* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Carbonyls
Homoaromaticity wikipedia , lookup
Kinetic resolution wikipedia , lookup
Elias James Corey wikipedia , lookup
Petasis reaction wikipedia , lookup
Wolff rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
Organosulfur compounds wikipedia , lookup
Baylis–Hillman reaction wikipedia , lookup
Tiffeneau–Demjanov rearrangement wikipedia , lookup
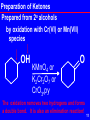
1,3-Dipolar cycloaddition wikipedia , lookup
Nucleophilic acyl substitution wikipedia , lookup
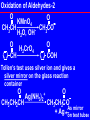
Metal carbonyl wikipedia , lookup
Wolff–Kishner reduction wikipedia , lookup
Strychnine total synthesis wikipedia , lookup
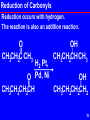
Aldol reaction wikipedia , lookup
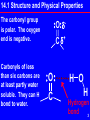
Power Point to Accompany Principles and Applications of Inorganic, Organic, and Biological Chemistry Denniston, Topping, and Caret 4th ed Chapter 14 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. 1 Carbonyl Compounds Contain the carbonyl group, C=O Aldehydes: R may be hydrogen usually a carbon containing group Ketones: R contains carbon O R C R O R C H RCHO Short forms O R C R RCOR 2 14.1 Structure and Physical Properties The carbonyl group is polar. The oxygen end is negative. Carbonyls of less than six carbons are at least partly water soluble. They can H bond to water. O + C O C H O H Hydrogen bond 3 Boiling Points Carbonyl compounds boil between alkanes and alcohols of similar molecular weight. O CH3CH2CH2CH3 butane, bp -43o O CH3C CH3 propanone, bp 56o CH3CH2CH propanal, bp 50o CH3CH2CH2OH propanol, bp 97o 4 14.2 Nomenclature Aldehydes Common: H2C=O formaldehyde (a gas) Used to make insulation and plastic dinnerware. Also using traditional names and Greek letter substitution patterns. E. g. O Cl CH3CH CH2CH2CH -chlorovaleraldehyde 5 Naming Aldehydes: IUPAC Names Base name: longest chain with the C=O Replace the -e of alkane name with -al O CH3CH CH2CH2CH CH3 4-methylpentanal 6 Naming Ketones Common: O acetone, an important solvent CH3 C CH3 Also by naming the two alkyl groups attached to the carbonyl in a) alphabetical order or b) by increasing size Methyl ethyl ketone or Ethyl methyl ketone O CH3 C CH2 CH3 7 Naming Ketones: IUPAC Base name: longest chain with the C=O Replace the -e of alkane name with -one Indicate position of C=O by number on chain Cl O CH3CH CH2C CH3 4-chloro-2-pentanone 8 14.3 Carbonyl Examples Methanal (b.p. –21 oC) is used in aqueous solutions as formalin to preserve tissue and embalm. Acetone and methyl ethyl ketone (MEK) are very versatile solvents. Other examples: CH3O HO O CH Vanillin Vanilla beans O CH3 CH2 5 C CH3 2-octanone Mushroom flavor 9 14.4 Reactions of Carbonyls Aldehydes are prepared from primary alcohols by oxidation with a mild oxidizer, eg (CrO3/py), pyridinium dichromate Example: Note: this oxidation removes two hydrogens. It is also an oxidative elimination reaction. CrO3 CH3CH2CH2OH in py O CH3CH2CH or H2CrO4 10 Preparation of Ketones Prepared from 2o alcohols by oxidation with Cr(VI) or Mn(VII) species OH KMnO4 or K2Cr2O7 or CrO3,py O The oxidation removes two hydrogens and forms a double bond. It is also an elimination reaction! 