* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download pain-1 - Thblack.com
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
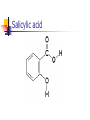
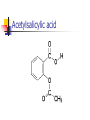
Plants used for the nervous system and pain relief What is the nervous system? Composed of billions of neurons that function by conducting impulses Coordinates functioning of all body systems Major parts of the nervous system Central nervous system (brain and spinal cord) Peripheral nervous system (sensory and motor systems) Neurotransmitters Chemicals that transmit nervous impulses from one neuron to the next There are over 25 different neurotransmitters known. Common ones include: Serotonin Epinephrine Dopamine Acetylcholine Norepinephrine Some plant compounds mimic neurotransmitters or interfere with their normal function Levels of neurotransmitters in brain can alter mood and perception and impact thinking and learning Pain Pain is detected by a class of neurons called nociceptors Different nociceptors respond to heat, pressure, or chemicals released from damaged or inflamed tissue Prostaglandins increase pain by sensitizing the receptors (lowers threshold) Chronic pain affects 97 million people in US and costs about $100 billion/year Endorphins Endorphins are polypeptides that act as chemical painkillers Produced naturally in the body Able to bind to the receptors in the brain to give relief from pain responsible for the so called runner's high, loss of pain when severe injury occurs analgesic effects of acupuncture released into the brain during laughter Endorphins Sometimes called the body’s natural opiates Morphine, codeine, heroin and other opiates mimic endorphins and bind to the same receptors in brain Plants and Pain Plants have been popular sources of pain remedies in just about every culture on earth Plants boiled and/or beaten and ground into teas, pastes, poultices, and ointments to ease the pain A short list of plants Willow bark, comfrey leaves, coriander, sage, and sarsaparilla root were common old world remedies Sweet birch bark, cinchona bark, and hot peppers were common plant remedies used by people in the new world Banana and aloe plants also fought pain, as compounds found in their leaves and stems were used to soothe burns and blisters An even shorter list Willow bark and others (salicylic acid – aspirin) Poppy (morphine and codeine) Chili peppers (capsaicin) Marijuana (THC) Ergot (ergotamine) Others Aspirin: willow bark to Bayer Most widely used synthetic drug but origins are botanical Bark of willow trees (Salix spp.) used by many cultures for reducing fever and relieving pain - in form of a tea Old world ancient Greece New world - Native American tribes Path to a synthetic In 1828 salicin was first isolated and over the next decade the extraction method was refined Salicin is a glycoside of salicylic acid Salicylates occur widely in species of Salix as well as many other plants including meadowsweet (Spirea ulmaria) Salicylic acid Next step Laboratory synthesis of salicylic acid in the mid-19th century Salicylic acid was an inexpensive treatment for many ailments rheumatic fever, gout, arthritis Had side effects - especially gastric In 1898 Felix Hoffman, a chemist at Bayer Company came across acetylsalicylic acid Acetylsalicylic acid Acetylsalicylic acid Effective and more palatable Soon given the name aspirin "a" is from the acetylsalicylic acid and the "spirin" from Spirea the plant from which salicylic acid was first isolated Physiological action Three classic properties anti-inflammatory antipyretic (fever reducing) analgesic (pain relieving) New uses in the prevention of heart attacks, strokes, and colon cancer Drawbacks: irritates the stomach Reye's syndrome Mode of action Key to understanding some of the action of aspirin was discovery by British researcher John Vane Looking at role of aspirin and heart attacks Vane showed that low doses of aspirin suppressed the aggregation of blood platelets which is necessary for blood clots Blood clots can block blood vessels and lead to heart attacks Prostaglandins Mechanism is suppression by way of effects on prostaglandins Prostaglandins are hormone-like substances that regulate numerous other activities in the body influence the elasticity of blood vessels direct the functioning of blood platelets that controls blood flow cause redness and fever Prostaglandins Prostaglandins are released from injured cells Also released from cells stimulated by other hormones Over production of prostaglandins can lead to headaches, fever, menstrual cramps, inflammation, blood clots, etc Salicylic Acid in Plants Since initial discover identified in many plants Now believed that salicylic acid is a naturally occurring plant hormone involved in many reactions including plant protection Plants respond to attack by a host of defenses - many already discussed Plants also respond with a broad based defense mechanism known as Systemic Acquired Resistance Systemic Acquired Resistance Helps plant protect against secondary infections Salicylic acid is signal that turns on SAR SAR turns on synthesis of specific proteins that increase resistance External application of salycylic acid will turn on response Will also turn on responses in nearby plants by conversion to volatile methyl salicylic acid