* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diabetes (type II) treatment, Dec. 7
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Adenosine triphosphate wikipedia , lookup
Paracrine signalling wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Drug design wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
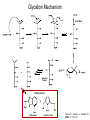
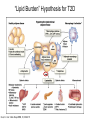
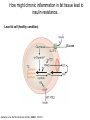
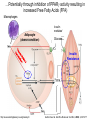
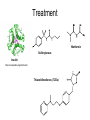
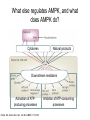
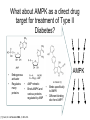
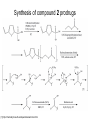
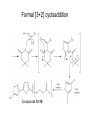
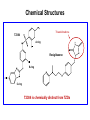
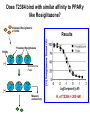
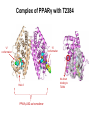
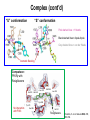
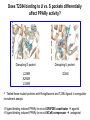
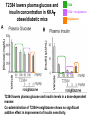
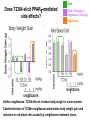
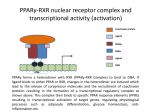
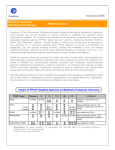
Andrew Mumma, Shwetha Manjunath, and Asha Mahajan Chemistry 315/515 What is Type II Diabetes (T2D)? • Metabolic disorder involved in abnormally high blood glucose levels caused by insulin insensitivity • Insulin insensitivity is caused by deficiency of or unresponsiveness to insulin • Risk Factors: – High food intake – Decreased exercise – Genetics Why Is Increased Blood Glucose Detrimental? • Non-enzymatic glycation of proteins alter their structure and function • Measuring Blood Glucose: D-Glucose + O2 glucose oxidase D-Glucono--lactone + H2O2 • This can lead to: – Diabetic Nephropathy – Neuropathy – Retinopathy – Heart complications – Stroke Glycation Mechanism Schiff Base Amadori Product AGE products Pentosidine Pyrraline Imine Horvat, Š.; Jakas, A. J. Peptide Sci. 2004, 10, 119-137. “Lipid Burden” Hypothesis for T2D Cusi, K. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2010, 10, 306-315 How might chronic inflammation in fat tissue lead to insulin resistance… Lean fat cell (healthy condition) Glucose Guilherme et al. Nat Rev Molecular Cell Biol., 2008, 9, 367-377 …Potentially through inhibition of PPAR activity resulting in increased Free Fatty Acids (FFA) Macrophages Insulinmediated Adipocyte (obese condition) Glucose Insulin Resistance FFA http://www.aamdsglossary.co.uk/glossary/m Guilherme et al. Nat Rev Molecular Cell Biol., 2008, 9, 367-377 Treatment Metformin Sulfonylureas Insulin http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Insulin Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) What is AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) and its main role in the body? • Balances catabolism (processes that produce ATP) with ATP consumption to maintain high levels of ATP • Expressed primarily in liver, skeletal muscle, and the brain, which are all involved in energy intake, consumption, and storage • Heterotrimeric kinase (α, β, and γ subunits) • Activated in two ways[1] – Kinases that phosphorylate Thr172 on α subunit – AMP binding of γ subunit that blocks dephosphorylation of Thr172 on α subunit [1] Zhang, BB. Cell Metab. 2009, 9, 407-416. The master switch of AMPK and energy homeostasis: the ratio of ATP to AMP • ATP is depleted by decreased production or increased consumption • AMP is a byproduct of ATP consumption • Decreased ATP and increased AMP activate AMPK • AMPK triggers mechanisms that restore the balance of ATP to AMP Hardie, DG. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 8, 774-785. What else regulates AMPK, and what does AMPK do? Cytokines Natural products Downstream mediators Activation of ATPproducing processes Hardie, DG. