* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 22 Organic chemistry
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
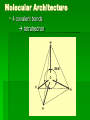
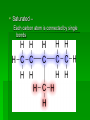
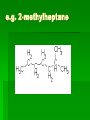
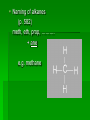
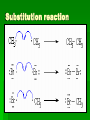
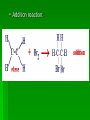
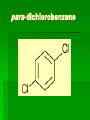
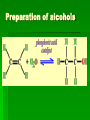
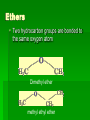
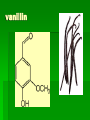
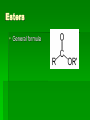
Chapter 22 Organic chemistry chemical compounds consisting primarily of carbon original definition came from the misperception that these compounds were always related to life processes Structure of carbon 1s2 2s2 2p2 4 valence electrons (2s2 2p2) Strong tendency to share electrons Strong tendency to form covalent bonds Molecular Architecture 4 covalent bonds tetrahedron Strong tendency to form covalent bonds w/ H, O, N, S, P, and halogens Molecular Diversity Also bond to other carbons to form chains, rings, plates, networks Forms of carbon 1. Diamond Hardest known material High density (3.514 g/ cm3) High mp (3550 deg. C) 2. Graphite Soft Conducts electricity High mp (3570 deg. C) Used as a lubricant, “lead” pencils 3. Coal Black, rock-like Burns readily 4. Coke Made by heating coal Used for making steel 5. Charcoal Carbon Compounds Over 4 million known cmpds., natural and synthetic Almost limitless # of possible structures Can form isomers Compounds w/ same formula but different structures Hydrocarbons Compounds of hydrogen and carbon 1. Alkanes Hydrocarbons in which all carbon atoms are connected by single bonds Saturated – Each carbon atom is connected by single bonds e.g. 2-methylheptane Naming of alkanes (p. 582) meth, eth, prop, ………. + ane e.g. methane Alkyl groups Sources and uses of alkanes Most from petroleum & natural gas e.g. natural gas is 90 % methane gasoline: heptane, isooctane, …. Substitution reaction Alkenes Double bond between carbons e.g. ethene Naming: use alkane name, drop –ane, add –ene Unsaturated (one or more double bond) Addition reaction: Alkadienes 2 double bonds e.g. 1,3 butadiene Polymers Lg. molecule made of repeating subunits e.g. polyethylene Alkynes Triple bond e.g. ethyne Common name: acetylene Cycloalkanes e.g. cyclopentane Aromatic hydrocarbons e.g. benzene Exhibit resonance: para-dichlorobenzene Examples of hydrocarbons 1. Petroleum fractional distillation 2. Rubber vulcanization Alcohols Hydrocarbons with one or more hydroxyl (-OH) groups e.g. 1-propanol Drop the –e of propane and add -ol Preparation of alcohols Common alcohols Methanol (wood alcohol) Ethanol (grain alcohol) often denatured = Ethylene glycol Halocarbons Alkanes in which one or more halogens are substituted e.g. e.g. dichloromethane tetrachloromethane (carbon tetrachloride) Dichloro-diphenyl-trichloroethane (DDT) Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or Teflon Ethers Two hydrocarbon groups are bonded to the same oxygen atom Dimethyl ether methyl ethyl ether Aldehydes and Ketones Substituted hydrocarbons with a carbonyl group Aldehydes The carbon of the carbonyl group is attached to at least one H Aldehyde naming Drop the –e from the alkane name anf add –al methanal ethanal (common name formaldehyde) Ketones Both bonds of the carbonyl group attached to carbons Ketone naming Drop the –e of the alkane name and add –one propanone (common name acetone) cinnamaldehyde vanillin piperine Carboxylic Acids Contain the carboxyl group Carboxylic acid naming Drop the –e and add –oic acid ethanoic acid (common name: acetic acid) Esters General formula Ester naming Name of the R’ group first + name of acid represented before substitution of H with R’ group Drop –ic of acid name and add -ate Preparation of esters saponification Common esters Interesting organic compounds 1.polystyrene 2. trinitrotoluene