTKTTVDHMAIIKKYTSGRQEKNPALRMKWMMAMKYPITAD KRIMEMIPERNEQGQTLWSKTNDAGSDRVMVSPLAVTWWNRNGPTTSTVHYPKVYKTYFE KVERLKHGTFGPVHFRNQVKIRRRVDINPGHADLSAKEAQDVIMEVVFPNEVGARILTSE SQLTITKEKKEELQDCKIAPLMVAYMLERELVRKTRFLPVAGGTSSVYIEVLHLTQGTCW EQMYTPGGEVRNDDVDQSLIIAARNIVRRATVSADPLASLLEMCHSTQIGGIRMVDILRQ NPTEEQAVDICKAAMGLRISSSFSFGGFTFKRTNGSSVKKEEEVLTGNLQTLKIKVHEGY EEFTMVGRRATAILRKATRRLIQLIVSGRDEQSIAEAIIVAMVFSQEDCMIKAVRGDLNF ... Prediction algorithms MHC binding data Prediction algorithms Genome scans Antigen Discovery Lauemøller et al., 2000 Influenza A virus (A/Goose/Guangdong/1/96(H5N1)) >Segment 1 Genome agcaaaagcaggtcaattatattcaatatggaaagaataaaagaactaagagatctaatg tcgcagtcccgcactcgcgagatactaacaaaaaccactgtggatcatatggccataatc aagaaatacacatcaggaagacaagagaagaaccctgctctcagaatgaaatggatgatg gcaatgaaatatccaatcacagcagacaagagaataatggagatgattcctgaaaggaat and 13350 other nucleotides on 8 segments Proteins 9mer peptides >polymerase“ MERIKELRD MERIKELRDLMSQSRTREILTKTTVDHMAIIKKYTSGRQEKNPALRMKWMMAMKYPITAD ERIKELRDL KRIMEMIPERNEQGQTLWSKTNDAGSDRVMVSPLAVTWWNRNGPTTSTVHYPKVYKTYFE RIKELRDLM KVERLKHGTFGPVHFRNQVKIRRRVDINPGHADLSAKEAQDVIMEVVFPNEVGARILTSE IKELRDLMS SQLTITKEKKEELQDCKIAPLMVAYMLERELVRKTRFLPVAGGTSSVYIEVLHLTQGTCW KELRDLMSQ EQMYTPGGEVRNDDVDQSLIIAARNIVRRATVSADPLASLLEMCHSTQIGGIRMVDILRQ ELRDLMSQS NPTEEQAVDICKAAMGLRISSSFSFGGFTFKRTNGSSVKKEEEVLTGNLQTLKIKVHEGY LRDLMSQSR EEFTMVGRRATAILRKATRRLIQLIVSGRDEQSIAEAIIVAMVFSQEDCMIKAVRGDLNF RDLMSQSRT ... DLMSQSRTR LMSQSRTRE and 9 other proteins and 4376 other 9mers Experimental validation of Bioinformatics predictions Peptide Sequence PB1591-599 VSDGGPNLY HLA Restriction Elispot assay1 KD (nM) + peptide - peptide Elispot assay2 + peptide - peptide HLA-A1 6 18 ± 2 3±3 12 ± 4 1±1 HLA-A1 7 34 ± 5 4±1 13 ± 4 0±0 PB1166-174 FLKDVMESM HLA-A2 51 74 ± 10 11 ± 6 140 ± 36 20 ± 7 PB141-49 HLA-A26 6 40 ± 3 20 ± 7 38 ± 5 24 ± 3 PB1540-548 GPATAQMAL HLA-B7 6 7±2 2±1 13 ± 2 6±1 NP225-233 ILKGKFQTA HLA-B8 664 9±4 1±1 19 ± 7 2±2 PA601-609 SVKEKDMTK HLA-B8 NB 23 ± 6 1±1 119 ± 8 2±1 PB1349-357 ARLGKGYMF HLA-B27 246 10 ± 6 1±1 14 ± 4 1±1 NP383-391 SRYWAIRTR HLA-B27 38 39 ± 6 1±1 40 ± 6 2±1 M1173-181 IRHENRMVL HLA-B39 13 14 ± 3 3±1 84 ± 11 3±1 NP199-207 RGINDRNFW HLA-B58 42 28 ± 5 1±1 15 ± 6 2±2 PB1347-355 KMARLGKGY HLA-B62 PB1566-574 TQIQTRRSF HLA-B62 178 77 ± 20 3±2 91 ± 8 10 ± 3 88 15 ± 5 2±2 21 ± 2 2±0 NP44-52 CTELKLSDY DTVNRTHQY Wang et al., 2006 Results are deposited in public databases Peters B, et al. Immunogenetics. 2005 57:326-36, PLoS Biol. 2005 3:e91. Human MHC: ~1000 variants distributed over 12 types Virus epitope: up to 209 variants Figure by Anne Mølgaard, peptide (KVDDTFYYV) used as vaccine by Snyder et al. J Virol 78, 7052-60 (2004). Coverage of HLA alleles Supertype Selected allele A1 A*0101 A2 A*0201 A3 A*1101 A24 A*2401 A26 (new*) A*2601 B7 B*0702 B8 (new*) B*0801 B27 B*2705 B39(new*) B*3901 B44 B*4001 B58 B*5801 B62 B*1501 Clustering in: O Lund et al., Immunogenetics. 2004 55:797-810 Polyvalent vaccines • The equivalent of this in epitope based vaccines is to select epitopes in a way that that they together cover all strains. Uneven coverage, Average coverage = 2 Epitope Strain 1 Strain 2 Even coverage, Average coverage = 2 Strain 1 Strain 2 Processing Proteasome specificity • Low polymorphism – Constitutive & Immunoproteasome • Evolutionary conserved • Stochastic and low specificity – Only 70-80% of the cleavage sites are reproduced in repeated experiments Proteasome evolution (b1 unit) Human (Hs) - Human Drosophila (Dm) - Fly Bos Taurus (Bota) - Cow Oncorhynchus mykiss (Om) - Fish … Constitutive Immuno- and Constitutive proteasome specificity Immuno Constitutive P1 P1’ ...LVGPTPVNIIGRNMLTQL.. Predicting proteasomal cleavage • NetChop – Neural network based method • PaProc – Weight matrix based method • FragPredict – Based on a statistical analysis of cleavagedetermining amino acid motifs present