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2007, 8, 774-785. Inhibition of ATP-consuming processes A Potent and Selective AMPK Activator That Inhibits de Novo Lipogenesis Gómez-Galeno JE et al ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2010. What about AMPK as a direct drug target for treatment of Type II Diabetes? • • Endogenous activator • Regulates many • proteins AMPK AMP mimetic Binds AMPK and various proteins regulated by AMP [1] Cool, B. Cell Metab. 2006, 3, 403-416. • • Binds specifically to AMPK Different binding site from AMP[1] Basic residues in the binding site of the gamma subunit and phosphate interaction Xiao, B. Nature Let. 2007, 449, 496-501. How effective is compound 2 at activating human AMPK? Synthesis of compound 2 prodrugs [1] [1] http://chemistry2.csudh.edu/rpendarvis/aminrxn.html Formal [3+2] cycloaddition Compounds 12-18 How do various phosphonate prodrugs perform at inhibiting de novo lipogenesis in vitro and in vivo? EC50: inhibition of de novo lipogenesis (DNL) in rat and mouse hepatocytes in vivo DNL inhibition: inhibition of DNL in mice livers after intraperitoneal injection Compounds: 2: anionic, poor cellular permeability 8 and 12: Did not activate isolated enzyme – phosphonic acid important for AMPK activation by 2. 8 12-18 Is AMPK activation by compound 13 responsible for DNL inhibition? Pi AMPK inhibition ACC Acetyl-CoA carboxylase: Catalyzes fatty acid biosynthesis Inhibits free fatty acid oxidation Pi ACC Control 1000uM 10uM AICAR 3uM 1uM compound 13 Results and future direction • Evaluated compound 2, the phosphonic acid derivative that potently activates AMPK • Synthesized a line of compound 2 prodrugs that are esterase sensitive, bioavailable, and activators of AMPK • Future use of these AMPK-specific drugs can help clarify the exact role that AMPK has in modulating energy homestasis • Test the potential of these compounds as a therepeutic treatment for Type II diabetes Paper #2: http://diabetescure.hct.ac.ae/speaker-profiles/ Quest to Optimize T2D Treatment Thiazolidinediones (TZDs) •TZDs -Bind to PPARγ •Negative Side Effects: -Weight gain -Anemia Rationale • We know: Inhibition of PPARγ leads to T2D • A paradox exists: Reduction of PPARγ can lead to improvement of insulin sensitivity – A mutation in PPARγ resulting in partial loss of normal function reduced risk for T2D • Goal: Search for a partial agonist of PPARγ that increases insulin responsiveness without negative side effects Chemical Structures Thiazolidinedione T2384 A-ring Rosiglitazone B-ring C-ring T2384 is chemically distinct from TZDs Does T2384 bind with similar affinity to PPARγ like Rosiglitazone? Unlabeled Rosiglitazone or T2384 3H-labeled Results Rosiglitazone PPARγ (-) (+) (-) (+) (+) (+) Nitrocellulose Paper (+) (+) Measure radioactivity Ki of T2384 = 200 nM Does T2384 activate PPARγ in cells like Rosiglitazone? LBD = Ligand Binding Domain DBD = DNA Binding Domain PPARγ LBD PPARγ PPARγ LBD PPARγ DBD Gal4 DBD Rosiglitazone or T2384 PPARγ LBD Gal4 DBD DNA Gal4-UAS Luciferase Meneely, P. Advanced Genetic Analysis. Oxford University Press, New York. 2009. GLOW Results Partially activated PPARγ T2384 inhibited Rosiglitazone’s effect Log[Compound] (μM) Does T2384 trigger lipid accumulation in preadipocytes like Rosiglitazone? Little lipid accumulation T2384 inhibited Rosiglitazone’s effect How does PPAR regulate transcription? Coactivator complex DRIP205 Coactivator complex Sin3 DRIP205 NCoR/ HDACs Ac RXR PPAR Ac RXR Ac PPAR SMRT Transcription! PPRE Ac PPRE PPAR -RXR heterodimer when associated with Transcription of PPAR gene targets when Corepressor NOcomplex Trans cription associatedComplex with coactivator How does T2384 binding to PPAR