* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Document
Exchange rate wikipedia , lookup
Efficient-market hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Stock market wikipedia , lookup
Hedge (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Securities fraud wikipedia , lookup
High-frequency trading wikipedia , lookup
Algorithmic trading wikipedia , lookup
Derivative (finance) wikipedia , lookup
Foreign exchange market wikipedia , lookup
Day trading wikipedia , lookup
Currency intervention wikipedia , lookup
Trading room wikipedia , lookup
Stock exchange wikipedia , lookup
2010 Flash Crash wikipedia , lookup
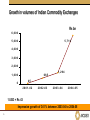
Growth in Indian Commodities Market Mr Narendra Gupta, CBO, NCDEX August 10, 2005 Why Commodity Exchange in India 2 47% of GDP is Commodity related 23% of GDP is from Agriculture Over 65% of 1 trillion population depend on agriculture directly Over 7500 physical market yards History of more than 150 years of derivatives trading Why Commodity Exchange in India Largest producer / consumer of: 3 Bullion Oilseeds Pulses Sugar Cotton Spices Economy growing at the rate of 8% Evolution of Commodity markets in India Ban in forward trading from mid-sixties Prior to ban Thriving commodity exchanges for cotton, gold, edible oils etc. more than 20 regional commodity specific exchanges Recent developments Ban completely lifted in 2003 Emergence of national level de-mutualised online multicommodity exchanges 3 National and 21 regional exchanges Trade in 60 commodities compared with just 8 in 2000 Growth exceeds 4 times in FY05 over FY04 Traded volume in 2004-05 around 20% of India’s GDP 4 Growth in volumes of Indian Commodity Exchanges Rs bn 6 ,0 0 0 5 ,7 1 0 5 ,0 0 0 4 ,0 0 0 3 ,0 0 0 2 ,0 0 0 1 ,2 9 4 1 ,0 0 0 665 45 0 2001-02 2002-03 2003-04 2004-05 1 USD = Rs 43 Impressive growth of 341 % between 2003-04 to 2004-05 5 Choice of Product: Calculator Parameters considered Price volatility Share in GDP Correlation with global markets Share in external trade Government intervention Warehousing facilities Traders distribution Geographical spread Number of varieties Only Physical commodities allowed in Commodity Exchanges 6 Contract Specifications Rigorous Product Research Underlying specifications identification 7 Proxies- Benchmarking to all other varieties Identification of location basis Linking entire value chain Location premium & discount Grade premium & discount Challenges ahead 8 From open outcry to online Discipline trading environment Nuances of Physical settlement Educating about commercial relevance To bring actual users on the exchange platform Farmers Corporate Investors Generating liquidity Involvement of all value-chain entities in contract formulation Relationship group provides relentless momentum Awareness Programmes 9 Generates interests of all members & clients Wide media coverage Easy access to Exchange information Market to be opened up for banks, fund houses and Foreign Investors Foreign Access 10 Foreign access permitted in securities marketequities & bonds Foreign investment regulation for investment in commodity derivatives – a committee constituted by the regulator Currently can access by setting up a domestic entity – for broking & investment Options trading Options allowed in securities market Single Stock options Index Options Interest rate Options Currency Options Options not yet permitted in the commodity markets Law to be amended shortly Informal options trading prevalent 11 Regulatory Environment Separate regulator for capital markets & commodity markets Capital Markets Commodity Markets 12 Securities Exchange Board of India (SEBI) Autonomous body Under Ministry of Finance Forward Markets Commission (FMC) Part of Ministry of Consumer Affairs Law being amended to make it autonomous body About NCDEX 13 NCDEX – Current shareholders 15% 15% 14 15% 15% 12% 12% 8% 8% Product Calendar Dec 2003 Gold, Silver, Crude Palm oil, RBD Palmolein, Cotton, Mustard seed, Mustard oil Soybean, Refined soy oil Apr-Dec 2004 Guar seed, Jute sacking, Chana, Rubber, Pepper, Wheat, Castor seed, Guar gum, Raw jute, Urad, Yellow peas, Sugar, Turmeric, Soymeal Jan – Jun 2005 Gur, Rice, Maize, Raw silk, Cocoon, Jeera, Chilli, Steel, Cashew, Cottonseed oilcake, Sesame seed, Tur, Arabica & Robusta Coffee, Copper Cathode In pipeline Other base Metals, Energy Products, More Agricultural products IndicesNCDEXAGRI FUTEXAGRI NCDEXRAIN Each product is selected after an in-depth research & market feedback 15 Average daily volumes Rs mn 35000 30400 30000 25750 Peak Volume for a single day 25000 22310 Rs. 47200 mn on Jul ‘05 20150 20950 20000 16190 14440 15000 12310 10000 12290 6910 210 550 Q1 -2 0 0 4 Q2 -2 0 0 4 5000 J u ly '0 5 J u n e '0 5 M a y '0 5 A p r '0 5 M a r '0 5 Fe b '0 5 J a n '0 5 D e c - '0 4 Oct -N ov 0 4 Q3 -2 0 0 4 0 Impressive growth of NCDEX with 85% volume contribution from agriculture Volumes in Steel & Copper picking up- daily average steel trade- 10,000 tonnes 16 Question & Answers 17 Thank You 18