11 Reactions of Carbonyls 1. Redox a) Aldehydes: oxidized to carboxylic acids b) Aldehydes and ketones are reduced to alcohols: aldehydes to primary alcohols and ketones to secondary alcohols 2. Addition a) of hydrogen to give alcohols b) of alcohols to give hemiacetals, acetals, hemiketals, and ketals c) of aldehydes/ketones to give aldol (hydroxy carbonyl) products 12 Oxidation of Aldehydes Aldehydes are easily oxidized to carboxylic acids by almost any oxidizing agent. Visual tests for the aldehyde functional group based on its easy oxidation are: Tollen’s Test Silver ion is the oxidizer, as Ag(NH3)2 + Benedict’s Test Cu2+ in a basic solution is the oxidizer. Solution is a distinctive blue color. Color fades with rxn. 13 Oxidation of Aldehydes-2 O O KMnO4 CH3CH CH3C O H2O, OH O H CrO 2 4 CH O C OH Tollen’s test uses silver ion and gives a silver mirror on the glass reaction container O O + Ag(NH3)2 CH3CH2C O CH3CH2CH As mirror + Ag on test tube14 Oxidation of Aldehydes-3 Fehling’s test uses copper ion. The blue color fades giving a red ppt of Cu2O. (Often used to test for simple reducing sugars.) O O O H C C H C OH H C OH HO C H 2 Cu2+ HO C H H C OH OHH C OH H C OH H C OH CH2OH CH2OH + Cu2O 15 Reduction of Carbonyls Reduction occurs with hydrogen. The reaction is also an addition reaction. O CH3CH2C CH3 OH CH3CH2CH CH3 H2 Pt, O Pd, Ni OH CH3CH2CH2CH CH3CH2CH2CH2 16 Additions to Carbonyls: Alcohols Carbonyls add one molecule of alcohol to give usually unstable hemiacetals and hemiketals O CH3CH2CH2CH + CH3OH OH CH3CH2CH2CH O CH3 Hemiacetal(ketal) carbons are H+ part of both alcohol and ether functions and are a new functional group OH O + H CH3CH2C CH3 CH3CH2C CH3 + CH3OH O CH3 17 Additions to Carbonyls: Alcohols-2 Acid catalyzes both aldehydes and ketones to react with two molecules of alcohol to give acetals and ketals O O CH3 + H CH3CH2CH + 2 CH3OH CH3CH2CH O CH3 Acetal(ketal) carbons are part of two ether groups and are a new functionalOgroup CH3CH2C CH3 + 2 CH3OH H+ O CH3 CH3CH2C CH3 O CH3 18 Additions to Carbonyls: Alcohols-3 Glucose forms a cyclic hemiacetal when the alcohol group on C-5 reacts with the aldehyde group C=O. hemiacetal carbon this H is involved in hemiacetal formation CH2OH OH C O OH H OH OH hemiacetal link forms here CH2OH O OH OH C H OH OH 19 Hydrolysis of (Hemi)acetals/ketals Both hemiacetals and acetals (and ketone analogs) hydrolyze (react with water). An acid catalyst takes them back to the carbonyl compound and the alcohol(s). O CH3 H+ CH3CH2CH + H2O acetal O CH3 O CH3CH2CH + 2 CH3OH O OH + H CH3CH2C CH3 CH3CH2C CH3 + CH3OH hemiketal O CH3 20 Keto-enol Tautomers Tautomers are isomers which differ in the placement of an atom of hydrogen and a double bond. The keto form has a C=O while the enol form has a C=C. The keto form is usually the most stable. H O R1 C C R3 R2 H O H C CH H R1 OH C C R2 R3 OH H C C H H 21 Additions to Carbonyls: Aldol Condensation Self Addition or Condensation Uses two molecules of the same aldehyde or ketone. The alpha carbon of the second molecule adds to the carbonyl carbon of the first molecule. Strong base such as hydroxide catalyzes the reaction. 22 Aldol Condensation-2 Self Addition/Condensation: aldehyde An aldol has an OH beta to the carbonyl group OH O O O OHCH3CH CH2CH CH3CH + CH3CH alpha carbon, second molecule original alpha carbon carbonyl carbon of first molecule becomes alcohol carbon in aldol 23 Aldol Condensation: Aldolase Dihydroxyacetone phosphate + D-glyeraldehyde-3-phosphate 1 2- 1 2CH2 OPO3 CH2 OPO3 2 2 C O C O 3 H C OH aldolase H 3C OH Bond formed 4 H H5C O H 4 H5C O HC OH 26 HC OH OPO CH 3 2 26 D-fructose-1,6-bisphosphate CH2 OPO3 Alpha carbon (3) adds to carbonyl carbon (4). (Gluconeogenesis) 24 The End Carbonyl Compounds 25