LBD affect its interactions with transcriptional regulatory proteins? TR-FRET 665 nm Emission 620 nm FRET APC Excitation strepavidin GST PPAR LBD biotin Ligand Peptide Corepressor/ Coactivator No interaction Interaction Quantification of Protein-Protein Binding Emission Intensity @ 665 nm Emission Intensity @ 620 nm How does T2384 binding affect PPAR LBD interactions with corepressor/coactivator derived peptides? T2384 partial agonist profile Emission Intensity @ 665 nm Emission Intensity @ 620 nm T2384 antagonist profile T2384 displays partial agonist activity at concentrations < 0.1M and antagonist activity at concentrations > 0.1M Complex of PPARγ with T2384 “S” conformation “U” conformation Helix 3 PPARγ LBD as homodimer No direct binding to T2384 Complex (cont’d) “U” conformation “S” conformation Pink dashed lines = H bonds Black dashed lines= dipole-dipole Grey dashed lines = van der Waals Aromatic Stacking Comparison: PPARγ with Rosiglitazone His 323 His 449 Leu 330 Met 364 Leu 353 Cys 285 No interaction with F363 Tyr 473 Ser 289 Ile 341 Rosiglitazone Chandra, V. et al. Nature 2008, 456, 350-356. Does T2384 binding to U vs. S pockets differentially affect PPARγ activity? Disrupting S pocket: Disrupting U pocket: L228W A292W L333W G284I • Tested these mutant proteins with Rosiglitazone and T2384 ligand in coregulator recruitment assays: -If ligand binding induced PPARγ to recruit DRIP205 coactivator agonist -If ligand binding induced PPARγ to recruit NCoR corepressor antagonist Mutation in U pocket disrupts rosiglitazone’s agonist affect on PPARγ activity • Mutations in S pocket do not hinder activity of Rosiglitazone (data not shown) • Mutations in U pocket disrupted agonist activity of Rosiglitazone T2384’s interactions with U and S binding sites trigger different PPARγ responses • Mutations in S pocket disrupt T2384’s antagonist activity • Mutations in U pocket disrupt T2384’s agonist activity • Biphasic phase was disrupted • Different binding conformations of T2384 can elicit different PPAR activity. T2384 lowers plasma glucose and insulin concentration in KKA obese/diabetic mice T2384 T2384 + rosiglitazone rosiglitazone T2384 lowers plasma glucose and insulin levels in a dose-dependent manner. Co-administration of T2384+rosiglitazone shows no significant additive effect in improvement of insulin sensitivity. T2384 Does T2384 elicit PPAR-mediated side effects? T2384 (100mg/kg) + rosiglitazone (3mg/kg) rosiglitazone Unlike rosiglitazone, T2384 did not increase body weight or cause anemia. Coadministration of T2384+rosiglitazone ameliorates body weight gain and reduction in red blood cells caused by rosiglitazone treatment alone. Conclusions and Future Directions • Conclusion – S pocket occupancy without interaction with AF2 helix may result in optimal PPARγ activity without side effects • Future Directions – Investigate how T2384 reduces fat accumulation and increases insulin sensitivity – Create and explore other drugs through structurebased drug design that bind to S pocket and note effects on PPARγ Quiz!!! • Which pocket (U or S) is associated with T2384’s antagonistic activity? • What additional binding interaction forms between PPARγ and T2384 that is not present between PPARγ and rosiglitazone? • Why is the phosphonic acid compound 2 not active when given to rat hepatocytes or injected in mice? • The dynamic between which two molecules directly modulates the activity of AMPK? • Multi-part question (BONUS for getting more than one!): – What two structures react in the formal [3+2] cycloaddition? – What is the name of the resulting ring structure? Quiz!!! • Is pursuing T2D drugs condoning personal irresponsibility to one’s own health?