* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Basic Concepts
Long-tail traffic wikipedia , lookup
Cellular network wikipedia , lookup
Computer network wikipedia , lookup
Quality of service wikipedia , lookup
History of smart antennas wikipedia , lookup
Cracking of wireless networks wikipedia , lookup
Digitization wikipedia , lookup
Serial digital interface wikipedia , lookup
Digital television wikipedia , lookup
Telephone exchange wikipedia , lookup
Packet switching wikipedia , lookup
Number Five Crossbar Switching System wikipedia , lookup
Norwegian Public Safety Network wikipedia , lookup
PSTN network topology wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications engineering wikipedia , lookup
Telecommunications in Russia wikipedia , lookup
History of telecommunication wikipedia , lookup
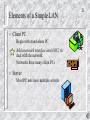
Basic Concepts and Principles Chapter 1 Copyright 2001 Panko 2 Network A Network is an Any-to-Any Communication System – Can connect any station to any other Network 3 Network Each Station has a Unique Network Address – – To connect, only need to know the receiver’s address Like telephone number GHI DEF ABC MNO “Connect to GHI” JKL Data Communications Originally, There was a Sharp Distinction: – Voice and Video Communication versus – Data Communications, in which one or both parties is a computer Database Electronic mail World Wide Web – Distinction is fading because voice and video communication are increasingly computerbased 4 5 Voice and Video Networks Telephone Network – – Customer premises (home or office) Local loop (access line) connects customer premises to first switching office Switching Office Local Loop (Access Line) Connection Customer Premises Customer Premises Voice and Video Networks Hierarchy of switches Trunk lines connect switches Trunk Line Switch 6 7 Voice and Video Networks Circuit – – – End-to-End Connection between Phones May pass through multiple switches And trunk lines Circuit Circuit Voice and Video Networks Reserved Capacity – Circuit capacity is reserved during duration of each call – At each switch Reserved – On each trunk line Capacity Reserved Capacity Circuit 8 Voice and Video Networks Reserved Circuit Capacity Guarantees Throughput – – 9 Never get less than reserved capacity Nothing like congestion on the Internet Reserved Circuit Capacity is Expensive – – – Pay for it whether you use it or not Good for voice, because conversations are fairly constant Bad for data, because most data transmission is bursty; e.g., in World Wide Web, download, then stare at screen for a long time until next download Packet-Switched Data Networks 10 Packet Switching – – Circuit switching is expensive due to reserved capacity Packet switching breaks transmissions into messages – Messages are short (averaging a few hundred bytes) because switches handle short messages efficiently – Messages are called packets (sometimes, frames or other names) Message Packets Packet-Switched Data Networks 11 Switching Decision – – – When a packet arrives at a switch, the switch must decide which of several ports (connections) to use to send the packet back out Complex B Made at each switch B? D? Switch A D Packet C? C Packet Switched Data Networks Multiplexing – – – – Packets from many conversations are mixed (multiplexed) over each trunk line Only pay for the capacity used Dramatic trunk line cost savings The reason for packet switching Multiplexing on Trunk Line 12 13 Analog Transmission In analog transmission, the state of the line can vary continuously, rising and falling smoothly in intensity among an infinite number of states – – – State may be voltage, frequency or another line signal characteristic Voice and video analog Telephone network assumes analog input signals Strength Time 14 Digital Transmission In digital transmission, time is divided into periods of fixed length called clock cycles The line is kept in one of only a few possible states (conditions) during each clock cycle Strength Clock Cycle Time 15 Digital Transmission At the end of each clock cycle, the line may change abruptly to another of these few states – Can also stay the same Abrupt Change Strength Stays Same Clock Cycle Time Digital Versus Binary Transmission Digital transmission: a few states (2, 4, 8, 16, etc.) Binary transmission: exactly two states – One state represents 1, the other 0 Few States Two States 1 0 Digital Binary 16 17 Digital Communication Modems – Computers have digital output – Telephone network assumes analog input – Modem translates between digital device and analog line for data transmission over the phone system Digital Signal (1101) Modem Analog Signal LANs and WANs Networks Have Different Geographical Scopes Local Area Networks (LANs) – – – Small Office Office Building Industrial Park / University Campus Wide Area Networks (WANs) – – Connect corporate sites or Connect corporate sites with sites of customers and suppliers 18 Elements of a Simple LAN Hub or Switch Hub or Switch connects all stations Wiring Wiring is standard business telephone wiring (4 pairs in a bundle) 19 Elements of a Simple LAN 20 Client PC Client PCs are used by ordinary managers and professionals; receive service Servers provide services to client PCs Server Server Server Client PC Elements of a Simple LAN Client PC – Begin with stand-alone PC – Add a network interface card (NIC) to deal with the network Networks have many client PCs – Server – Most PC nets have multiple servers 21