* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Developmental Theory
Individualism wikipedia , lookup
Divine command theory wikipedia , lookup
Consequentialism wikipedia , lookup
Alasdair MacIntyre wikipedia , lookup
Role-taking theory wikipedia , lookup
Morality and religion wikipedia , lookup
School of Salamanca wikipedia , lookup
Ethics of artificial intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Critique of Practical Reason wikipedia , lookup
Ethical intuitionism wikipedia , lookup
Moral disengagement wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg wikipedia , lookup
Thomas Hill Green wikipedia , lookup
Moral responsibility wikipedia , lookup
Moral relativism wikipedia , lookup
Secular morality wikipedia , lookup
Moral development wikipedia , lookup
Lawrence Kohlberg's stages of moral development wikipedia , lookup
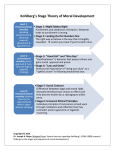
Educational Psychology A Practitioner-Research Model of Teaching A PowerPoint Presentation by Jo Alexander and Averil Loague Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Piaget’s Theory of Moral Development – two stage model: • External Morality or Moral Realism: Stage in which children tend to view rules as inflexible and not open to negotiation • Autonomous Reality or Morality of Cooperation: Stage in which a child begins to perceive rules as more flexible and subject to renegotiation © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Kohlberg's Theory of Moral Development: • Preconventional (4 to 10 years): Level of moral reasoning characterized by a focus on the consequence experienced by the person as a result of his/her actions • Conventional (10 to 13 years): Level of moral reasoning reflecting internalized rules and societal conventions • Postconventional (13 years and older): Level of moral reasoning where individuals move beyond the issues of pleasing or following concrete rules and begin to focus on the principles which underlie these rules © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Gilligan’s Model • Moral decisions of females based on an ethics of caring • Movement from self-interest to focus on specific individuals and relationships • Highest level of morality based on the principles of responsibility and care for all people © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Psychosocial Development - Erickson Principles • Critical periods of psychosocial development • Stages present specific ‘crisis’ • Development in accordance with one’s ability to interact with environment to resolve crisis © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Psychosocial Development - Erickson Stages • Stage 1: Trust vs. Mistrust (Birth to One Year). • Stage 2 : Autonomy vs. Shame and Doubt (Ages One to Three). • Stage 3: Initiative vs. Guilt (Ages Four to Five). • Stage 4: Industry vs. Inferiority (Ages Six to Eleven). © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Psychosocial Development - Erickson Stages Continued • Stage 5: Identity vs. Role Confusion (Ages Twelve to Eighteen). • Stage 6: Intimacy vs. Isolation (Ages Eighteen to Thirty-Five). • Stage 7: Generativity vs. Stagnation (Thirty-five to Sixty-five). • Stage 8: Integrity vs. Despair (Over Sixty-five). © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED Developmental Theory: Moral & Psycho-Social Development Chapter Three Contemporary Psychosocial Issues Teen pregnancy Eating disorders AIDS Child abuse Divorce Suicide © 2001 Wadsworth Group, a division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED