* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PowerfulMuslimEmpires-1
Islam and secularism wikipedia , lookup
Schools of Islamic theology wikipedia , lookup
History of Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and Sikhism wikipedia , lookup
Islamic schools and branches wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Indonesia wikipedia , lookup
Islam and war wikipedia , lookup
Islam and modernity wikipedia , lookup
Reception of Islam in Early Modern Europe wikipedia , lookup
Islam in Romania wikipedia , lookup
Protestantism and Islam wikipedia , lookup
Islam and other religions wikipedia , lookup
Hindu–Islamic relations wikipedia , lookup
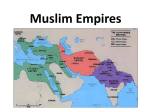
Bellringer 10-11-12 • PUT YOUR HOMEWORK IN THE BIN! • 1. What is the Islamic code of laws called? • 2. What are the two different type of Muslims called? • 3. What is a caliph? • 4. How did the Umayyad treat conquered peoples? • 5. Who killed the last Abbasid Caliph? Powerful Muslim Empires Islamic Invasion After the Gupta Empire fell in 550, India was divided into many little local kingdoms – ruled by warring princes. Despite power struggles between Princes, Indian culture flourished. Beautiful Buddhist and Hindu temples were built and trade networks connected India to many other empires. Around 1000, Muslim Turks and Afghans invaded India. They were fierce warriors and the sultan, or Muslim Ruler, was able to defeat Hindu armies. These Islamic tribes organized a sultanate, or land ruled by a sultan, in Dehli. The Dehli Sultanate would last from 1206 to 1526. This marked the start of Muslim rule in India. Muslims and Hindus Clash Muslims brought changes to Indian government and society. These newcomers created a brilliant civilization at Delhi where Persian art and architecture flourished. However, the Delhi Sultanate fell after Tamerlane invaded and destroyed Delhi in 1398. This led to conflict between Muslims and Hindus. The Muslim invasion of India brought two very different religions face to face. Unfortunately, many Buddhists and Hindus were killed and their temples destroyed. However, there was also a blending of the two religions because many Hindus converted to Islam and many Muslims absorbed Hindu culture. One holy man, Nanak, formed a new religion that was a blend of Hinduism and Islam called. Sikhism Sikhism: A Blend of Religious Beliefs Islam •Belief in One God • Religious and Moral duties defined in the 5 Pillars • Belief in Heaven and Hell, and a day of Judgment • No priests; all believers are religious equals Hinduism •Belief in many gods, all part of Brahman • Emphasis on religious and moral duties, or dharma • Belief in a cycle of birth, death, and rebirth Sikhism • Belief in the “Unity of God” • Belief in Reincarnation • Rejection of the Caste system The Mughal Empire In 1526, Babur, a military genius who was supposedly a descendent of Genghis Khan and Tamerlane, invaded India and founded the Mughal Empire. The chief builder of the Mughal Empire was Akbar the Great. He earned this title by creating a strong central government, promoting religious tolerance, modernizing the army, encouraging trade, and introducing land reforms. The golden age of the Mughal Empire was during the reign of Shah Jahan, Akbar’s grandson. He promoted literature, arts, and architecture throughout the empire. In addition, Shah Jahan built the greatest monument of the Mughal Empire, the Taj Mahal as a tomb for his wife. The Ottoman Empire While the Mughals ruled India, two other empires – the Ottoman and Safavid Empires – dominated the Middle East and Eastern Europe. The Ottoman and Safavid empires became known as the “Gunpowder Empires” because of the new technology they developed. The Ottomans were a Turkish speaking nomadic people who migrated from Central Asia (like the Seljuk Turks). They created a Sunni Muslim empire. As the Ottomans expanded across Asia, they threatened the Byzantine Empire. After many failed attempts to capture Constantinople, Mehmet II finally succeeded in 1453. After a two month siege, they basted through the city walls and took Constantinople and renamed it Istanbul. This would be the Ottoman capital for years! Suleiman the Magnificent The Ottoman empire enjoyed a golden age under Suleiman the Magnificent. Suleiman greatly expanded the empire by modernizing his powerful army and conquering many new lands. The Janizaries were an elite force of soldiers in the Ottoman Army that came from people they conquered in battle. Suleiman also created a strong government based on the Sharia. The Ottoman poets, artists, and architects were influenced from Persian and Arab forms of art. During Suleiman’s rule the arts flourished. Safavid Empire By the early 1500s, the Safavid Empire had created an Empire in Persia (modern-day Iran). The Safavids were Shiite Muslims who enforced their beliefs on their Empire. The Safavid King was called the Shah. The most famous was Shah Abbas the Great. Shah Abbas centralized government, created a strong army, strengthened the economy by reducing taxes on farmers and encouraging the growth of industry. He also tolerated non-Muslims in the Safavid Empire. In the late 1700s, the Safavid Empire fell due to fighting between Shiites and Sunni Muslims and the Qajars took power and established a capital at Tehran.