around the scissile bond • i.e. also weight matrix like NetChop 3.0 Cterm (MHC ligands) LDFVRFMGVMSSCNNPA NetChop-3.0 C-term – Trained on class I epitopes – Most epitopes are generated by the immuno proteasome – Predicts the immuno proteasome specificity LVQEKYLEYRQVPDSDP RTQDENPVVHFFKNIVT TPLIPLTIFVGENTGVP LVPVEPDKVEEATEGEN YMLDLQPETTDLYCYEQ PVESMETTMRSPVFTDN ISEYRHYCYSLYGTTLE AAVDAGMAMAGQSPVLR QPKKVKRRLFETRELTD LGEFYNQMMVKAGLNDD GYGGRASDYKSAHKGLK KTKDIVNGLRSVQTFAD LVGFLLLKYRAREPVTK SVDPKNYPKKKMEKRFV SSSSTPLLYPSLALPAP FLYGALLLAEGFYTTGA NetChop20S-3.0 In vitro digest data from the constitutive proteasome Toes et al., J.exp.med. 2001 Prediction performance FP TP AP AN Sens Aroc=0.8 Aroc=0.5 1 - spec Predicting proteasomal cleavage NetChop20S-3.0 NetChop-3.0 • Relative poor predictive performance –For MHC prediction CC~0.92 and AUC~0.95 Proteasome specificity • NetChop is one of the best available cleavage method – www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/NetChop-3.0 Transporter associated with antigen processing (TAP) What does TAP do? TAP affinity prediction • Transporter Associated with antigen Processing • Binds peptides 9-18 long • Binding determined mostly by N1-3 and C terminal amino acids Integration? Integrating all three steps (protesaomal cleavage, TAP transport and MHC binding) should lead to improved identification of peptides capable of eliciting CTL responses Identifying CTL epitopes HLA affinity 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 ... EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV EBN3_EBV YQAYSSWMY QSDETATSH PVSPAVNQY AYSSWMYSY LAAGWPMGY IVQSCNPRY FLQRTDLSY YTDHQTTPT GTDVVQHQL 2.56 2.22 1.55 1.31 1.02 0.99 0.94 1.15 0.96 1.00 0.01 0.01 0.34 1.00 0.10 0.46 1.00 0.01 Proteasomal cleavage 0.03 0.28 0.97 0.99 0.97 0.97 0.99 0.01 0.02 0.34 0.88 0.01 0.02 0.22 0.50 0.02 0.42 0.03 0.99 0.04 0.22 0.01 0.01 0.05 0.82 0.02 0.99 0.02 0.83 0.21 0.75 0.18 0.01 0.07 0.04 1.00 0.01 0.51 1.00 0.94 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.02 0.75 0.30 0.02 0.92 0.06 0.01 0.63 0.02 0.46 TAP affinity 0.94 0.11 0.04 0.09 0.01 0.02 0.01 0.54 0.30 0.92 2.97 0 2.80 0.99 -0.80 0 2.28 1.00 2.63 0 1.78 1.00 3.28 1 1.58 1.00 3.01 0 1.27 0.93 3.19 0 1.24 0.96 2.79 0 1.18 0.14 -0.87 0 1.12 1.00 0.53 0 1.09 Large scale method validation HIV A3 epitope predictions Class II MHC binding Human MHC II: ~1000 variants • MHC class II binds peptides in the class II antigen presentation pathway • Binds peptides of length 9-18 (even whole proteins can bind!) • Binding cleft is open • Binding core is 9 aa Peptide: up to 209 variants Humoral immunity Cartoon by Eric Reits Antibody - Antigen interaction Antigen The antibody recognizes structural properties of the surface of the antigen Fab Epitope Paratope Antibody Discontinuous B-cell epitopes An example: An epitope of the Outer Surface Protein A from Borrelia Burgdorferi (1OSP) SLDEKNSVSVDLPGEM KVLVSKEKNKDGKYDLI ATVDKLELKGTSDKNN GSGVLEGVKADKCKVK LTISDDLGQTTLEVFKE DGKTLVSKKVTSKDKS STEEKFNEKGEVSEKIIT RADGTRLEYTGIKSDGS GKAKEVLKG 1OSP, Li et al. 1997 The DiscoTope web server www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/DiscoTope http://tools.immuneepitope.org/stools/discotope/discotope.do Prediction servers at CBS for Immunological features • BepiPred » Linear B-cell epitopesDiscoTope » Discontinuous B-cell epitopes • NetChop » Proteasomal cleavages (MHC ligands)NetCTL » Integrated class I antigen presentation • NetCTLpan Pan-specific integrated class I antigen presentation • NetMHC » Binding of peptides to MHC class I allelesNetMHCII » Binding of peptides to MHC class II alleles • NetMHCIIpan » Pan-specific binding of peptides to MHC class II HLA-DR alleles of known sequence • NetMHCpan » Pan-specific binding of peptides to MHC class I alleles of known sequence • VDJsolver » Analysis of human immunoglobulin VDJ